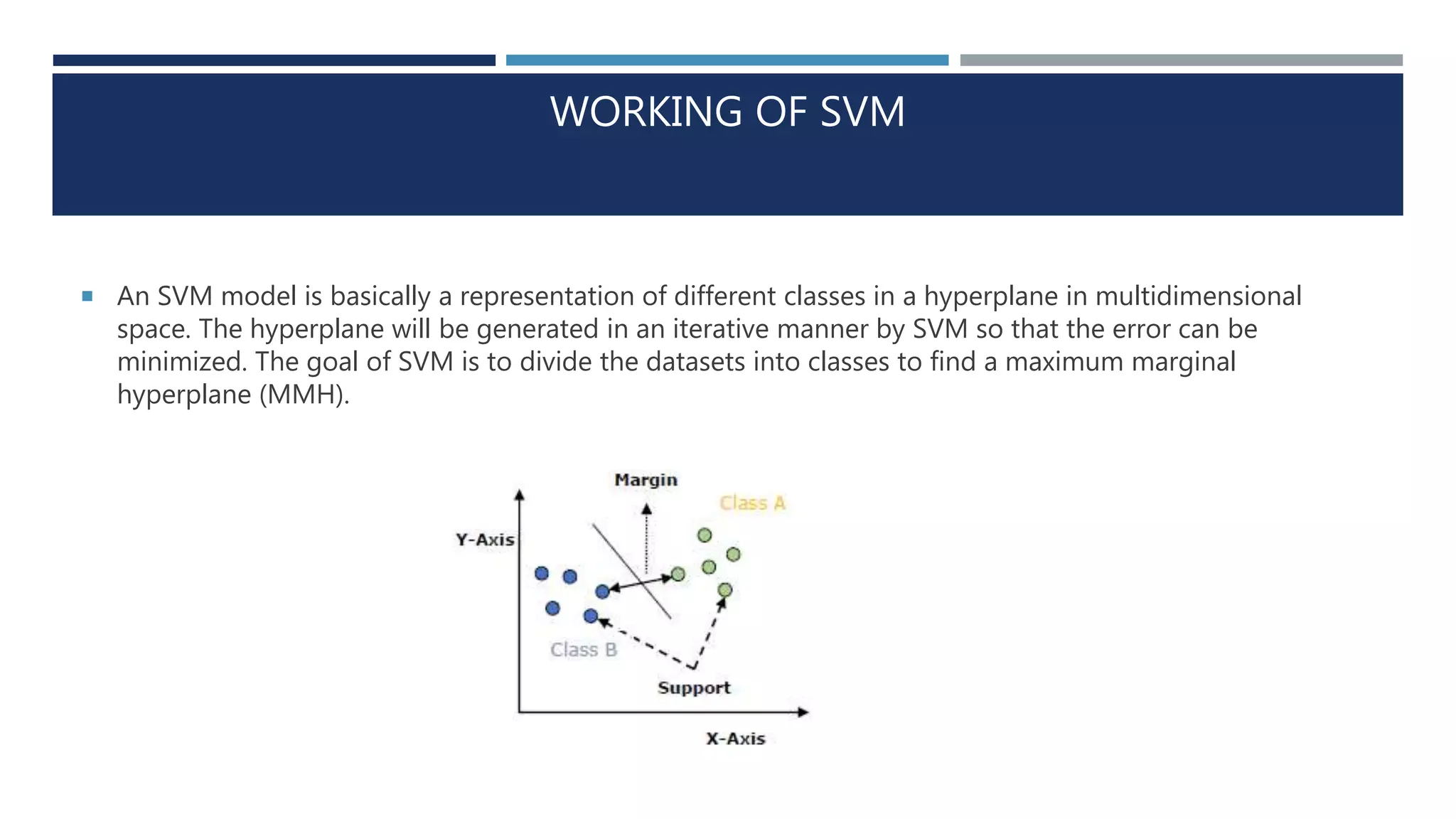
This document provides an overview of logistic regression and support vector machines (SVM). It discusses the key concepts, assumptions, and types of logistic regression, including binary, multinomial, and ordinal logistic regression. It also explains the working, concepts, and goal of SVM, which is to find a maximum marginal hyperplane to divide datasets into classes. The next session will cover implementing SVM in Python.