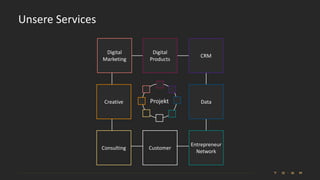
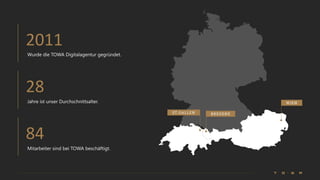
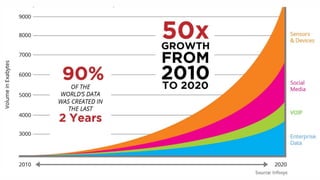
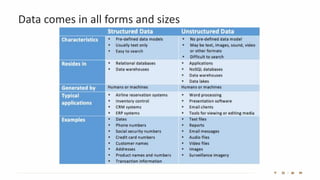
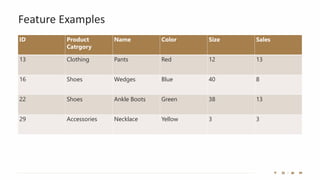
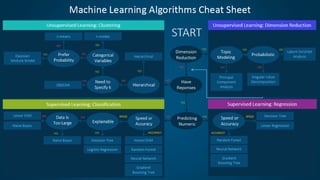
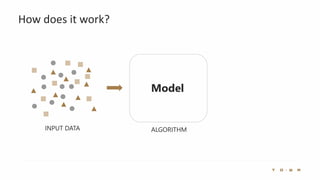
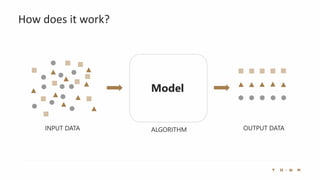
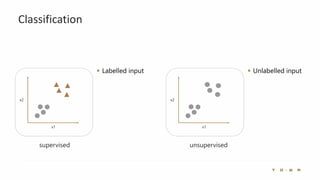
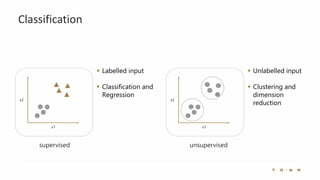
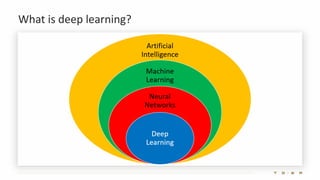
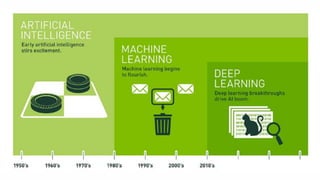
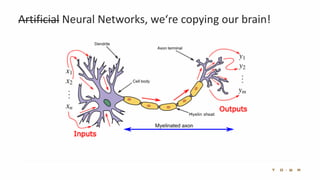
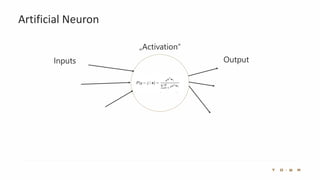
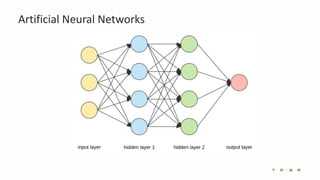
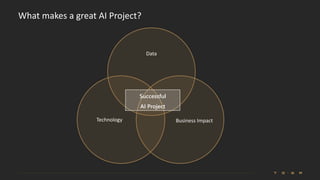
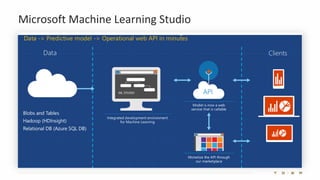
The document introduces the fundamentals of artificial intelligence and machine learning, highlighting the importance of data and algorithms in developing intelligent systems. It discusses how machine learning allows models to learn from data and make decisions, with an emphasis on supervised and unsupervised learning methods. Additionally, it outlines the impact of digital transformation and the role of various tools in implementing AI projects.