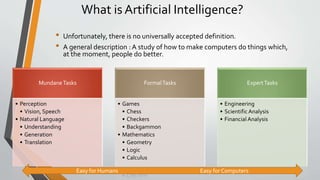
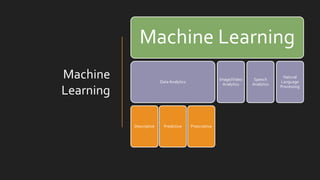
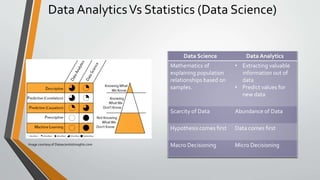
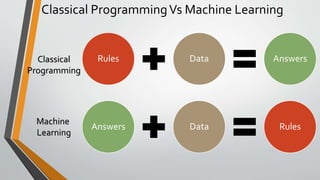
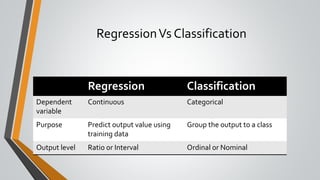
The document discusses the evolution and concepts of machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data science, highlighting the key differences among these fields. It covers topics like predictive analytics, error handling in machine learning, types of analytics, and various learning modes such as supervised and unsupervised learning. Additionally, it outlines the vision of 'must research' to promote excellence in data science and facilitate collaboration between academia and enterprises.