Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times






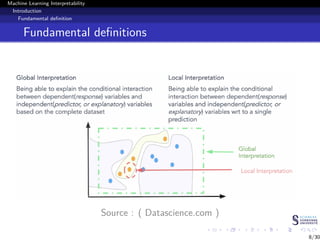
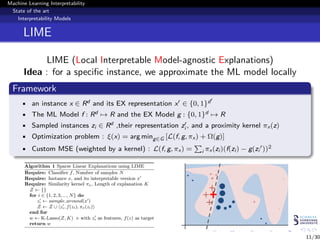
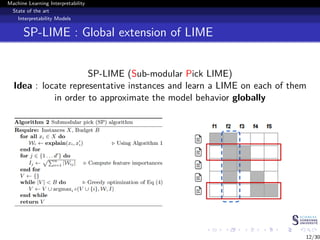

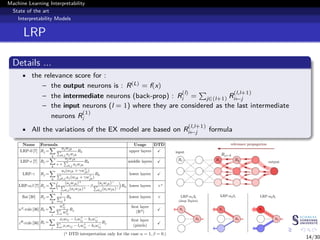

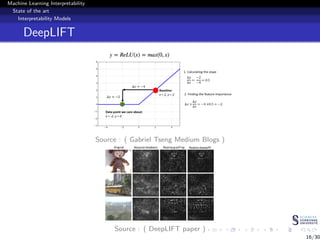
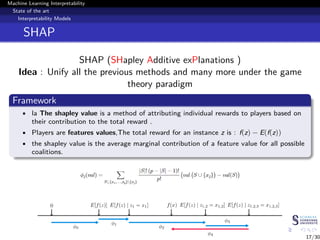
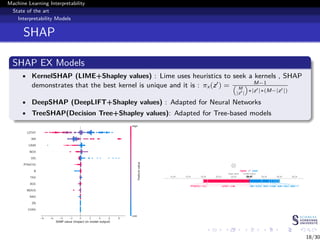



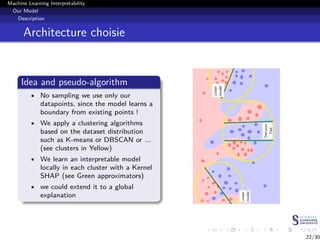






This document discusses machine learning interpretability and explainability. It begins with introducing the problem of making black box machine learning models more interpretable and defining key concepts. Next, it reviews popular interpretability methods like LIME, LRP, DeepLIFT and SHAP. It then describes the authors' proposed model CAMEL, which uses clustering to learn local interpretable models without sampling. The document concludes by discussing evaluation of interpretability models and important considerations like the tradeoff between performance and interpretability.





























