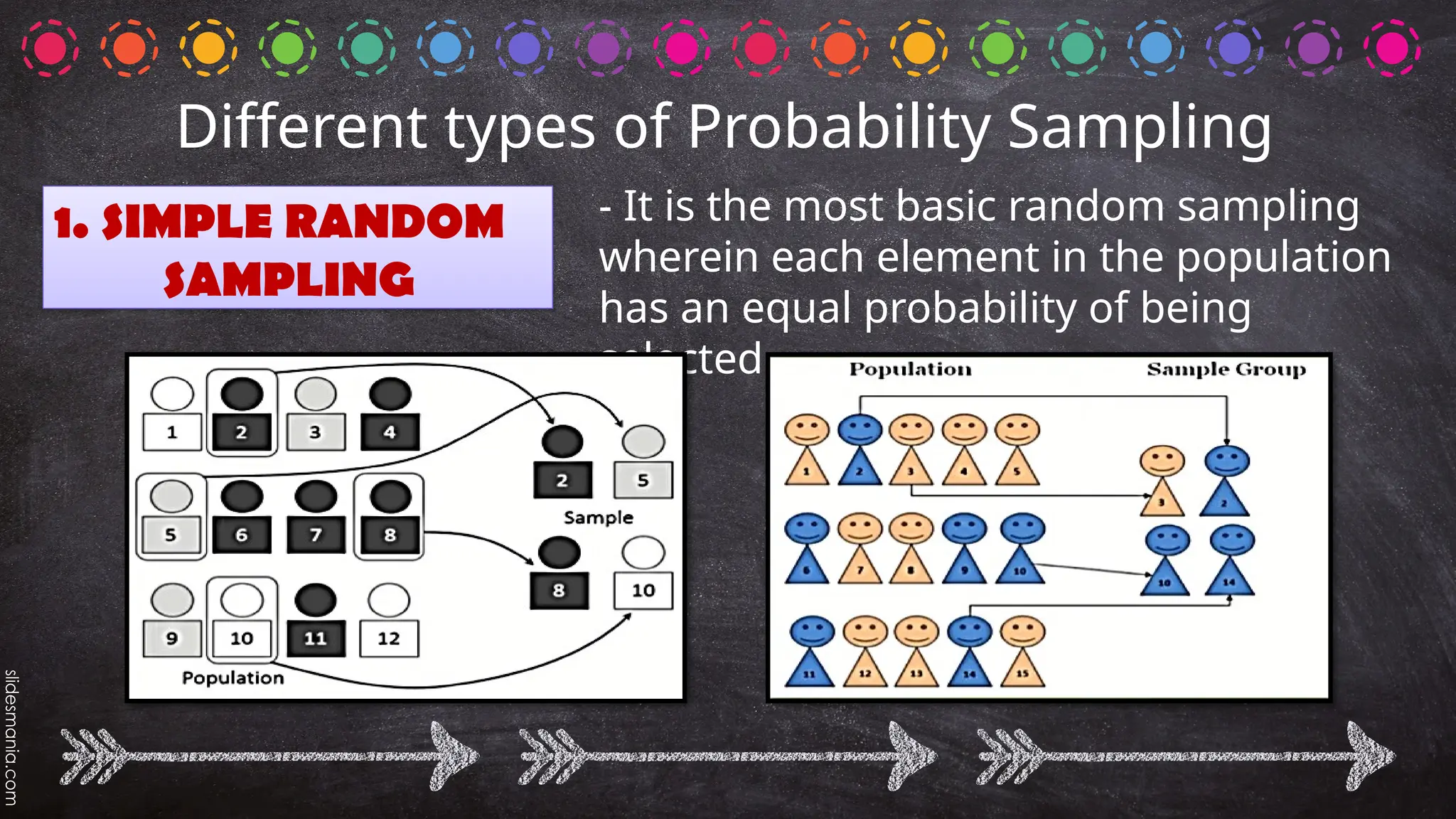
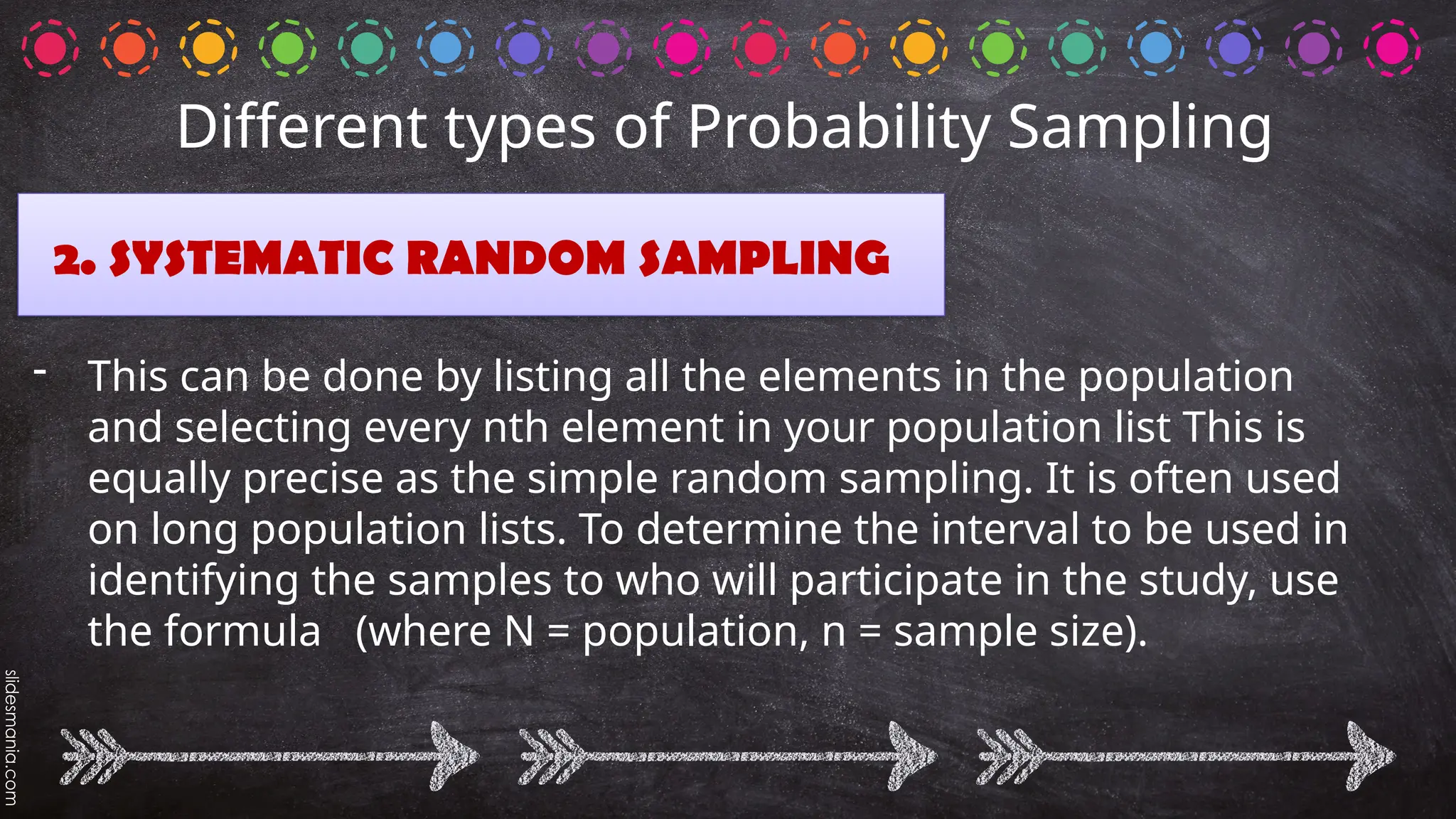
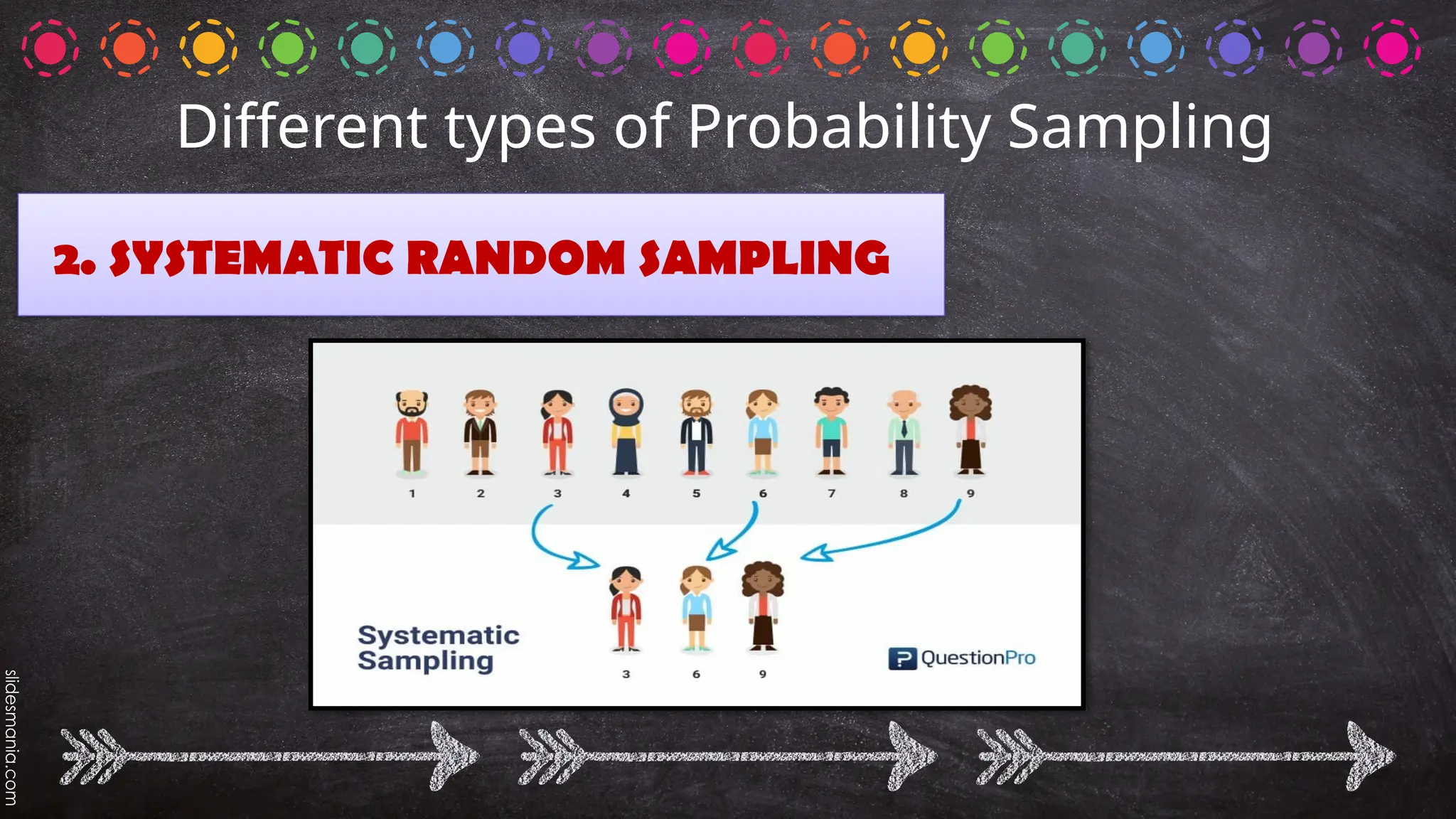
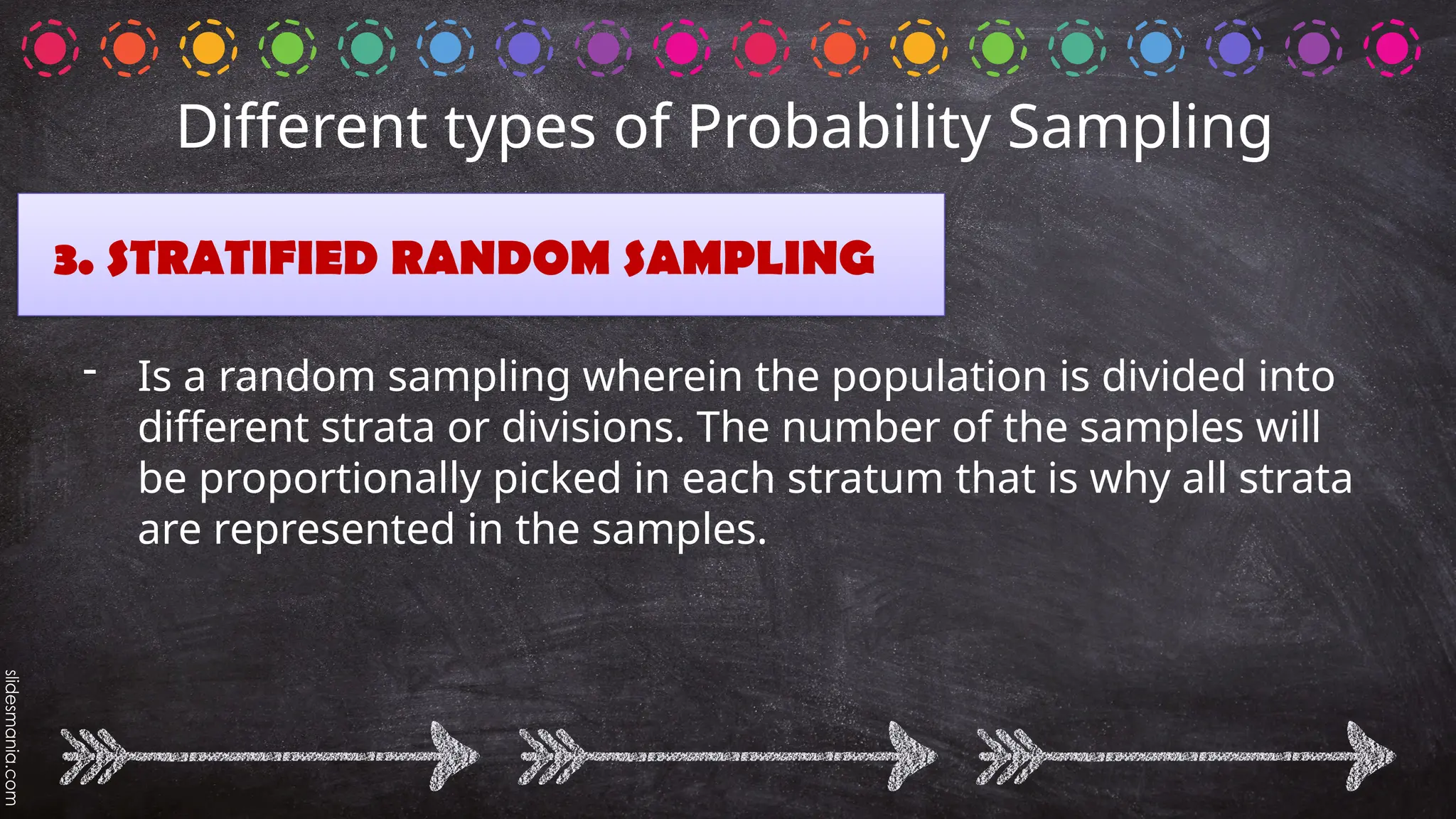
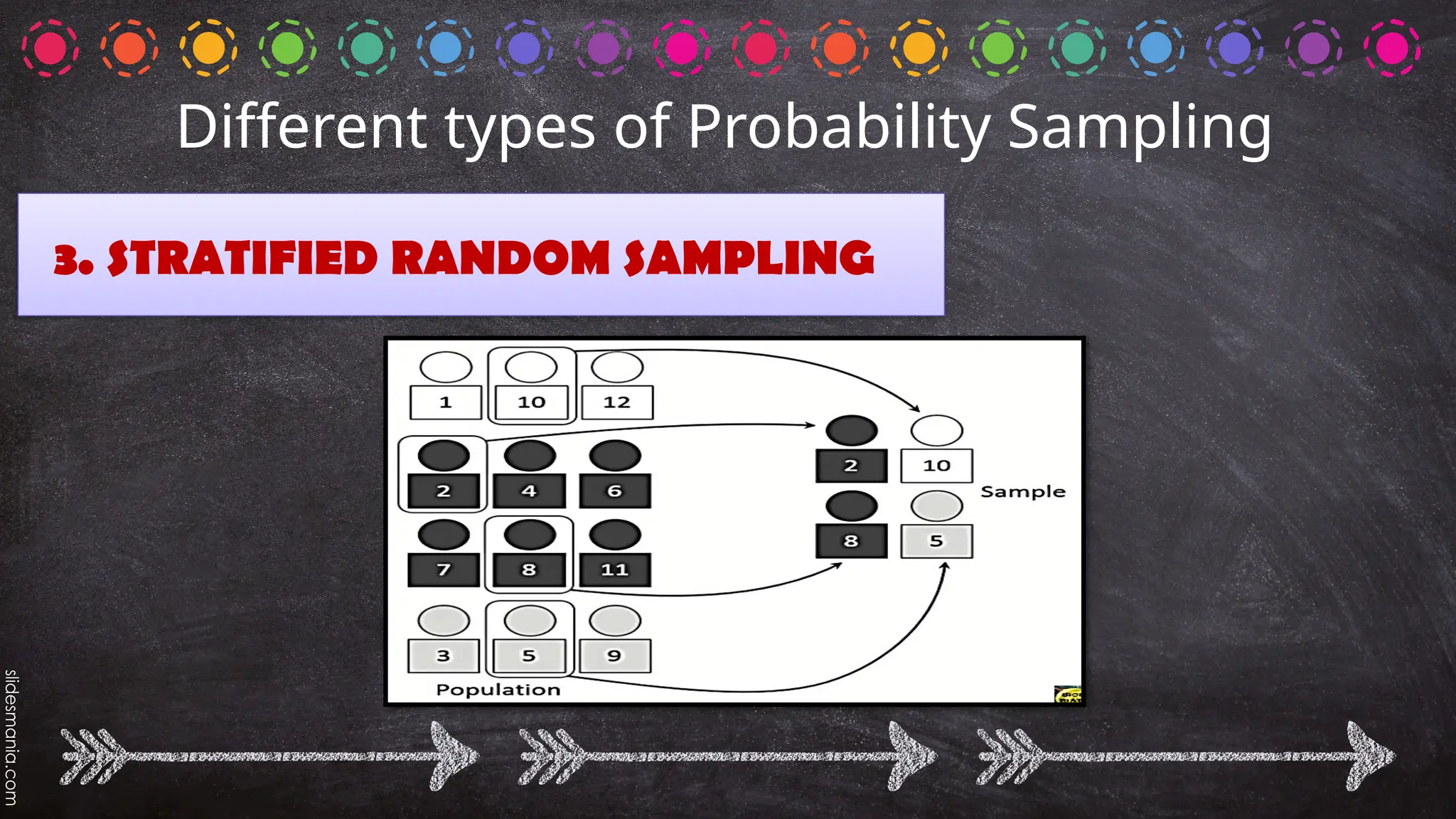
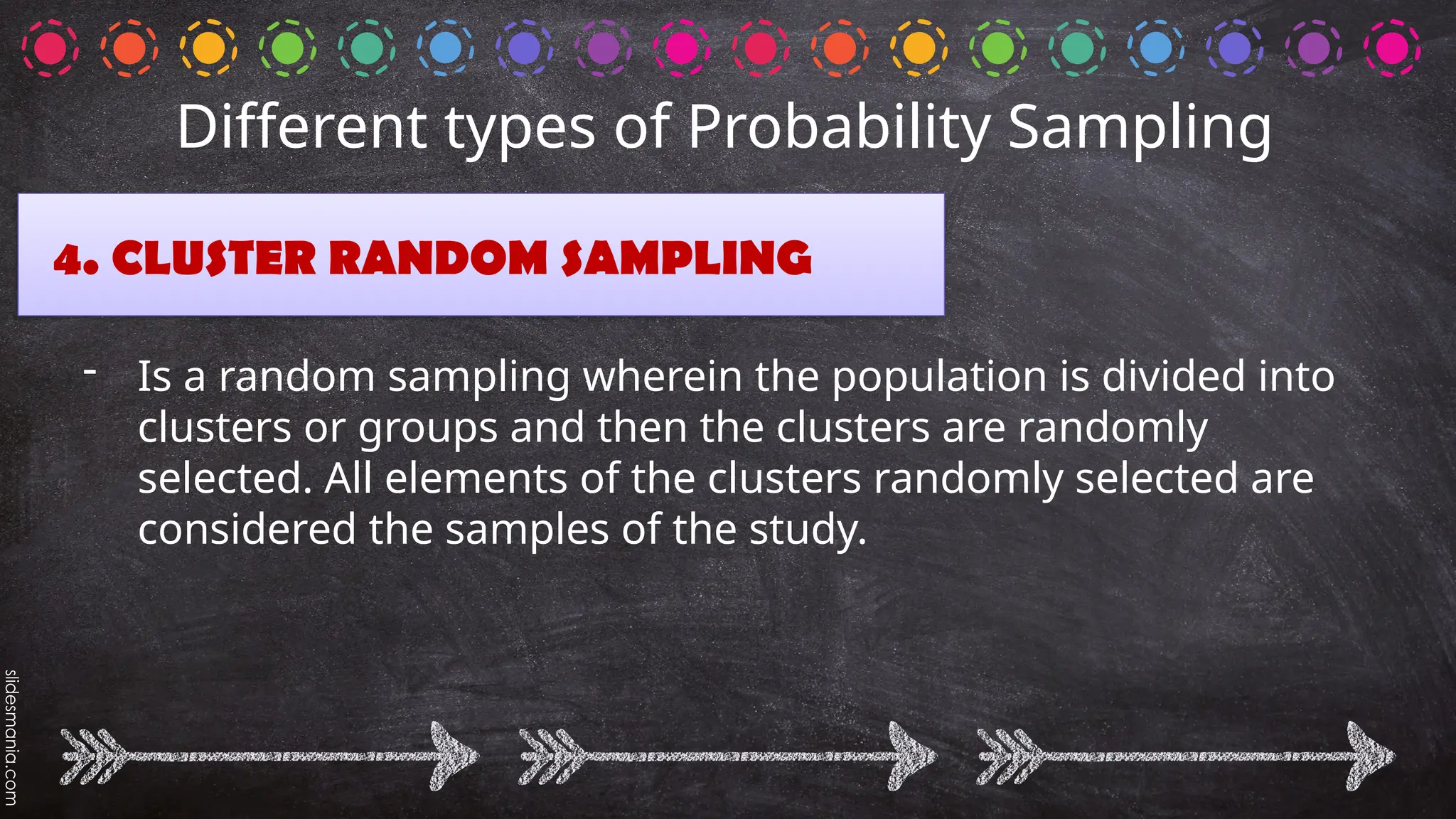
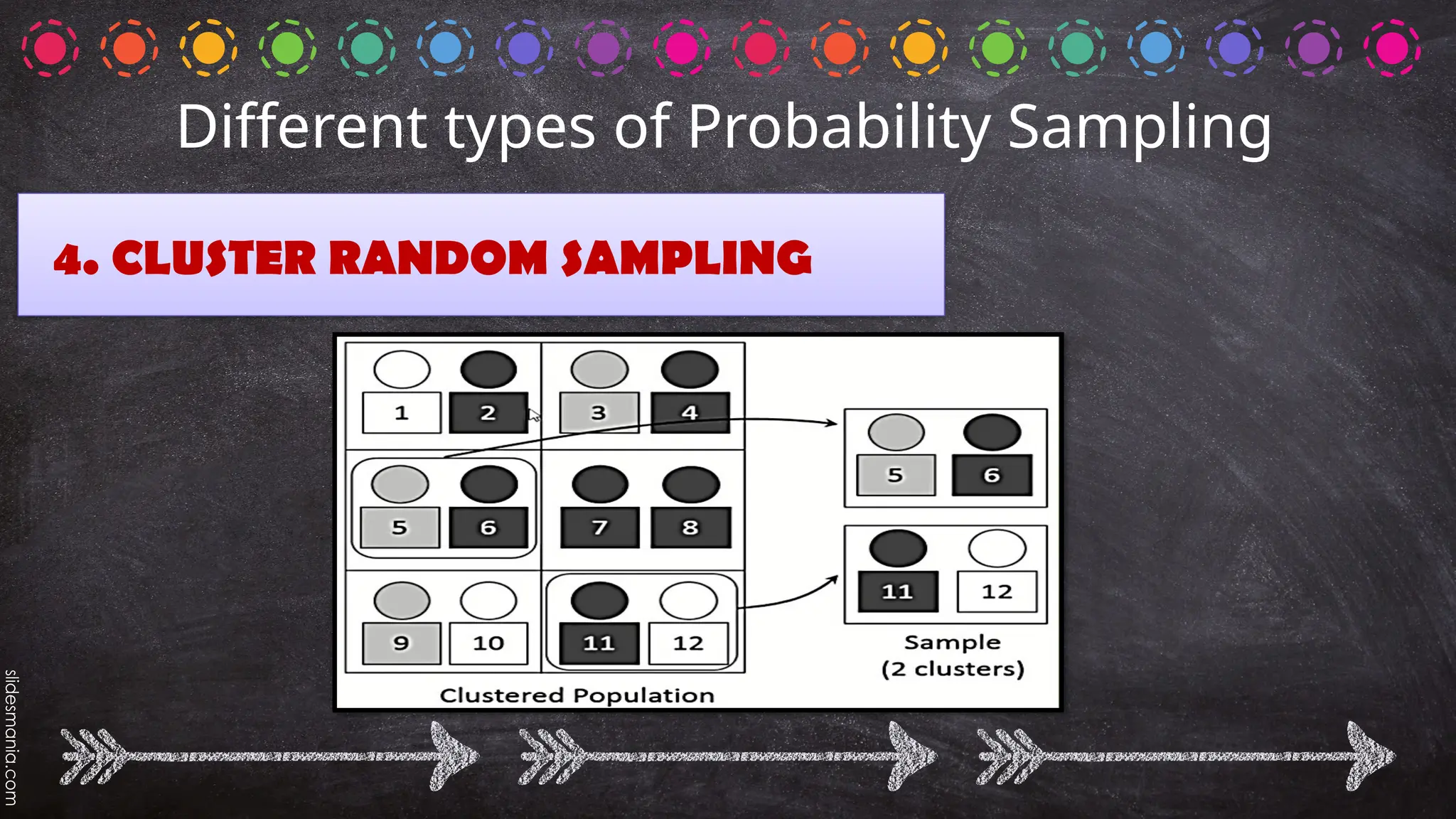
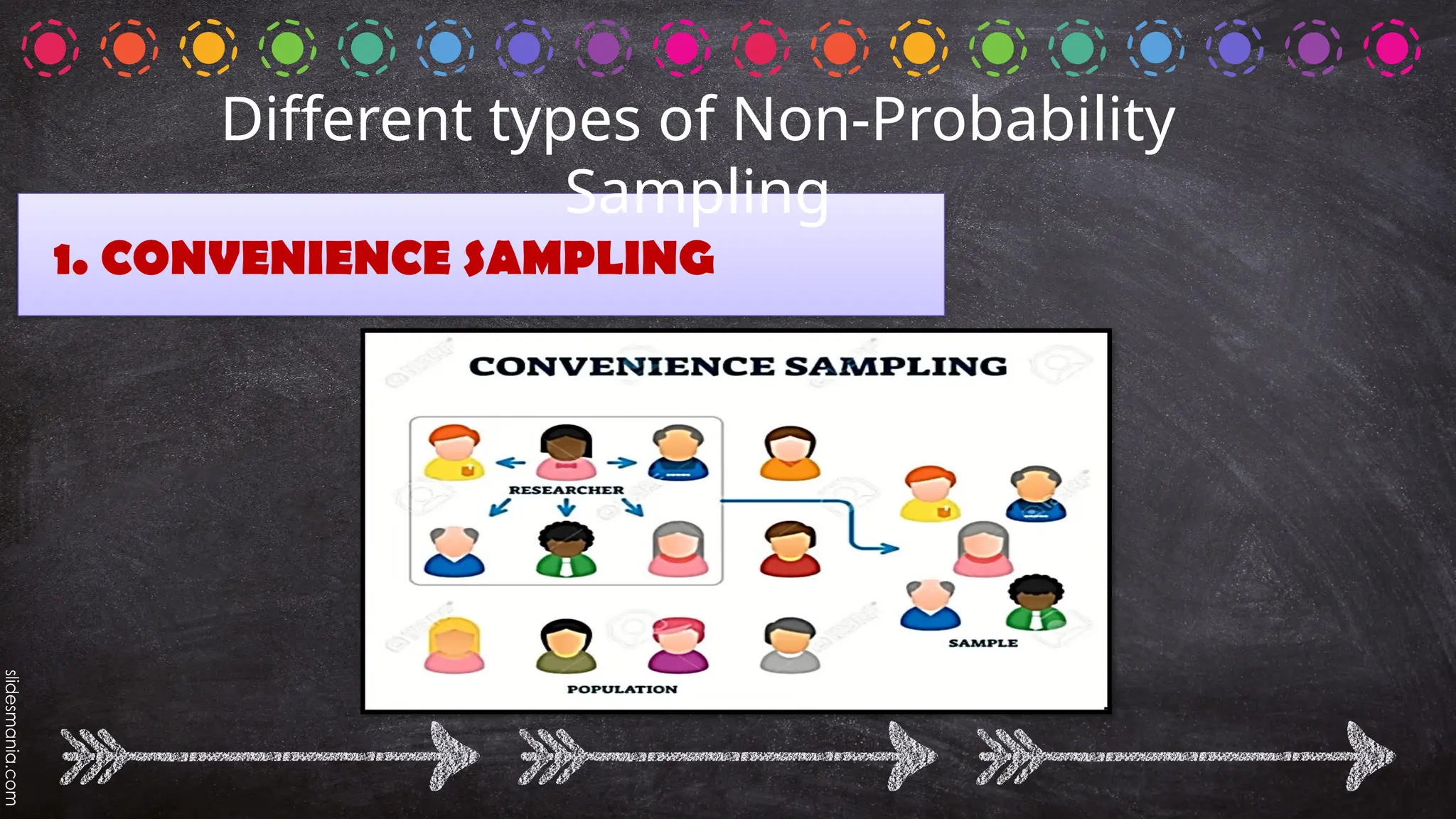
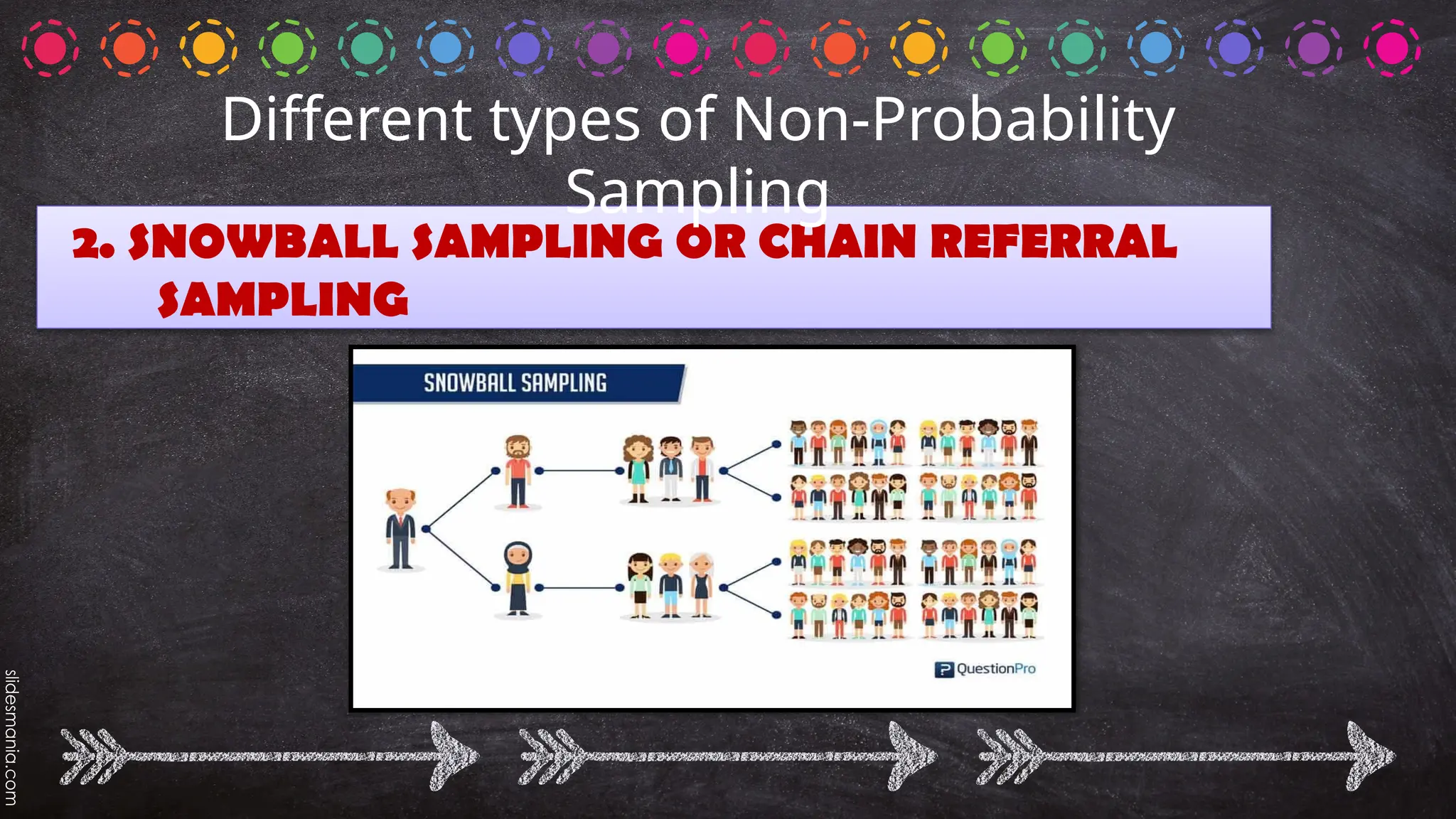
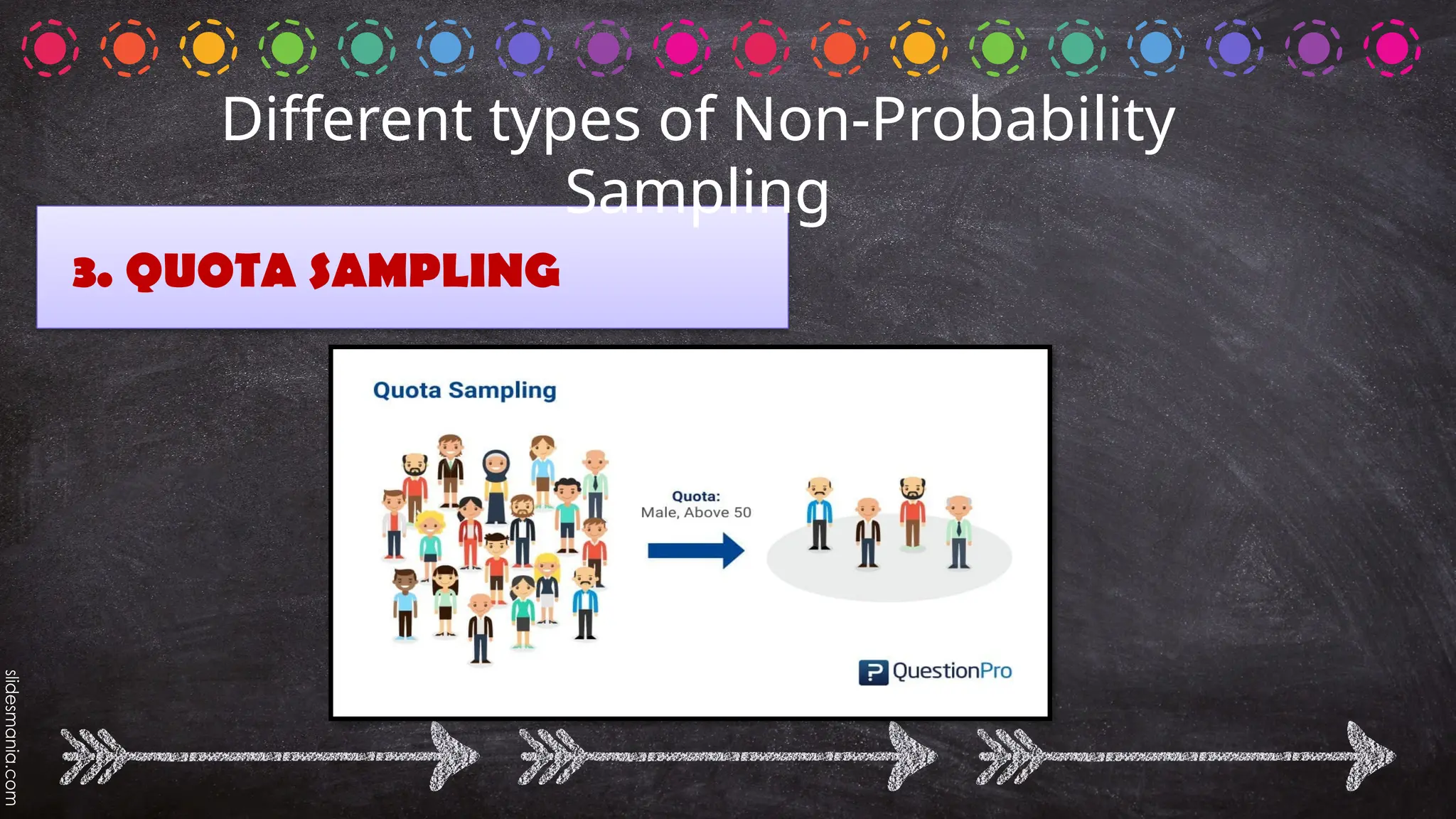
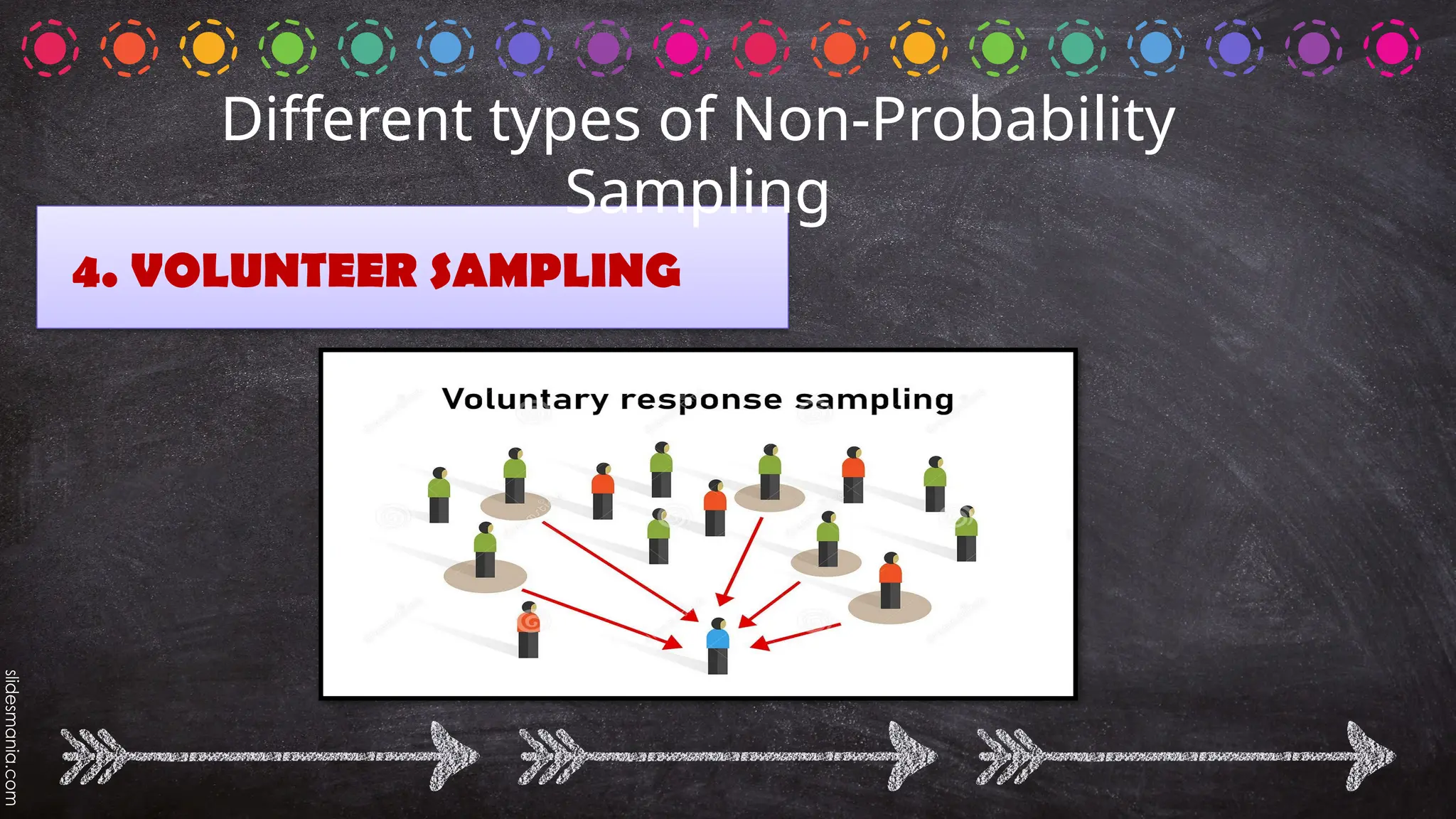
The document outlines various random sampling techniques, defining key terms such as population, sample, and the differences between probability and non-probability sampling. It details specific methods including simple random, systematic, stratified, cluster, convenience, snowball, quota, and volunteer sampling. The document also provides practical examples for identifying the applicable sampling method in different research scenarios.