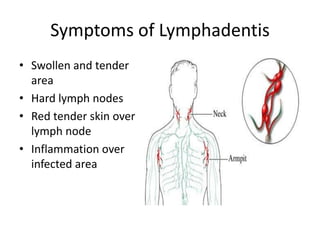
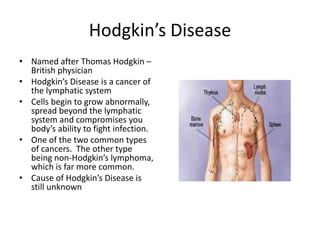
Lymphadenitis is an infection of the lymph nodes that causes swelling. It is usually caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi near the site of infection. Symptoms include swollen and tender lymph nodes. Treatment involves antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or pain medication. Hodgkin's disease is a cancer of the lymphatic system where cells grow abnormally. Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes and weight loss. Treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation, or stem cell transplant. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma occurs when lymphocytes overproduce, forming tumors. Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, and night sweats.