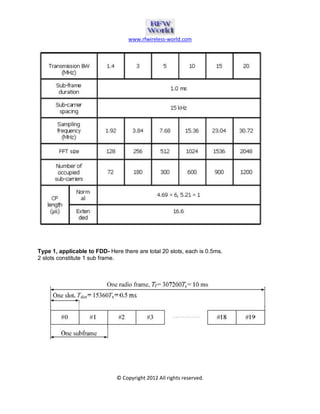
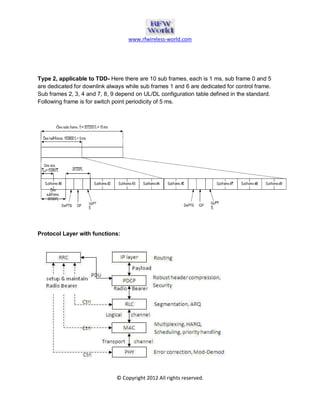
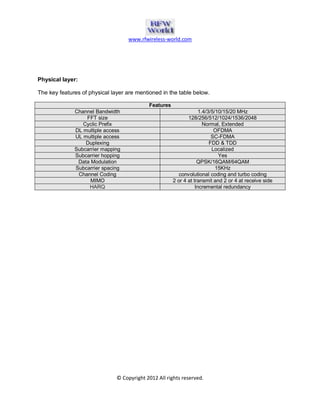
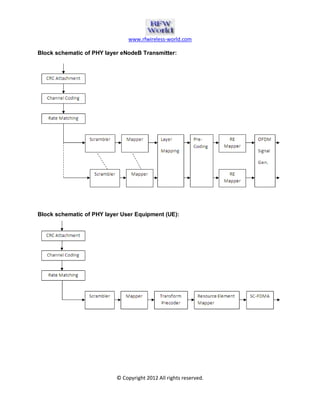
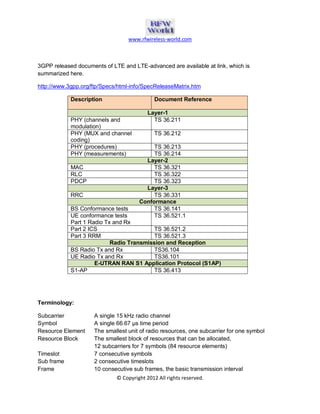
The document provides an overview of the Long Term Evolution (LTE) system, a crucial advancement of 3G technologies aimed at maintaining competitive wireless communication. It outlines specifications for radio transmission, including multiple access technologies such as OFDMA and SC-FDMA, along with detailed structure and parameters for frames and physical layer protocols. Additionally, it references technical standards and documentation related to LTE and LTE-Advanced for further information.