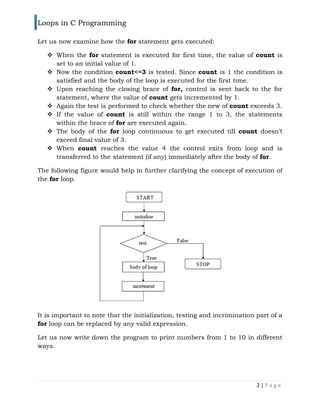
The document discusses loops in C programming, highlighting three main types: for loops, while loops, and do-while loops. It provides detailed explanations, examples, and syntactical structures for each loop type, emphasizing their applications in repetitive programming tasks. Additionally, it explains the concept of nested loops and illustrates how they can be combined to achieve more complex coding tasks.