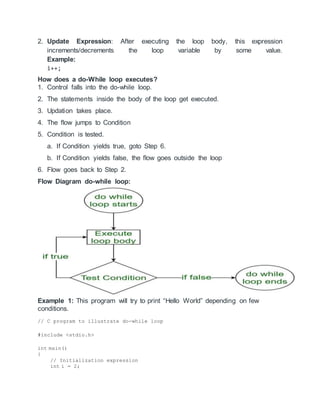
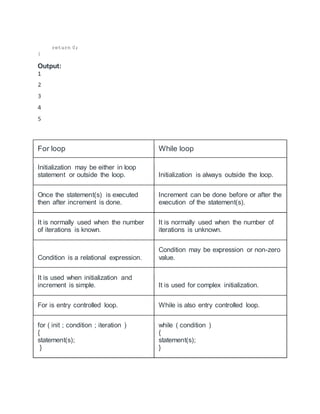
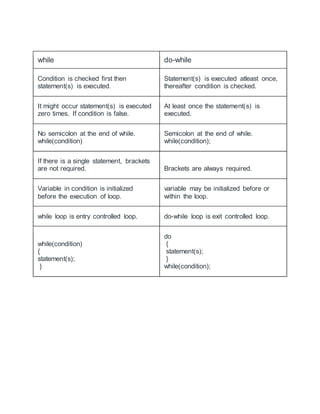
The document discusses different types of iteration logic or loops in C programming. It describes the repeat-for loop, repeat-while loop, for loop, while loop, and do-while loop. The key aspects of each loop type are defined, including initialization, condition checking, updating, and flow of execution through the loop body. Examples are provided to illustrate the usage and flow of each loop type.
![Iteration Logic (Repetitive Flow)
The Iteration logic employs a loop which involves a repeat statement
followed by a module known as the body of a loop.
The two types of these structures are:
Repeat-For Structure
This structure has the form:
Repeat for i = A to N by I:
[Module]
[End of loop]
Here, A is the initial value, N is the end value and I is the increment.
The loop ends when A>B. K increases or decreases according to
the positive and negative value of I respectively.
Repeat-For Flow
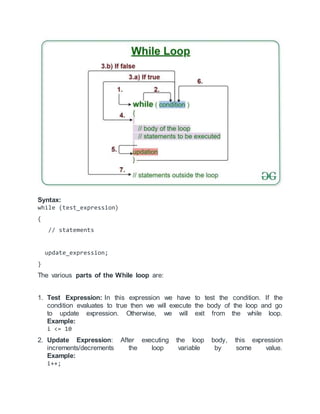
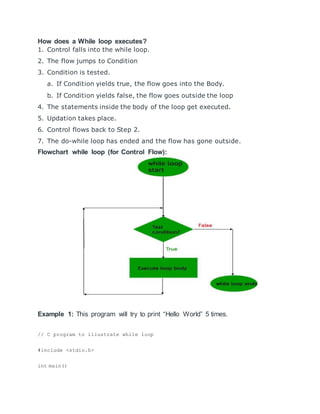
Repeat-While Structure
It also uses a condition to control the loop. This structure has the
form:
Repeat while condition:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itretion-220410135936/75/itretion-docx-1-2048.jpg)
![ [Module]
[End of Loop]
Repeat While Flow
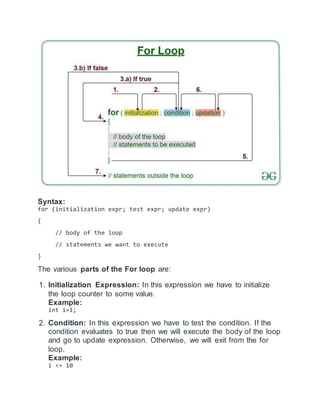
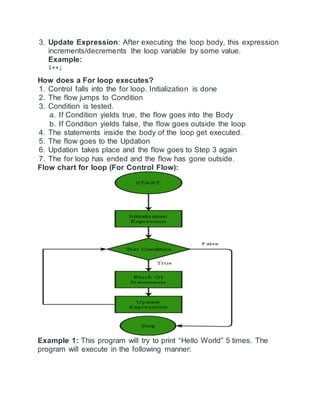
For loop is a repetition control structure which allows us to write a loop
that is executed a specific number of times. The loop enables us to
perform n number of steps together in one line.
For(init,condition,update)
For(i=1;1<10;i++) i=0 i=1,i=2 9<10,10<10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itretion-220410135936/85/itretion-docx-2-320.jpg)