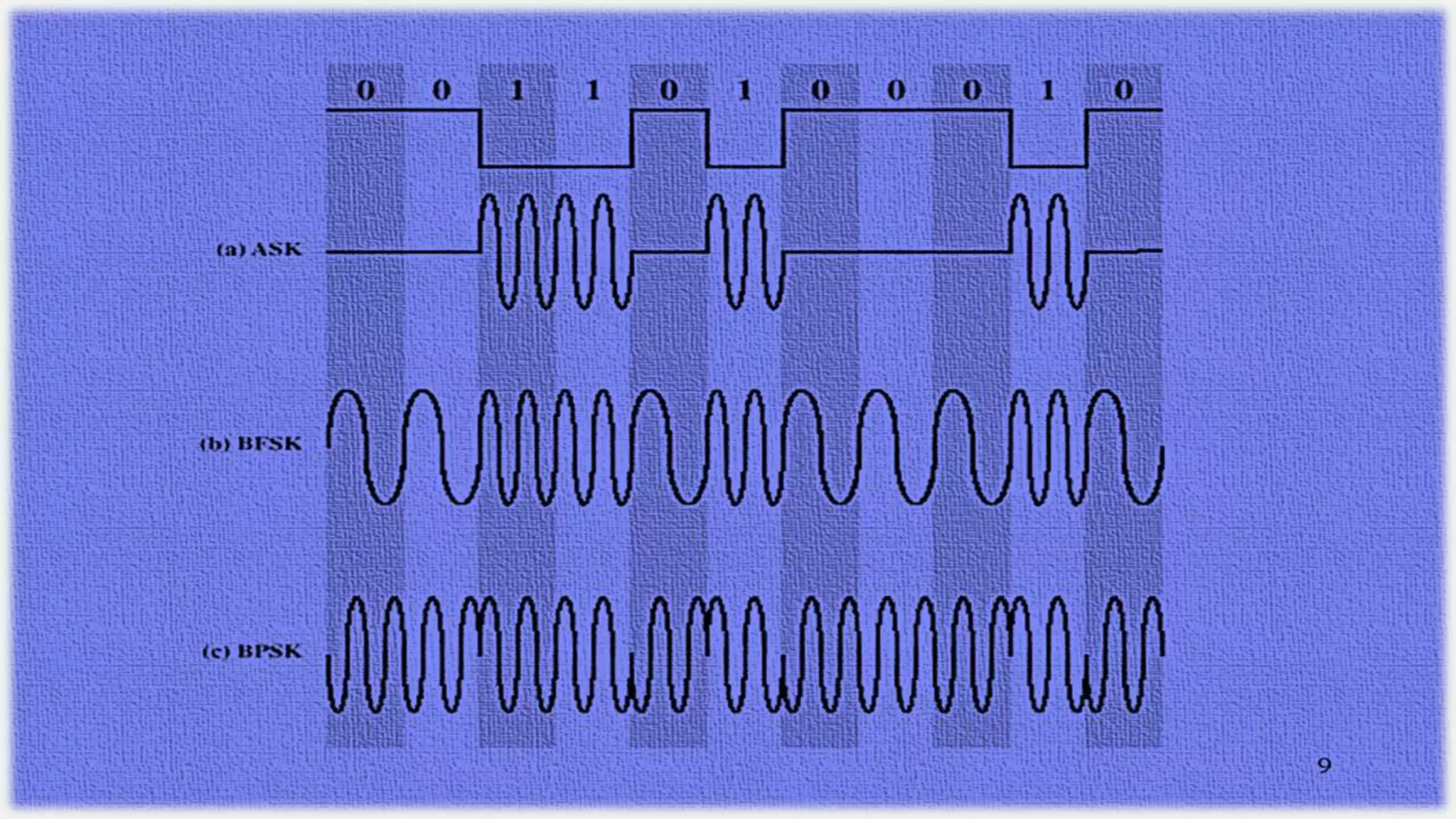
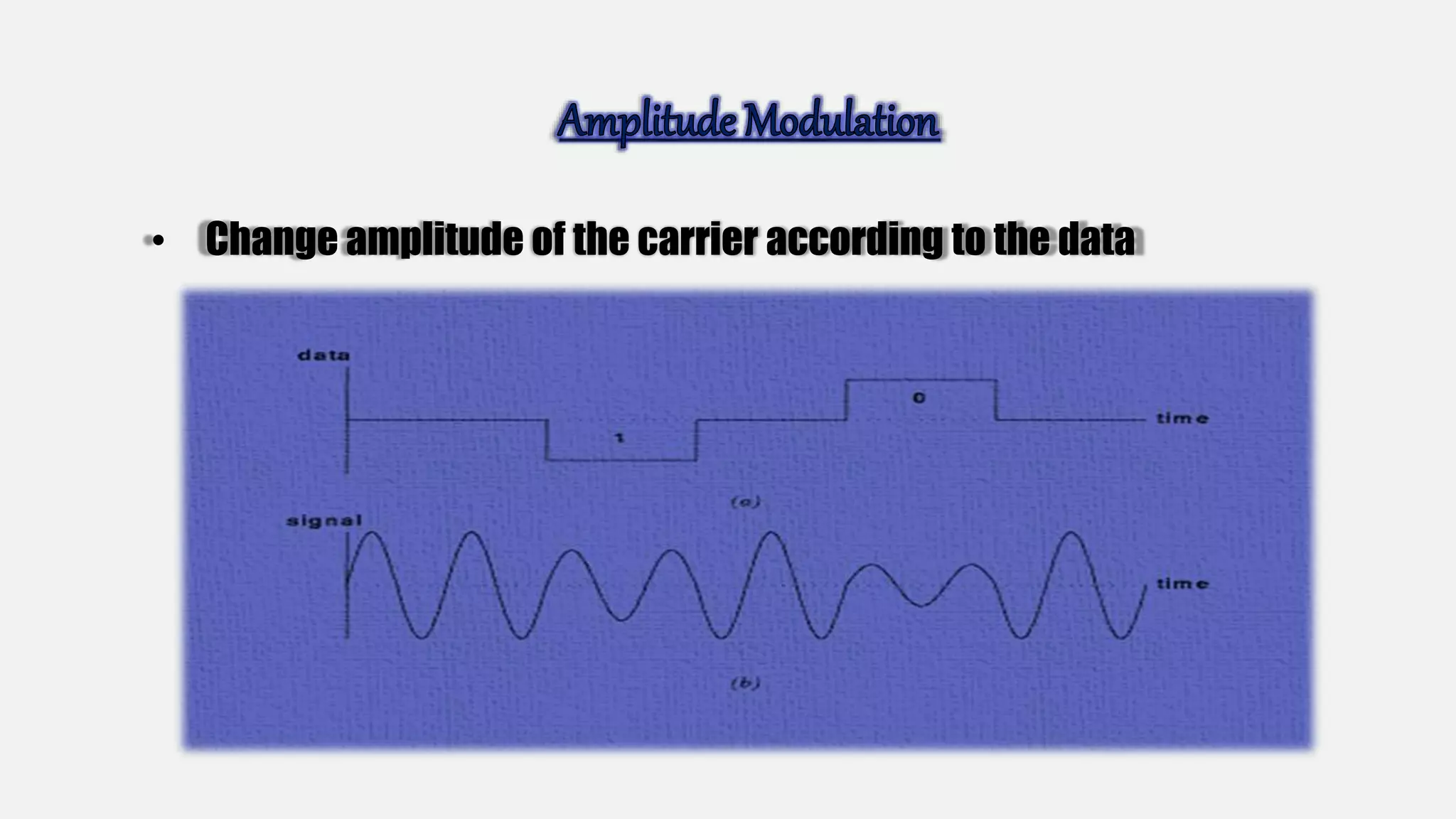
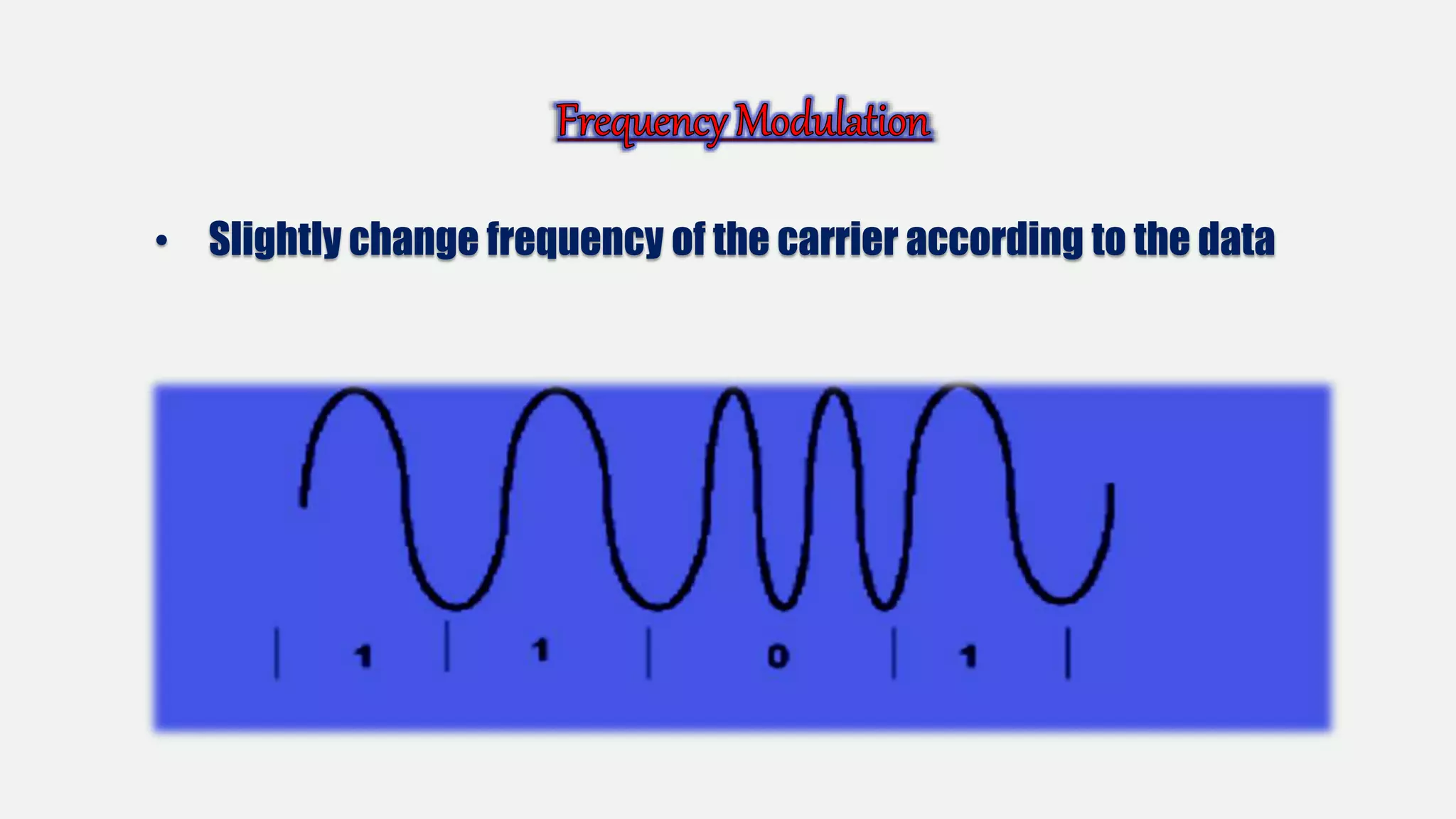
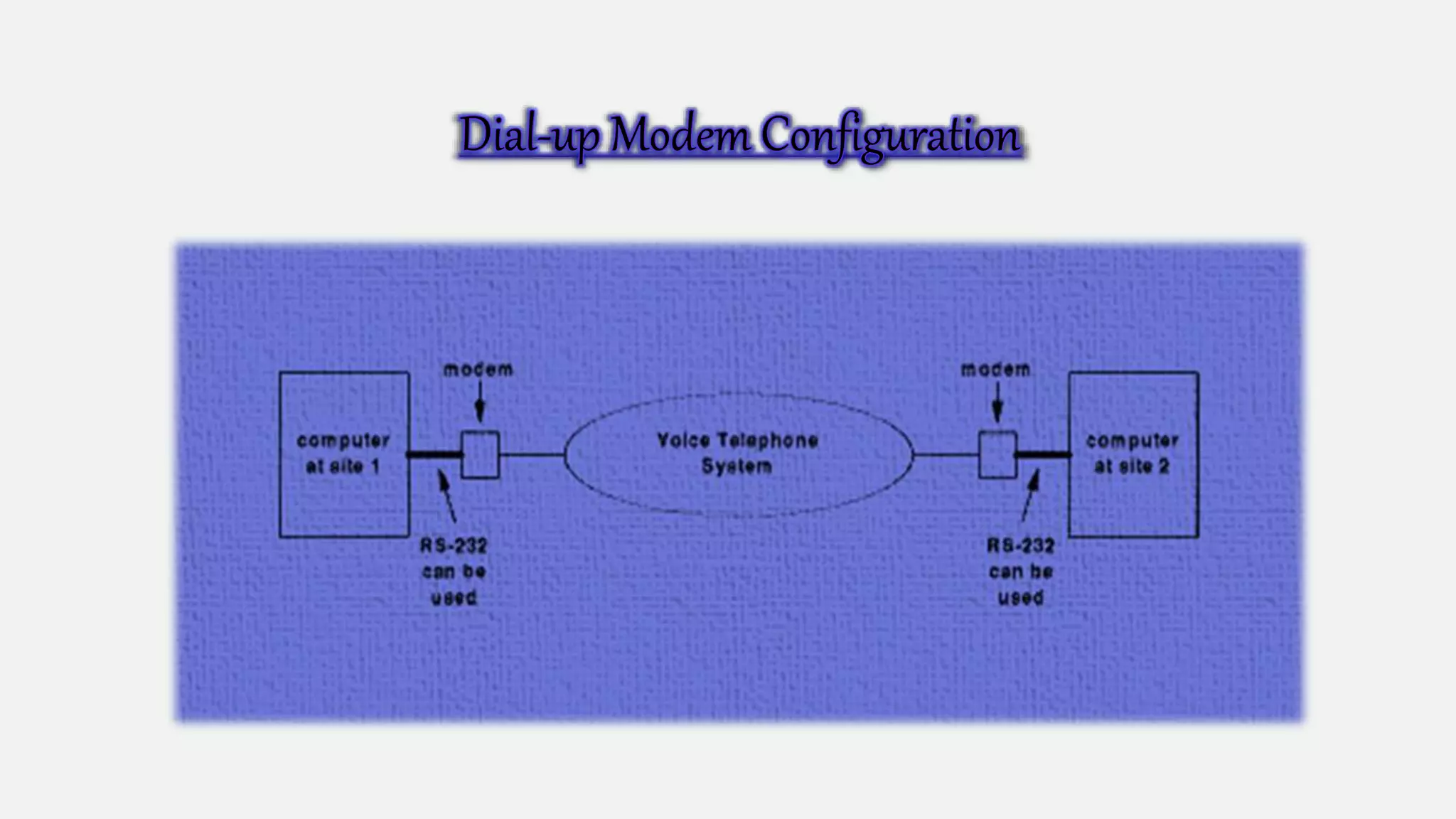
This document discusses long-distance communication and modulation techniques used for data transmission over long distances. It covers types of modulation like amplitude modulation and frequency modulation that are used to encode data onto a carrier signal. It also discusses modems, leased telephone circuits, and multiplexing techniques like frequency division multiplexing and time division multiplexing that allow multiple logical connections to share a single physical medium.