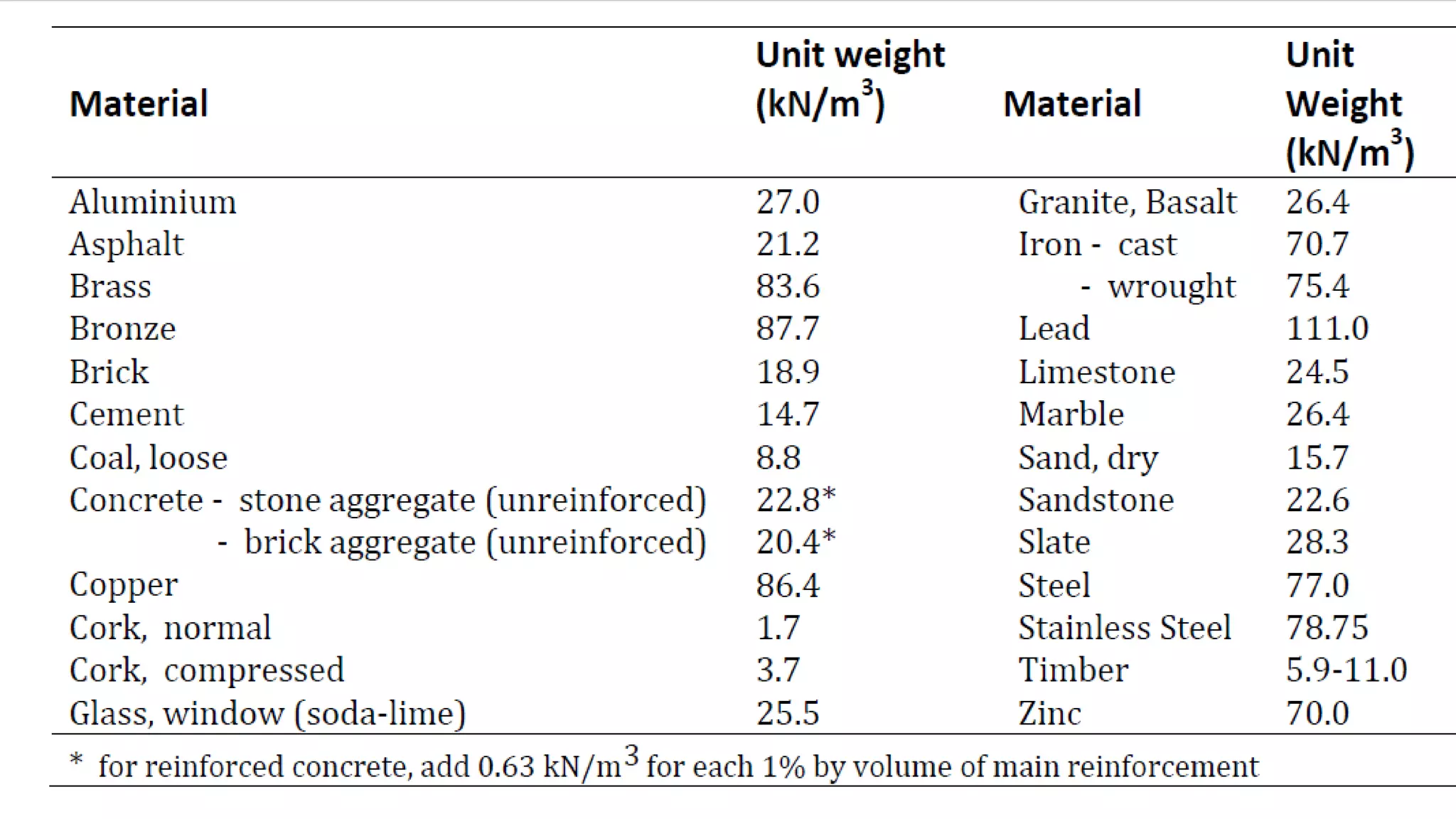
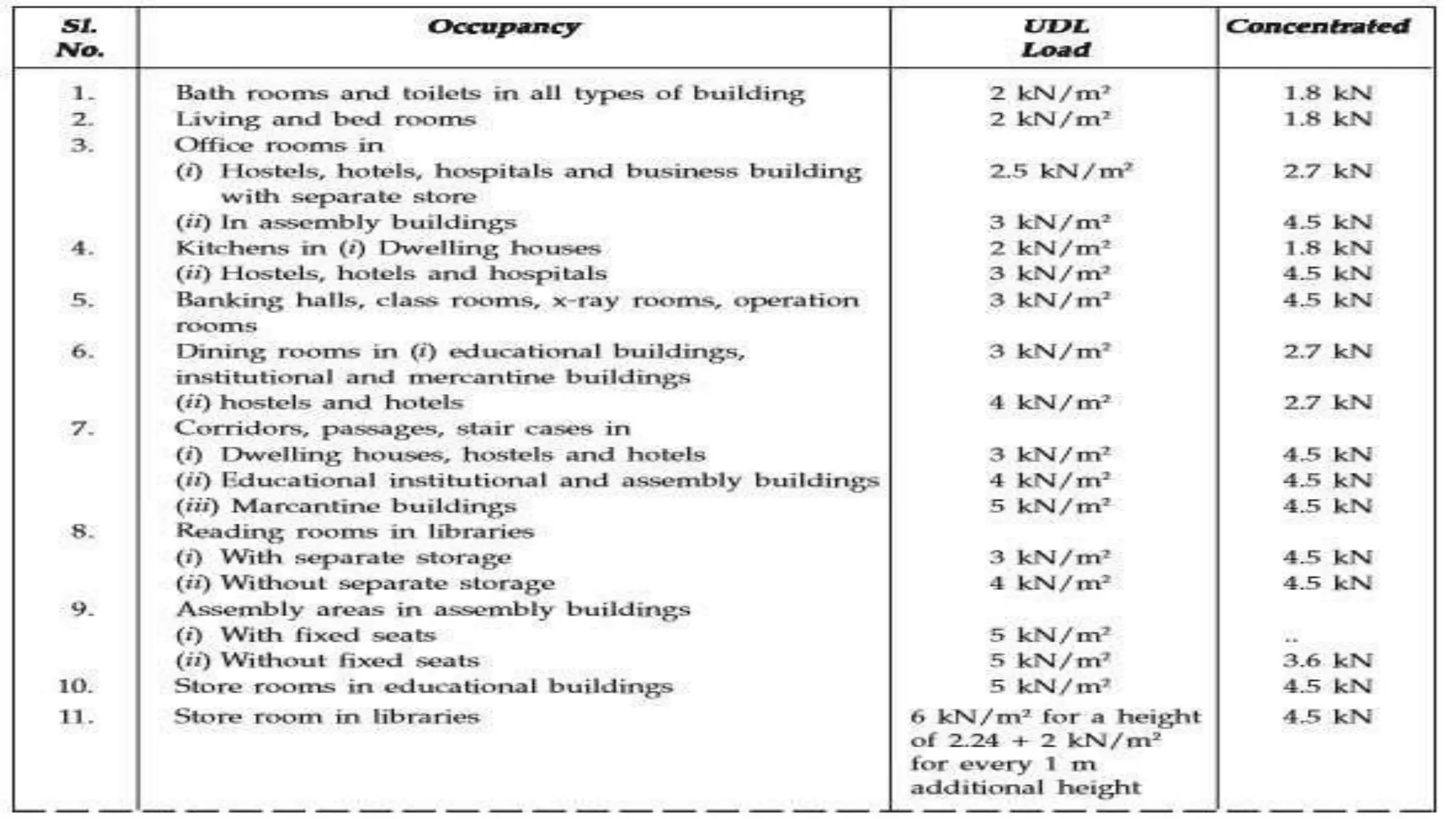
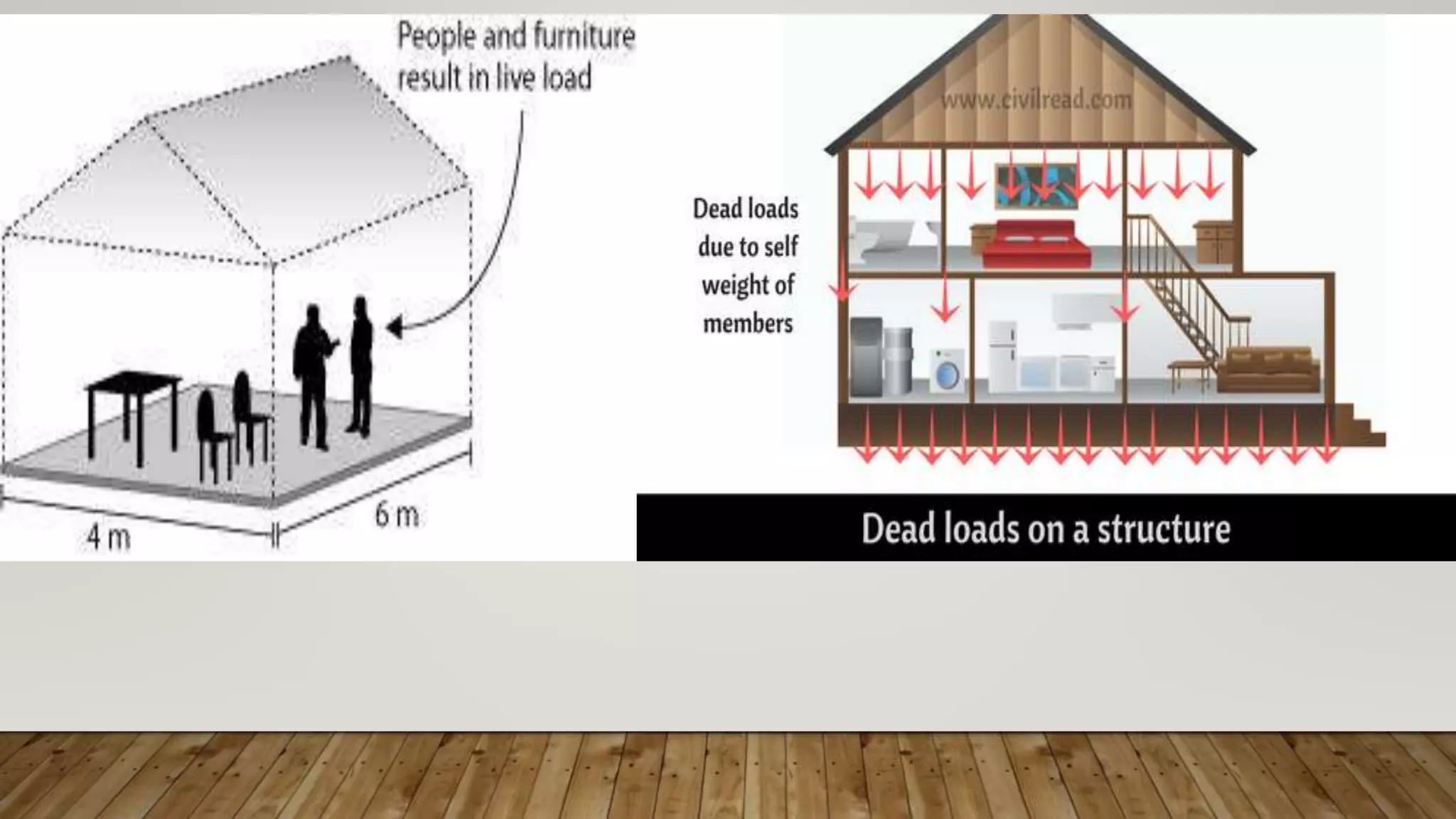
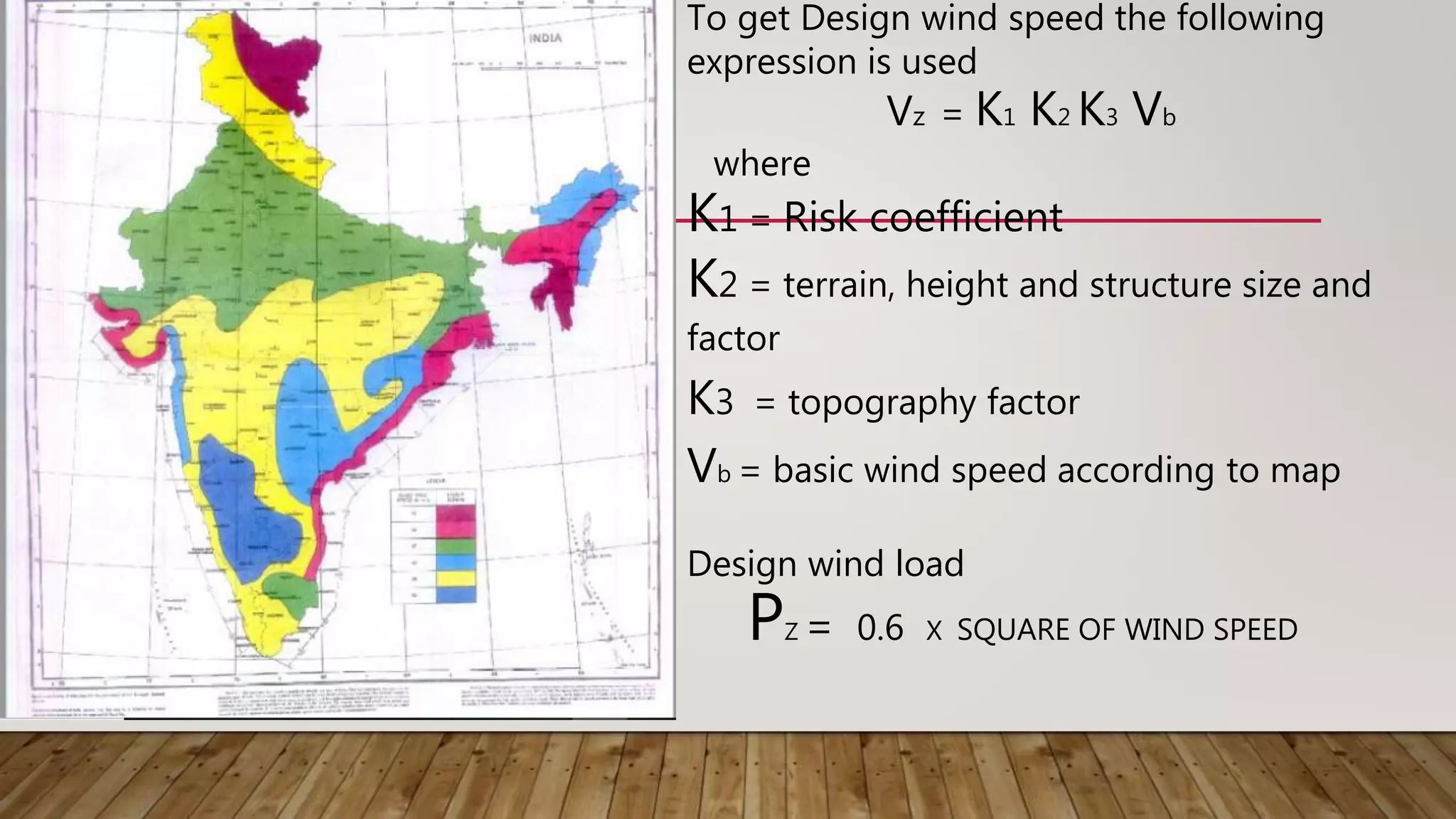
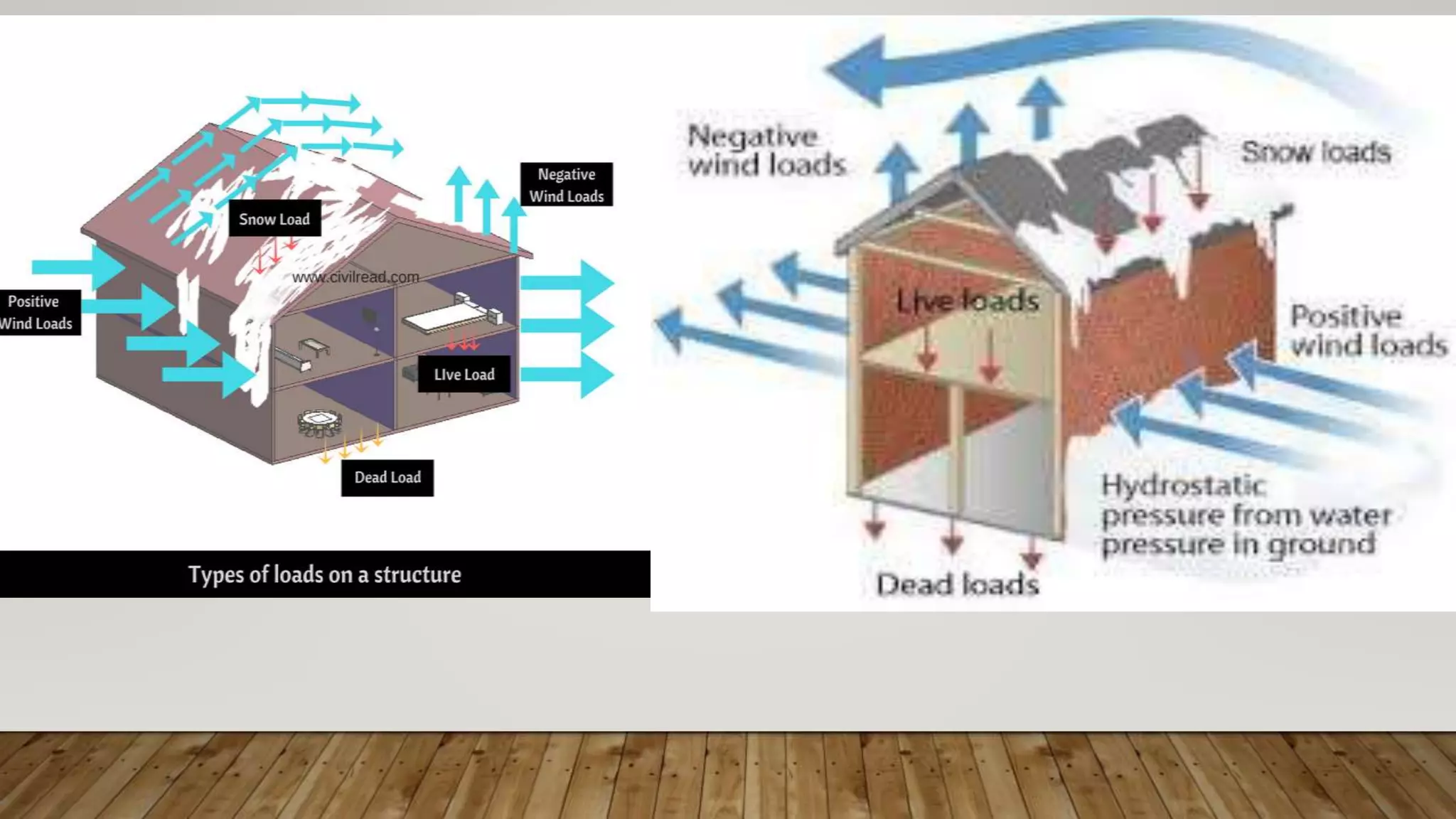
The document discusses the various loads considered in building design, including dead load, imposed load, wind load, snow load, and special loads, each governed by specific codes. It highlights how these loads affect structural safety, utility, and compliance with various standards based on the intended use and occupancy of the building. Additionally, it outlines the importance of load combinations for accurate structural assessments.