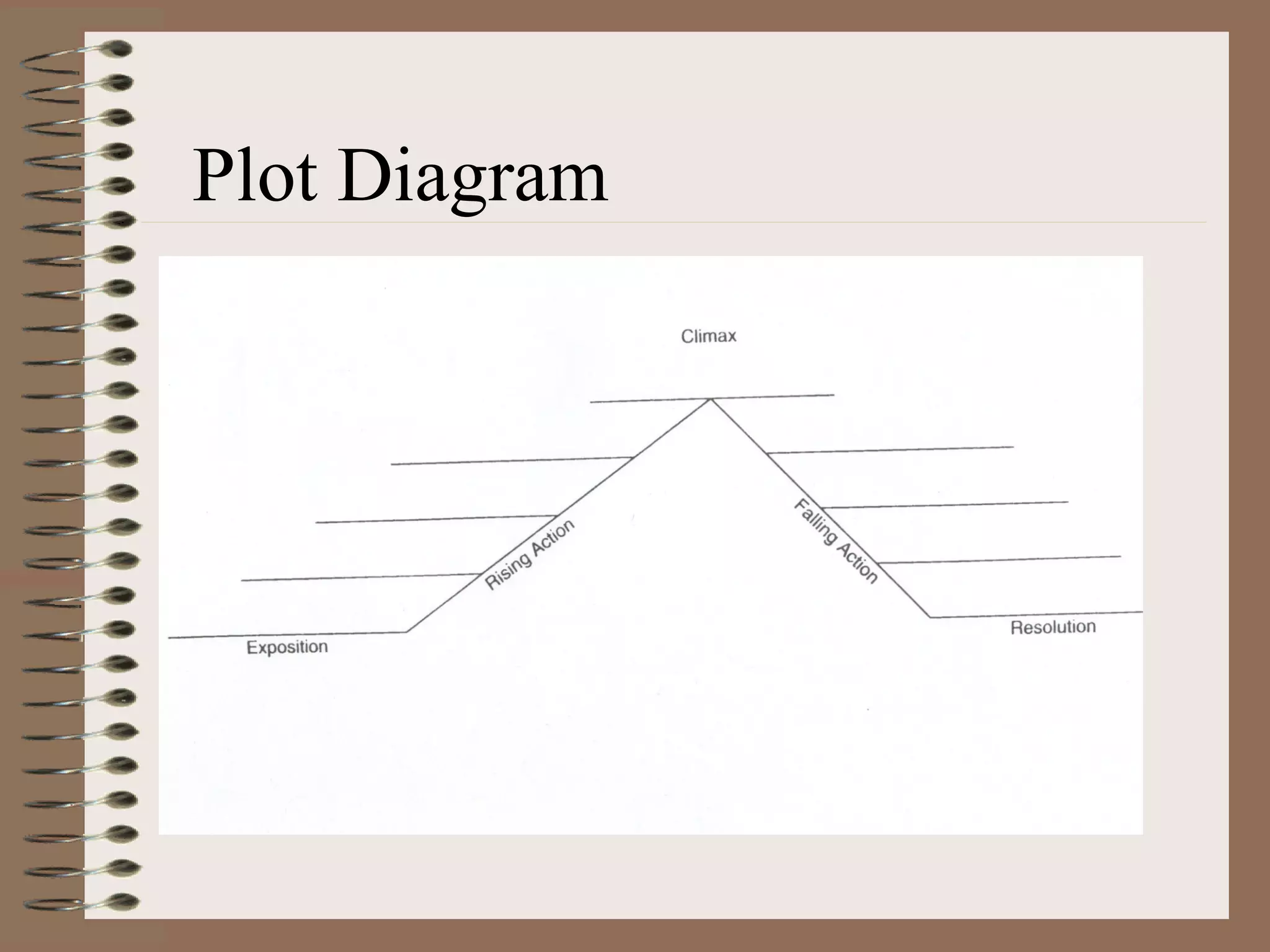
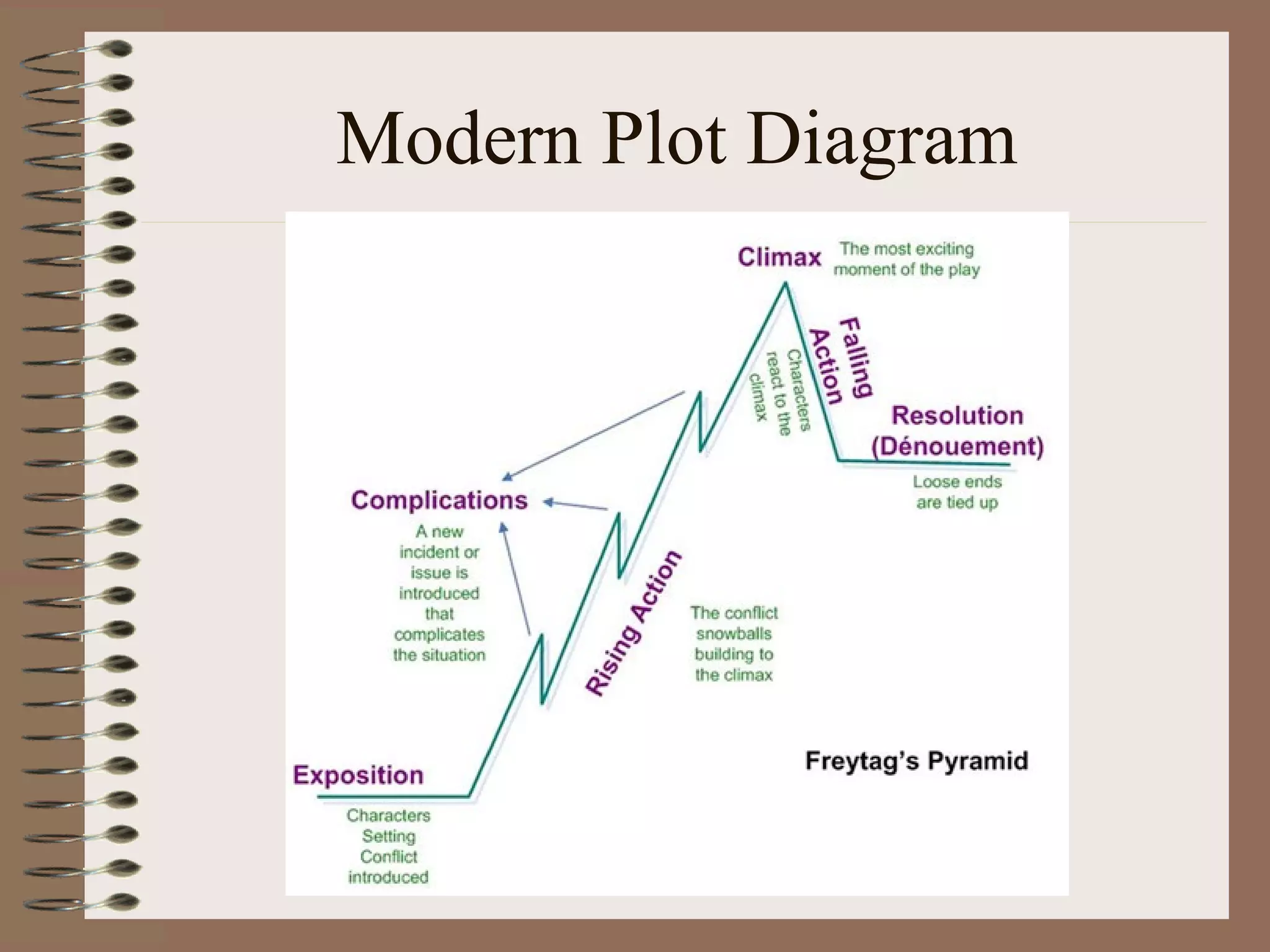
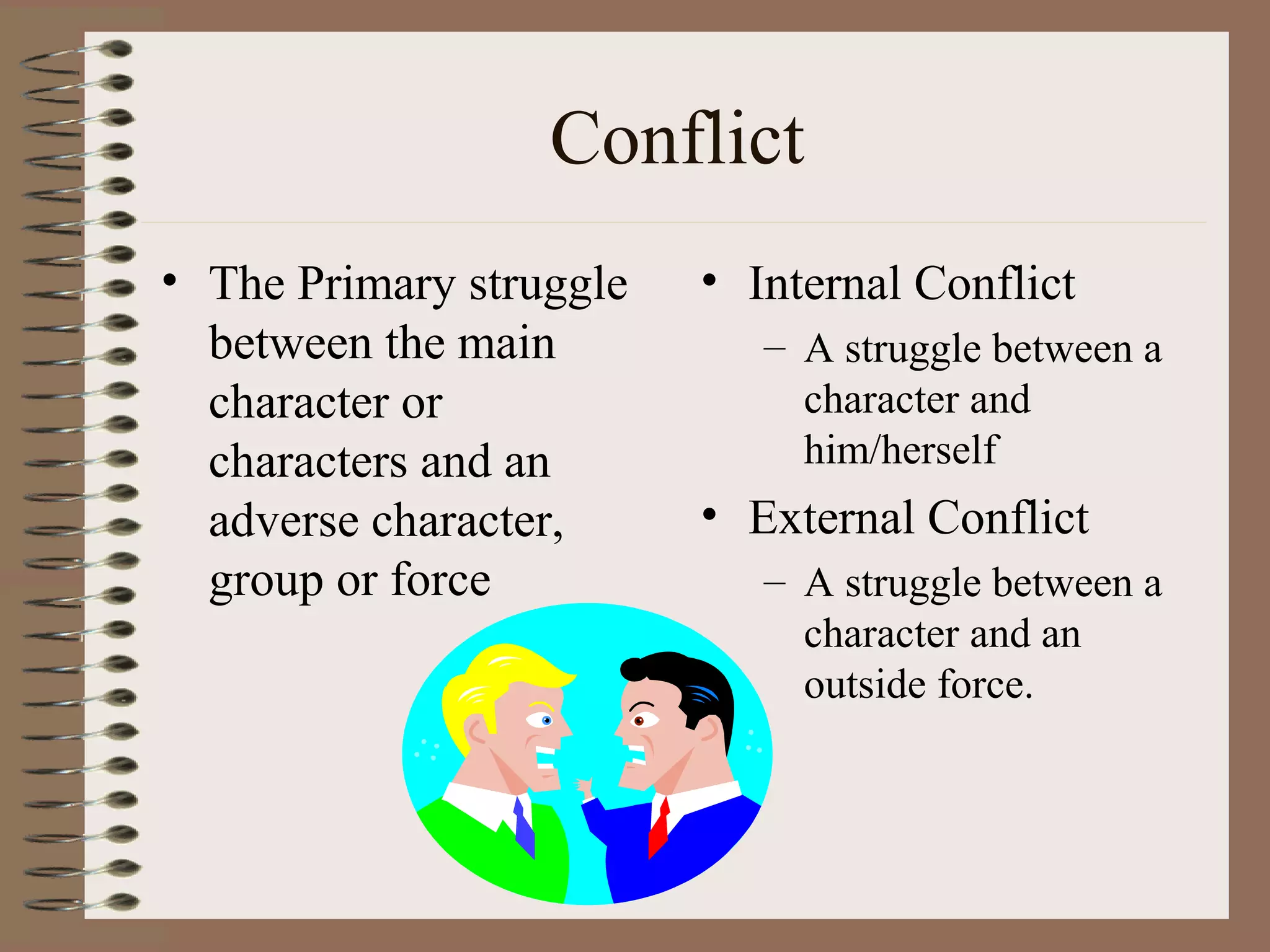
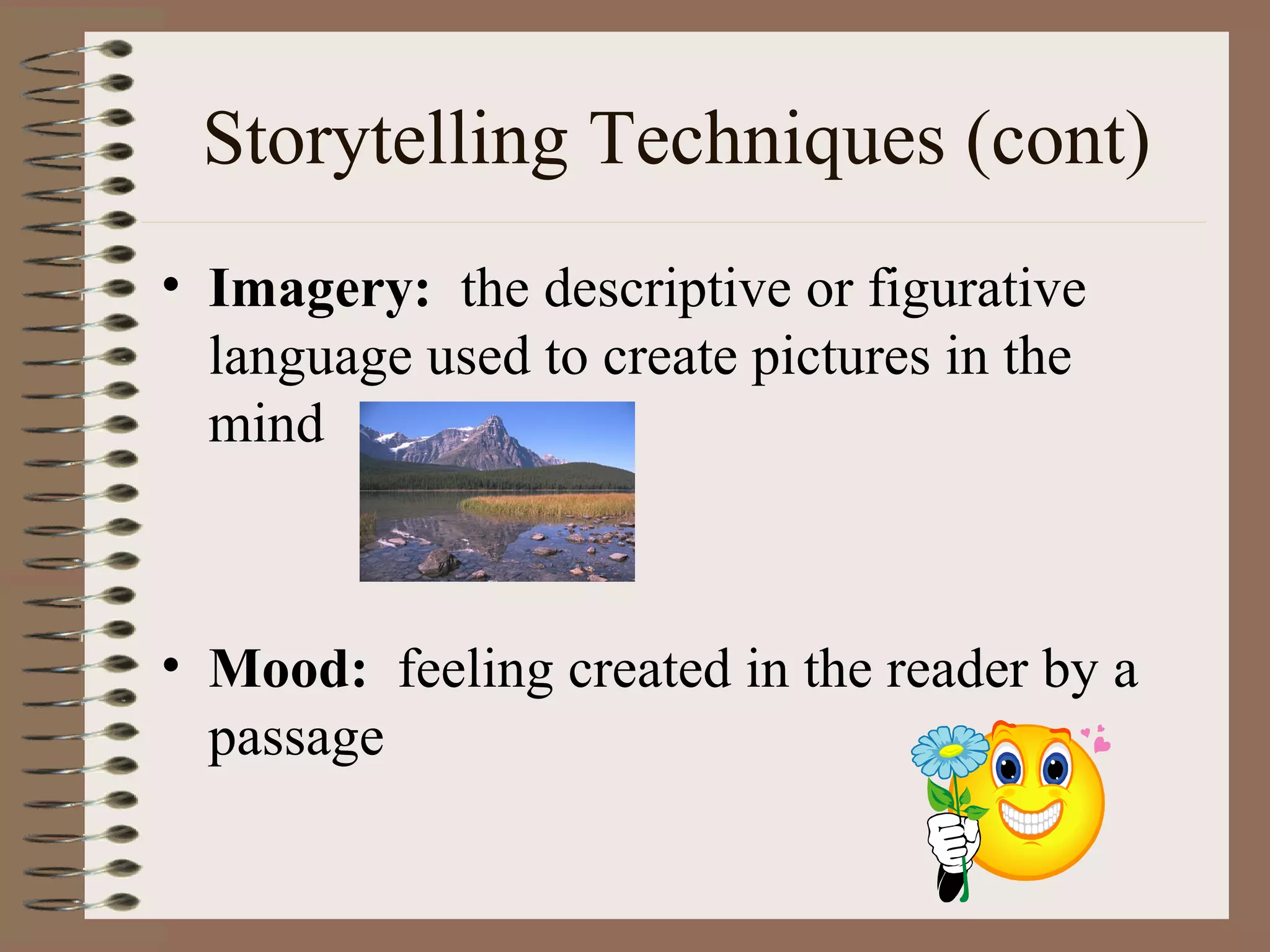
A short story is a brief work of fiction, often less than 50 pages. It contains elements such as plot, characters, setting, theme, point of view, and storytelling techniques. The plot involves a series of related events that present and resolve a conflict, and includes components like exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. Characters can be dynamic, flat, round, or static. The short story establishes a setting and conveys a theme or message through the use of techniques including dialogue, imagery, and symbolism.