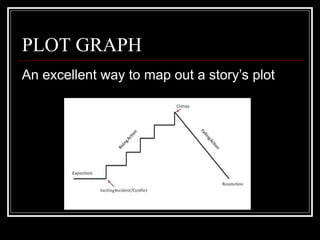
The document outlines the elements of a short story, defining it as a brief, imaginative narrative with key components such as plot, conflict, setting, character, theme, and point of view. It explains the structure of plot, types of conflict, the importance of character development, and the significance of theme without equating it to moral lessons. Additionally, it discusses various points of view from which stories can be told, detailing how each influences reader perception.