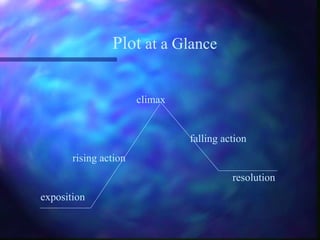
This document defines the key elements of a short story, including plot, characterization, setting, point of view, symbols, and theme. It explains that a short story's plot centers around conflict and features exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. Characterization can be direct or indirect, and characters can be main or minor, protagonist or antagonist. A story's setting, point of view, symbols, and theme all contribute to conveying the writer's message about life or human nature.