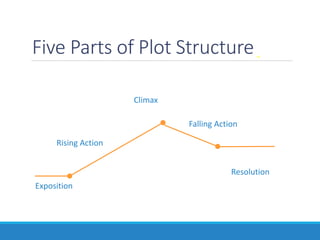
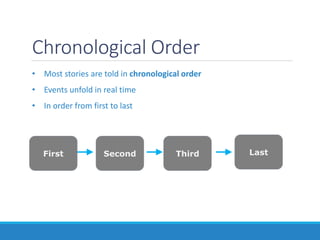
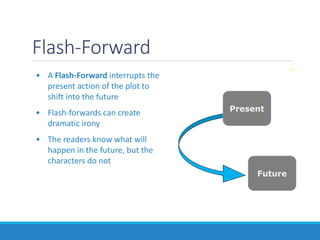
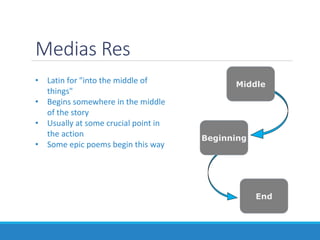
This document outlines essential elements in fiction, including setting, plot, conflict, and pacing. It defines setting as the time, place, and period of the story. Plot is described as a series of related events consisting of exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. Conflict can be internal, between a character and themselves, or external, such as between characters, a character and nature or society, or a character and supernatural elements. Pacing refers to how authors manipulate the timeline of events, such as through chronological order, flashbacks, flash-forwards, or starting in medias res.