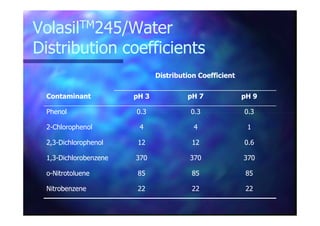
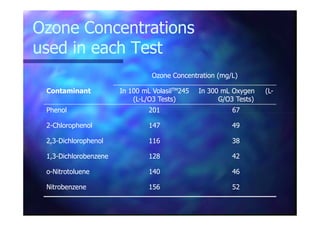
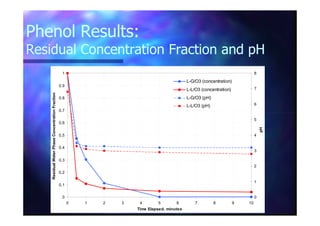
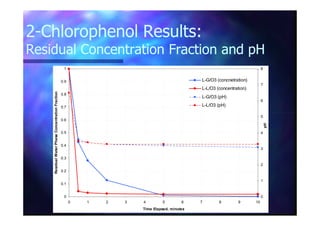
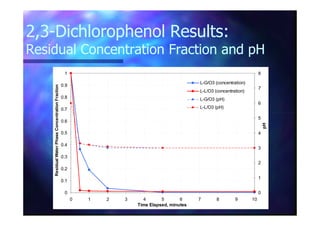
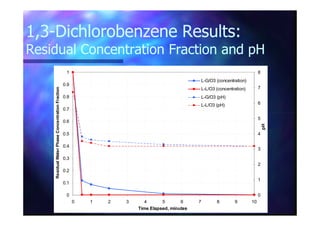
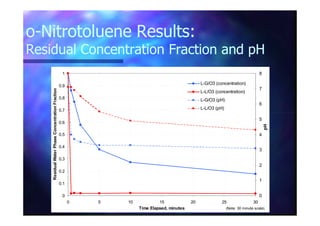
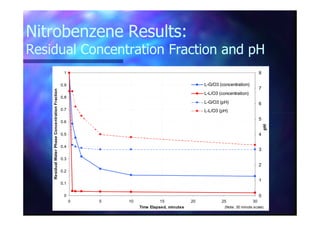
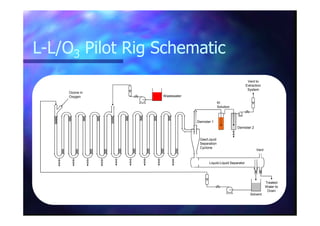
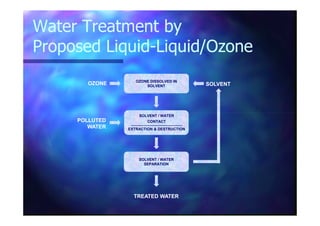
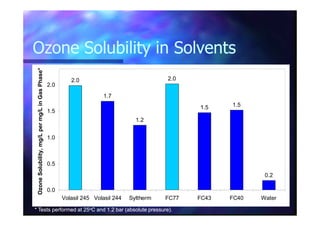
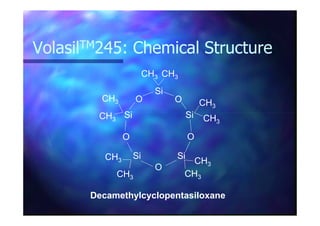
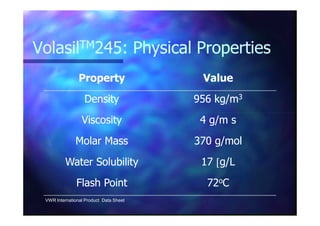
This document summarizes research on using ozone-loaded solvents to extract and destroy organic contaminants in wastewater. Volasil 245, a polydimethylsiloxane, was selected as a suitable solvent based on its properties like high ozone solubility, low toxicity, and resistance to oxidation. Preliminary tests showed Volasil 245 was effective at extracting various organic contaminants from water. Volasil 245 liquid-liquid contact with ozone achieved faster degradation of phenol and chlorophenol in water than conventional gas-liquid contact with ozone. Overall results indicate ozone-loaded solvents may provide an improved method for treating organics in wastewater.














![VolasilVolasilTMTM245: Henry’s Law245: Henry’s Law
Dissolved ODissolved O33 found to obey Henry’s Lawfound to obey Henry’s Law
(10(10 –– 90 mg/L gas phase).90 mg/L gas phase).(10(10 –– 90 mg/L gas phase).90 mg/L gas phase).
[O[O33 in Solvent]in Solvent] ∝∝ [O[O33 in Gas]in Gas]
H =H = 34 bar/mole34 bar/mole--fractionfraction @ 298 K@ 298 K](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03cc3a89-1619-4cae-a181-612d3941b8fe-150505060746-conversion-gate01/85/LiquidLiquidOzone-19-320.jpg)