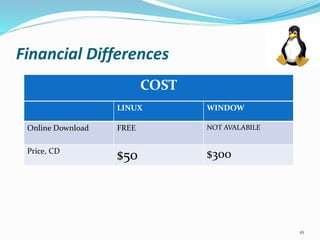
Linux is a free and open-source operating system based on UNIX. It was created in 1991 by Linus Torvalds and has since been developed by a large worldwide community. Linux can run on a variety of hardware and is widely used for servers, workstations, and embedded systems. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora, Ubuntu, and Mint. Linux offers advantages like low cost, stability, security, and broad hardware support. However, it can be more difficult for new users to install and use than other systems.