This document provides an overview of matrix algebra concepts including:
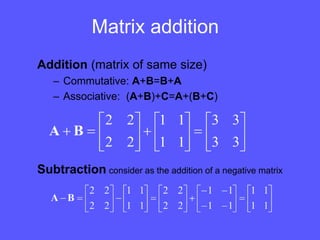
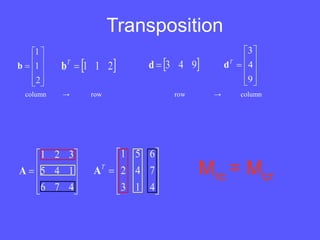
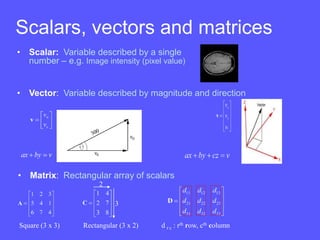
- Matrices are rectangular arrays of scalars that are defined by their number of rows and columns. Common matrix operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and transposition.
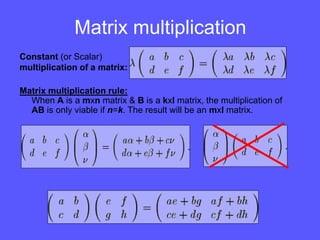
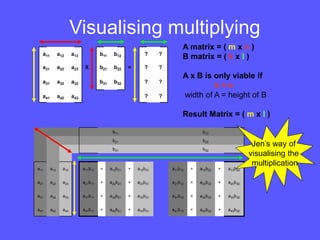
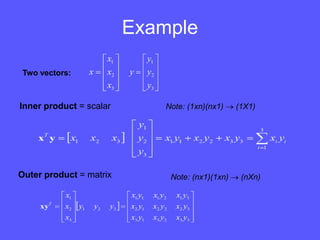
- Matrix multiplication involves multiplying the rows of the first matrix by the columns of the second, and can only be done if the number of columns of the first equals the number of rows of the second.
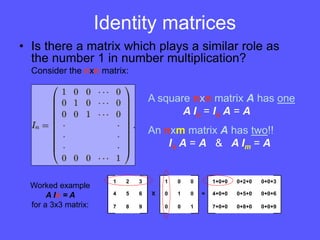
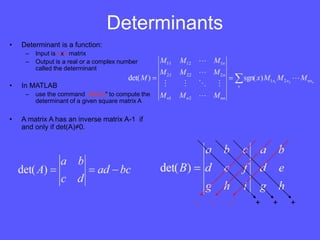
- Identity matrices play a similar role to the number 1 in regular multiplication. The determinant of a matrix is a single number that can be used to determine if a matrix is invertible.
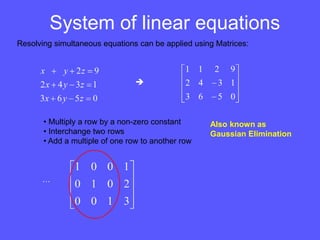
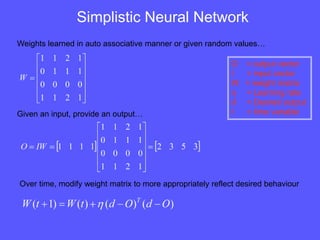
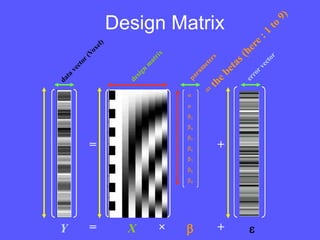
- Example applications of matrix algebra include solving systems of linear equations, simple neural networks, and general linear


![Matrices
• A matrix is defined by the number of Rows and the
number of Columns.
• An mxn matrix has m rows and n columns.
A = 4x3 matrix
• A square matrix of order n, is an nxn matrix.
21 2 53
5 34 12
6 33 55
74 27 3
Matlab notes ( ; End of matrix row )
A = [ 21 5 53 ; 5 34 12 ; 6 33 55 ; 74 27 3 ]
To extract data: Matrix name( row, column )
Scalar Data Point A( 1 , 2 ) = 2
Row Vector A( 2 , : ) = [ 5 34 12 ]
Column Vector A( : , 3 ) = [ 53 ; 12 ; 55 ; 3 ]
Smaller Matrix A(2:4,1:2) = [ 5 34 ; 6 33 ; 74 27 ]
Another Matrix A( 2:2:4 , 2:3 ) = [ 34 12 ; 27 3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearalgebramatrices-231225093300-fe1a9ecf/85/Linear_Algebra_Matrices-ppt-4-320.jpg)