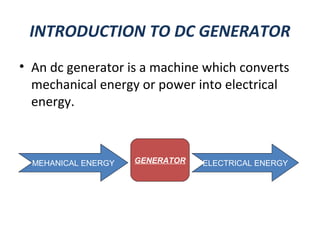
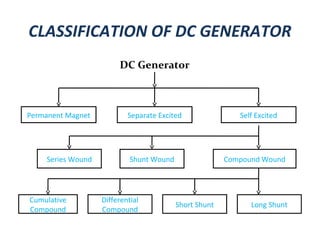
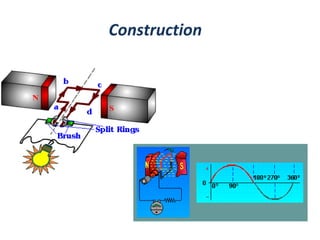
The document provides an overview of DC generators, detailing their function as machines that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. It covers the working principle based on electromagnetic induction, the various parts and classifications of DC generators, and their applications in different scenarios such as electroplating and battery charging. Additionally, it outlines the construction of a DC generator and includes a thank you note at the end.