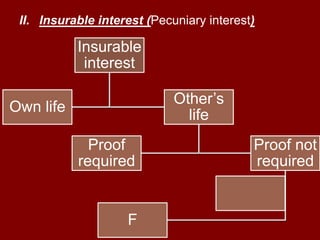
The document discusses the key concepts and principles of life insurance. It covers the nature of life insurance as a long-term contract that provides financial protection to beneficiaries in the event of death. It also discusses the various types of life insurance policies based on duration, premium payments, participation in profits, number of lives covered, and payment of claims. Finally, it outlines some important aspects like assignment and nomination procedures, surrender and loan values, age and death proofs, and payment of claims.