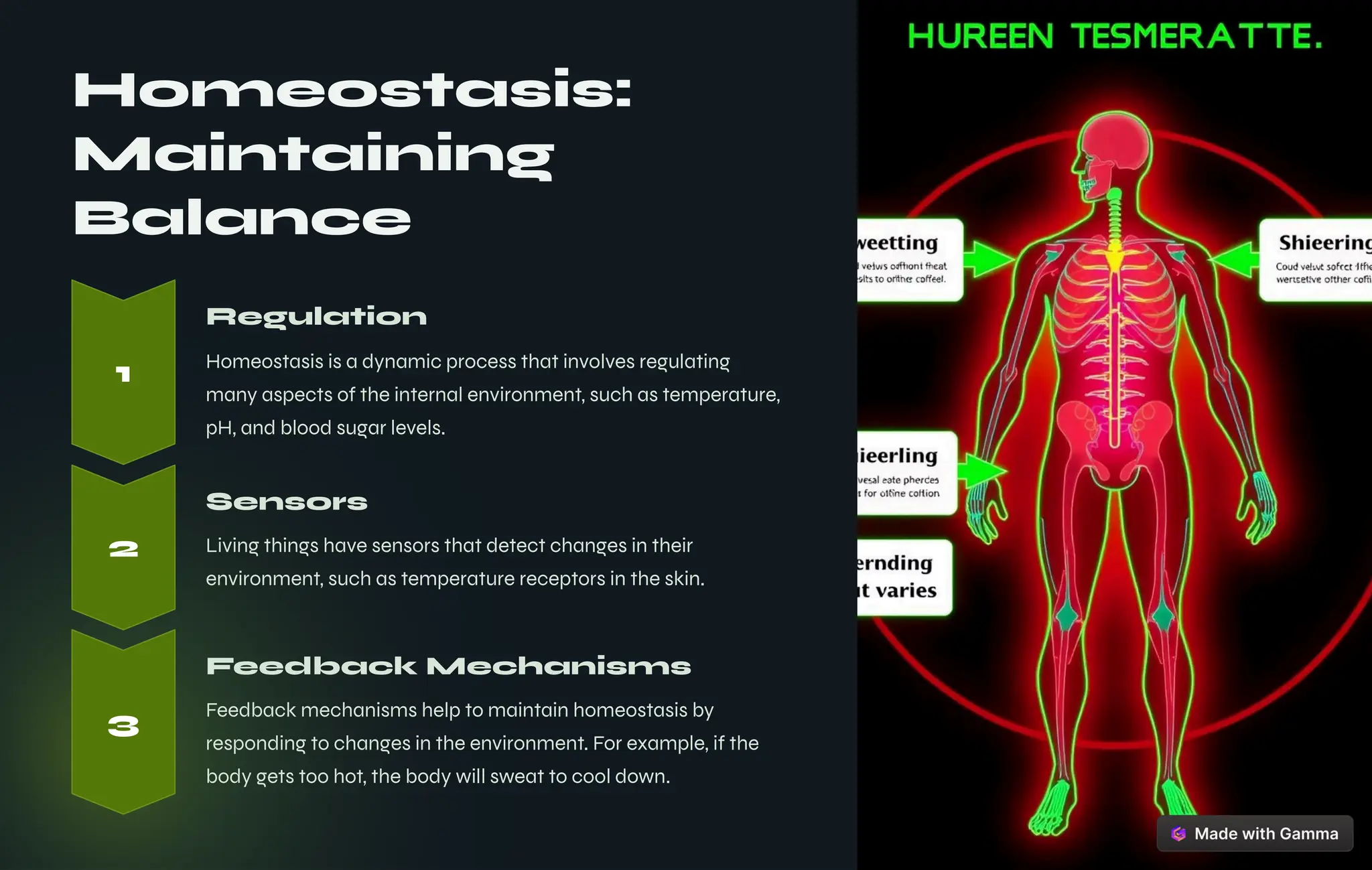
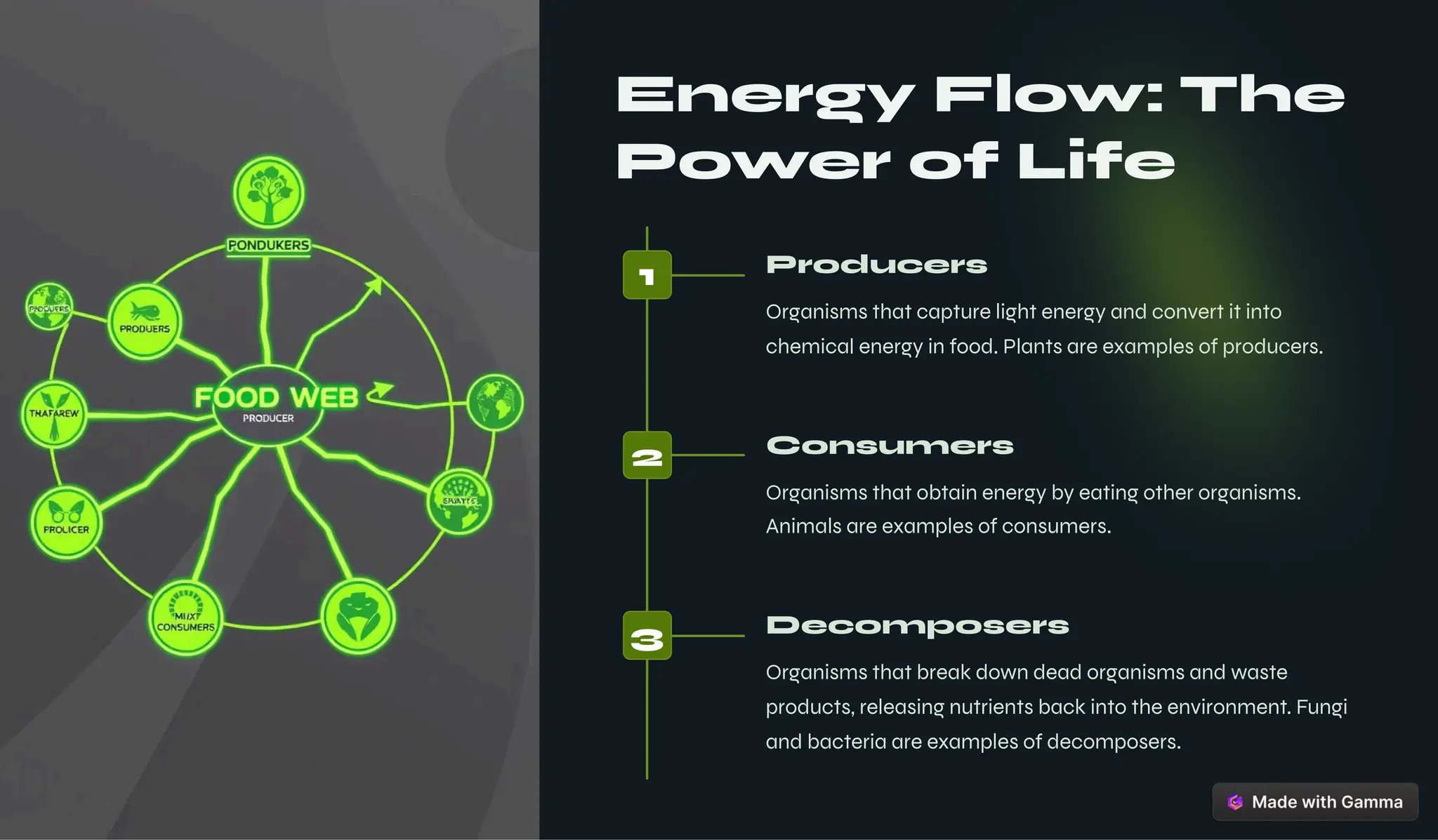
The document outlines key unifying themes in biology, such as organization, metabolism, homeostasis, growth, and evolution, that define living organisms. It discusses the processes of inheritance and reproduction, emphasizing the roles of genetic variation, natural selection, and adaptation in evolution. Additionally, it highlights the importance of interdependence within ecosystems and the impact of science and technology on society.