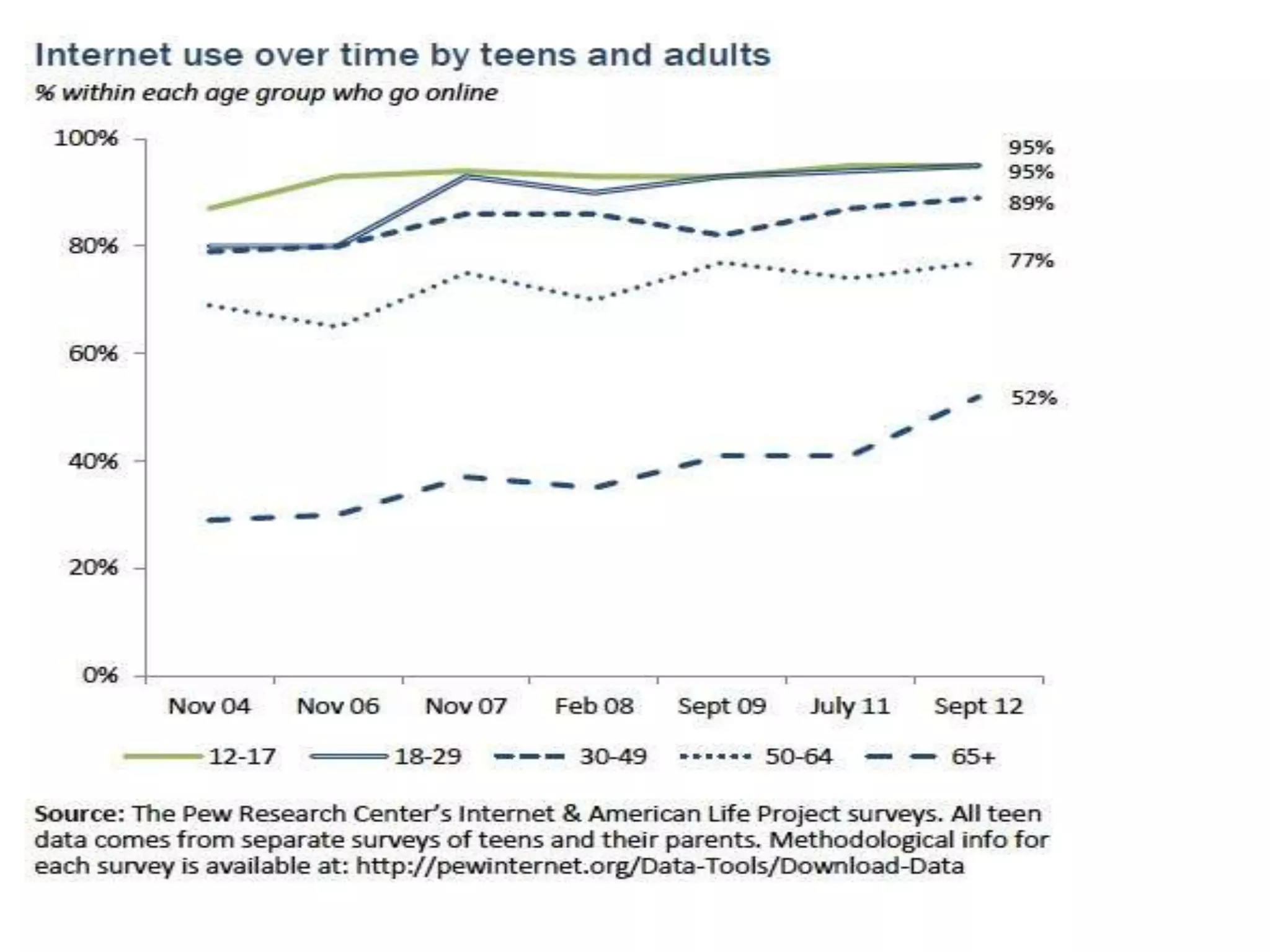
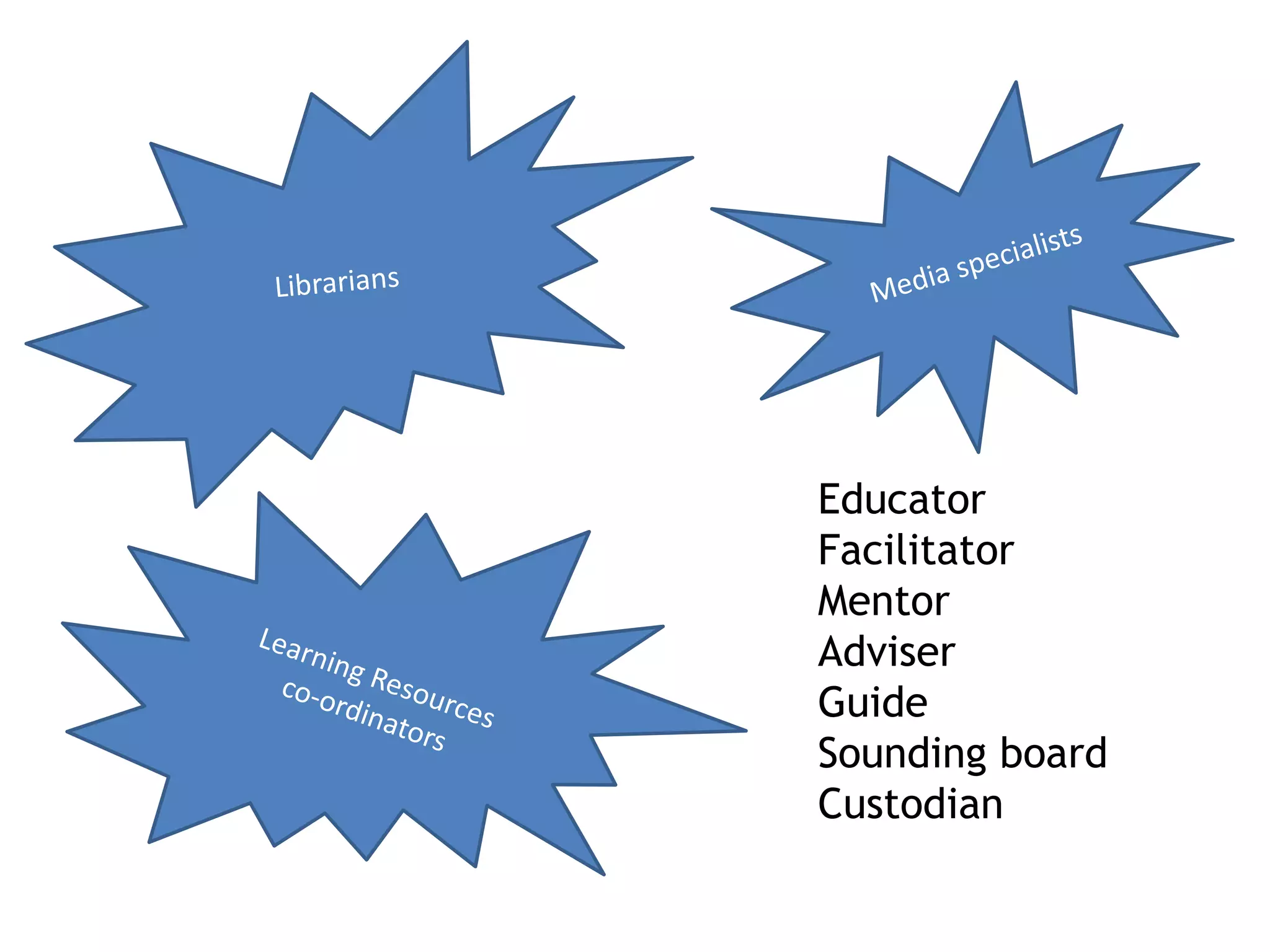
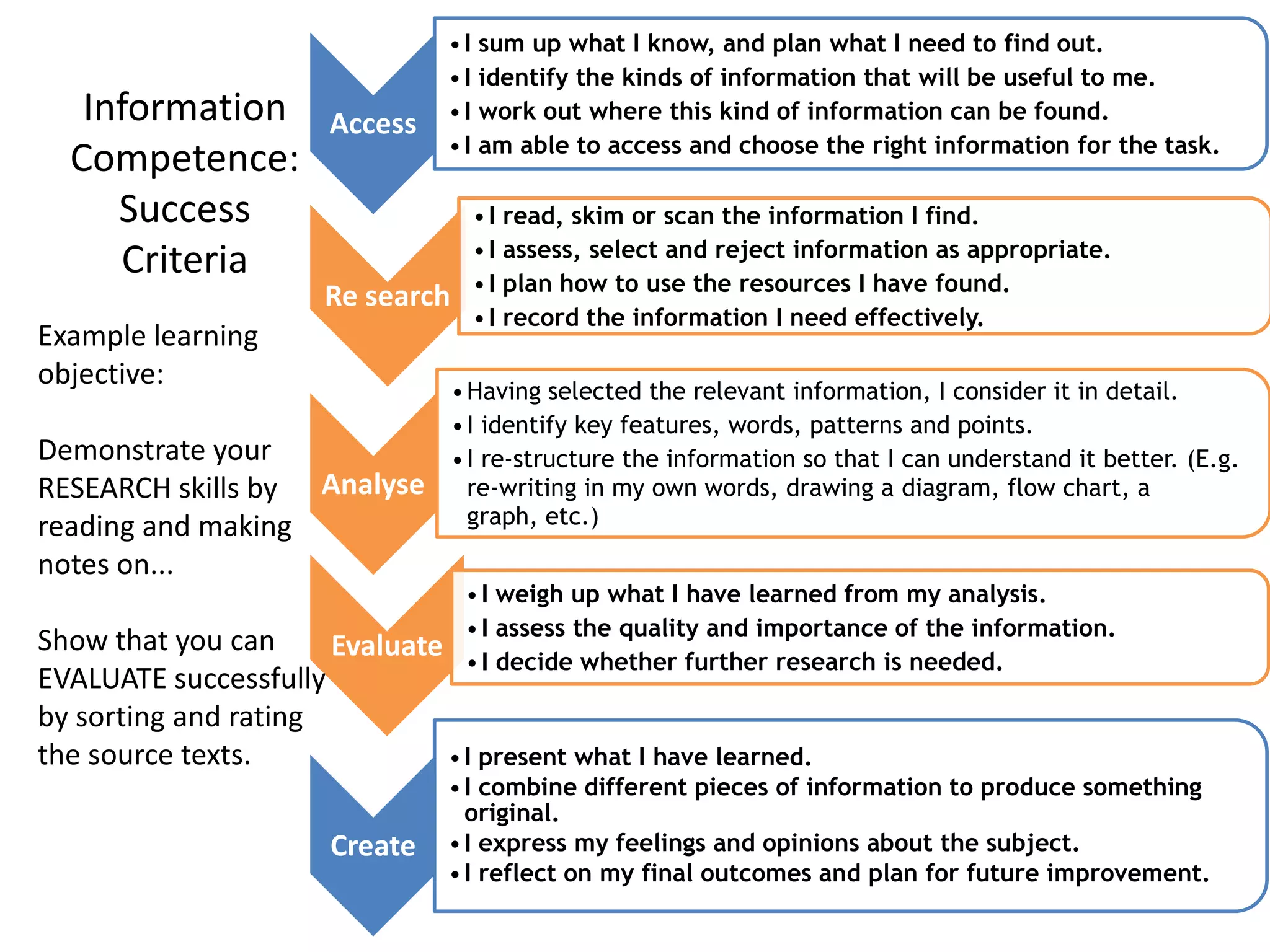
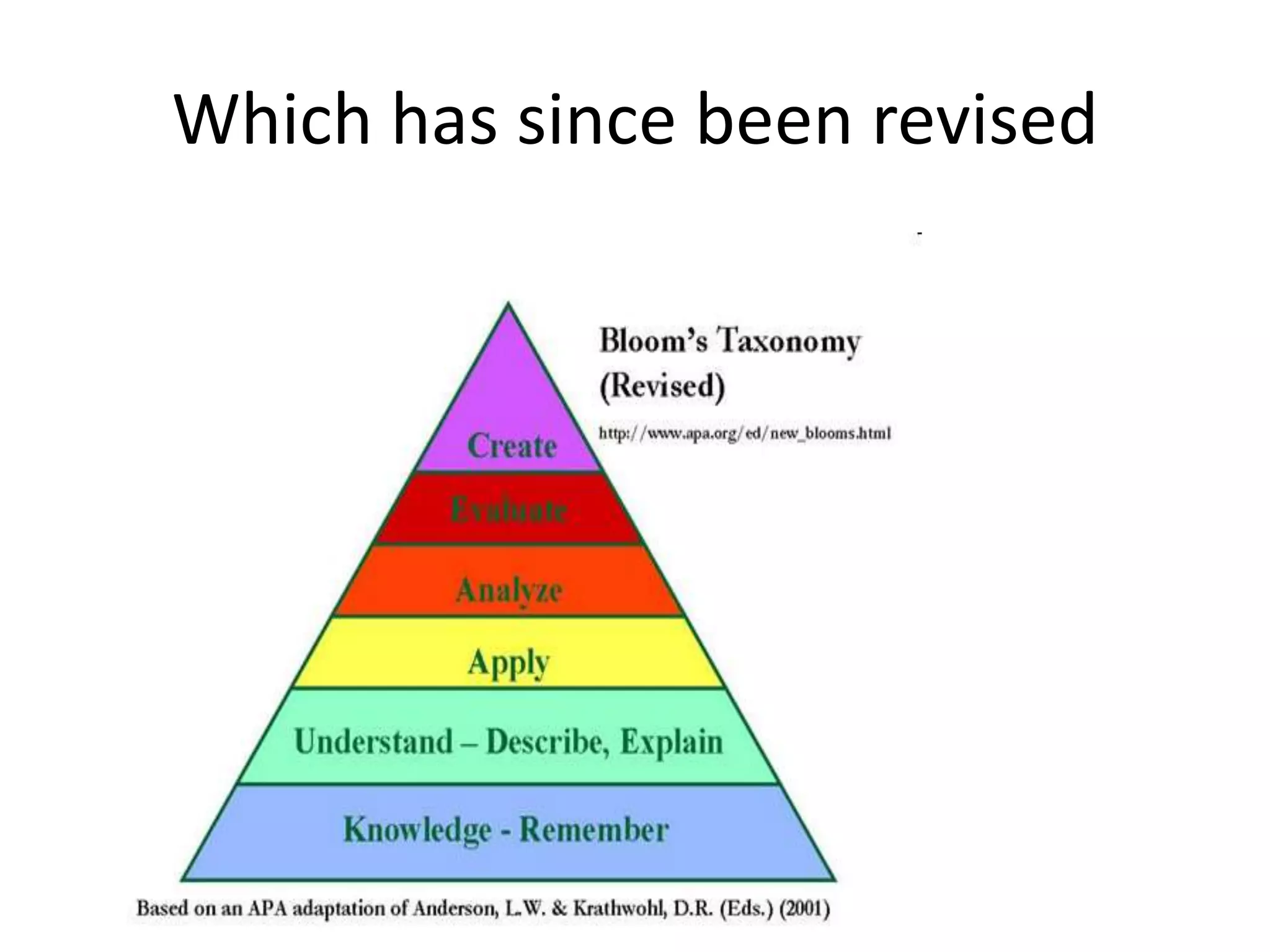
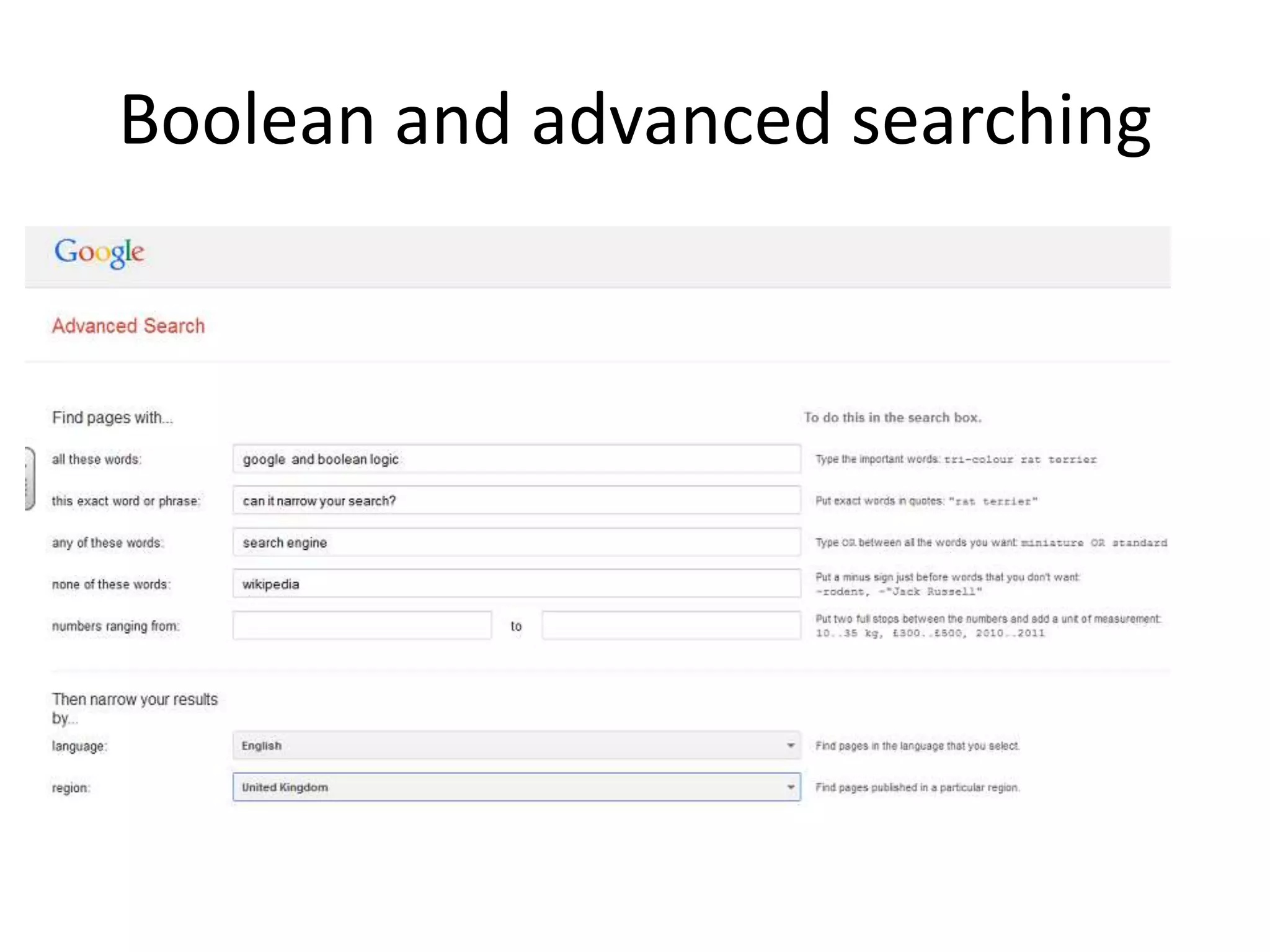
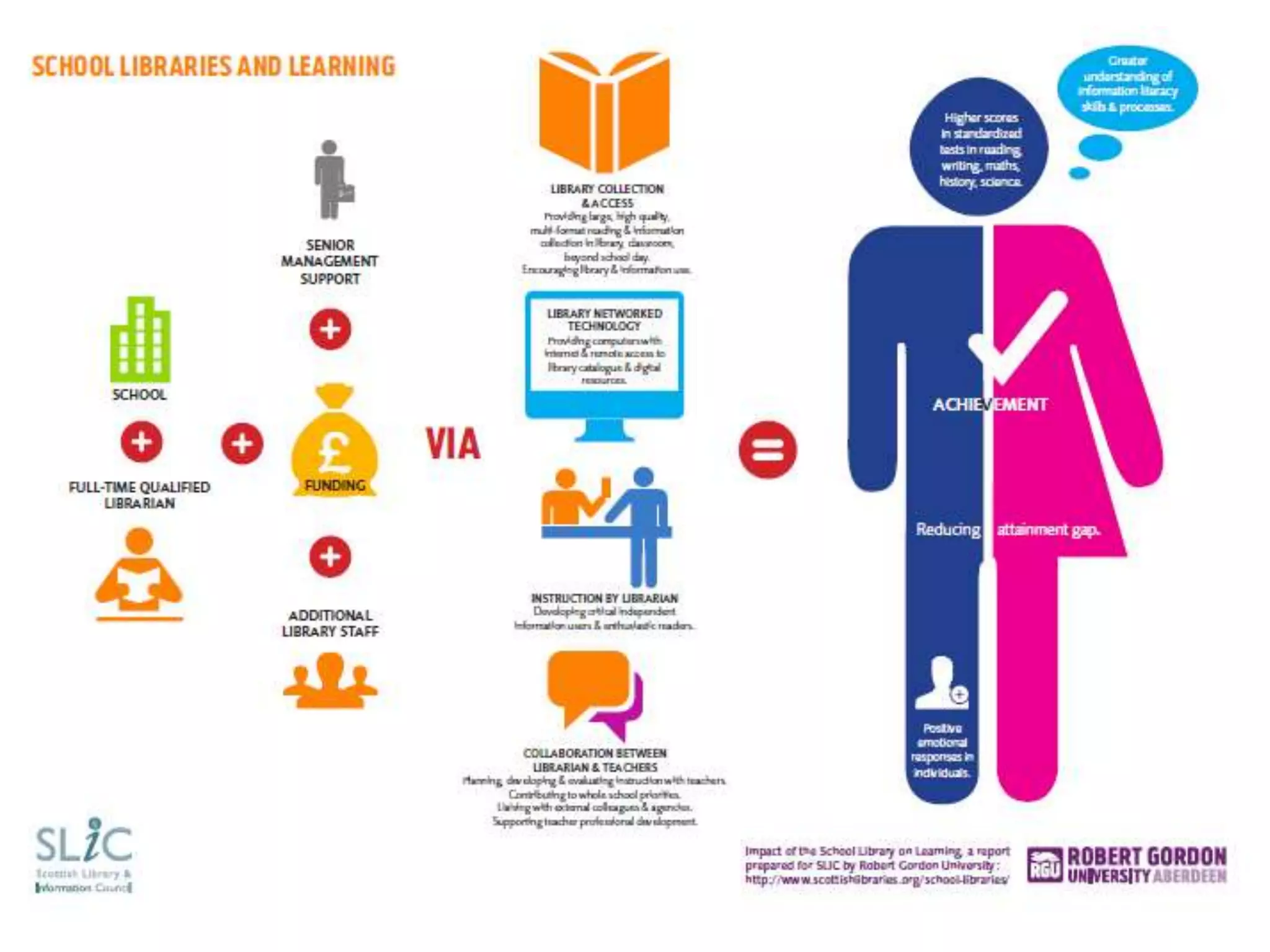
The document discusses the evolving role of librarians and educators in the digital age, emphasizing the importance of guiding students in navigating vast amounts of information and developing critical thinking skills. It highlights the increasing use of social media and smartphones, and lists strategies for effective research and information evaluation. Evidence is presented showing that well-resourced school libraries led by qualified professionals significantly enhance student achievement and engagement.