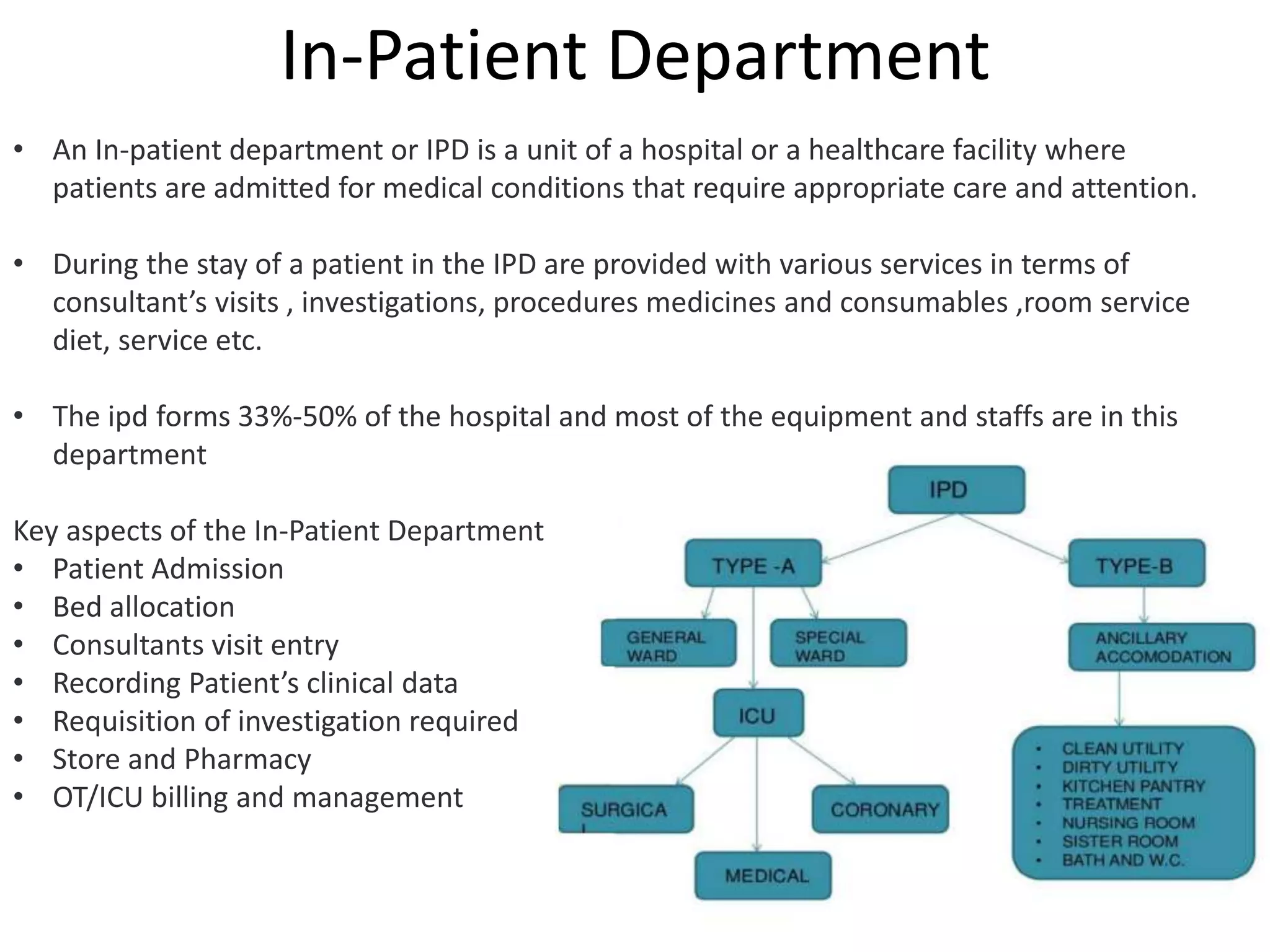
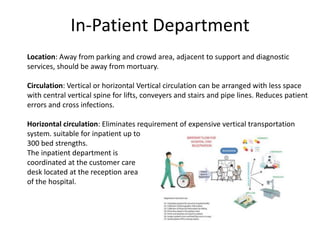
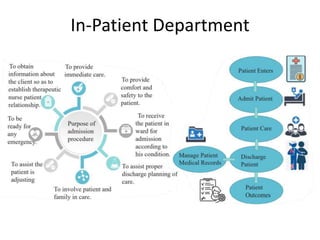
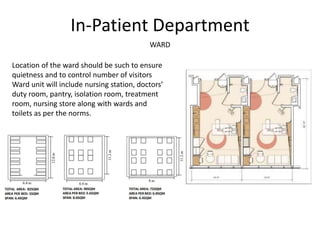
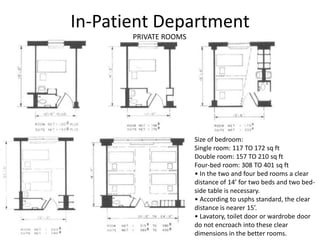
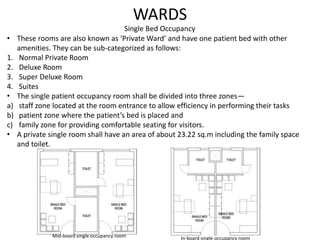
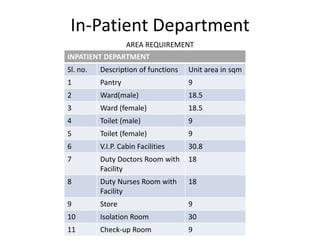
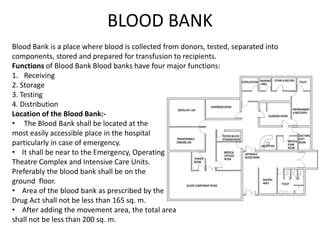
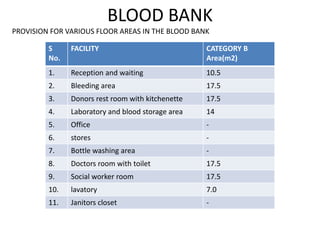
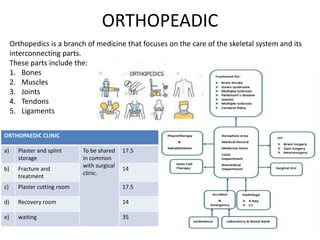
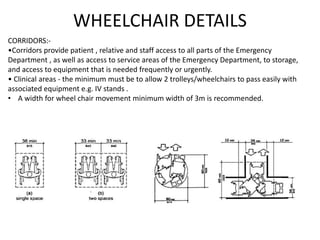
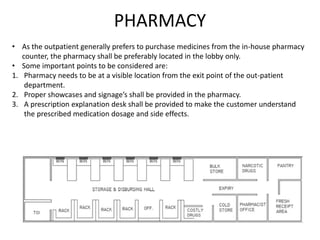
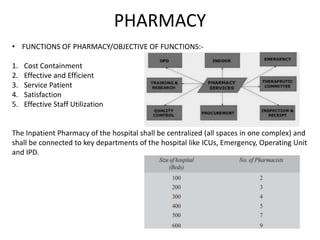
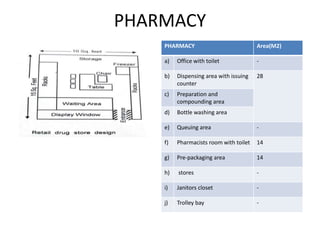
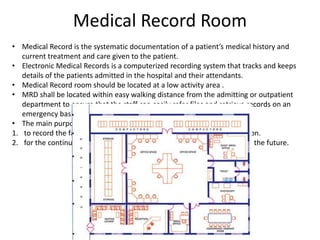
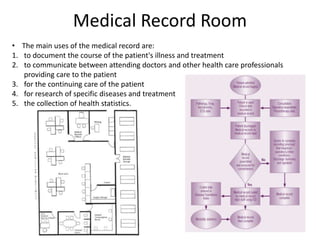
The document provides information about the in-patient department of a hospital. It describes the various units and wards that make up the in-patient department including medicine, surgery, obstetrics/gynecology wards. It also discusses the key functions of the in-patient department like patient admission, investigations, consultations. The in-patient department forms a major part of the hospital and houses many critical care units and services.