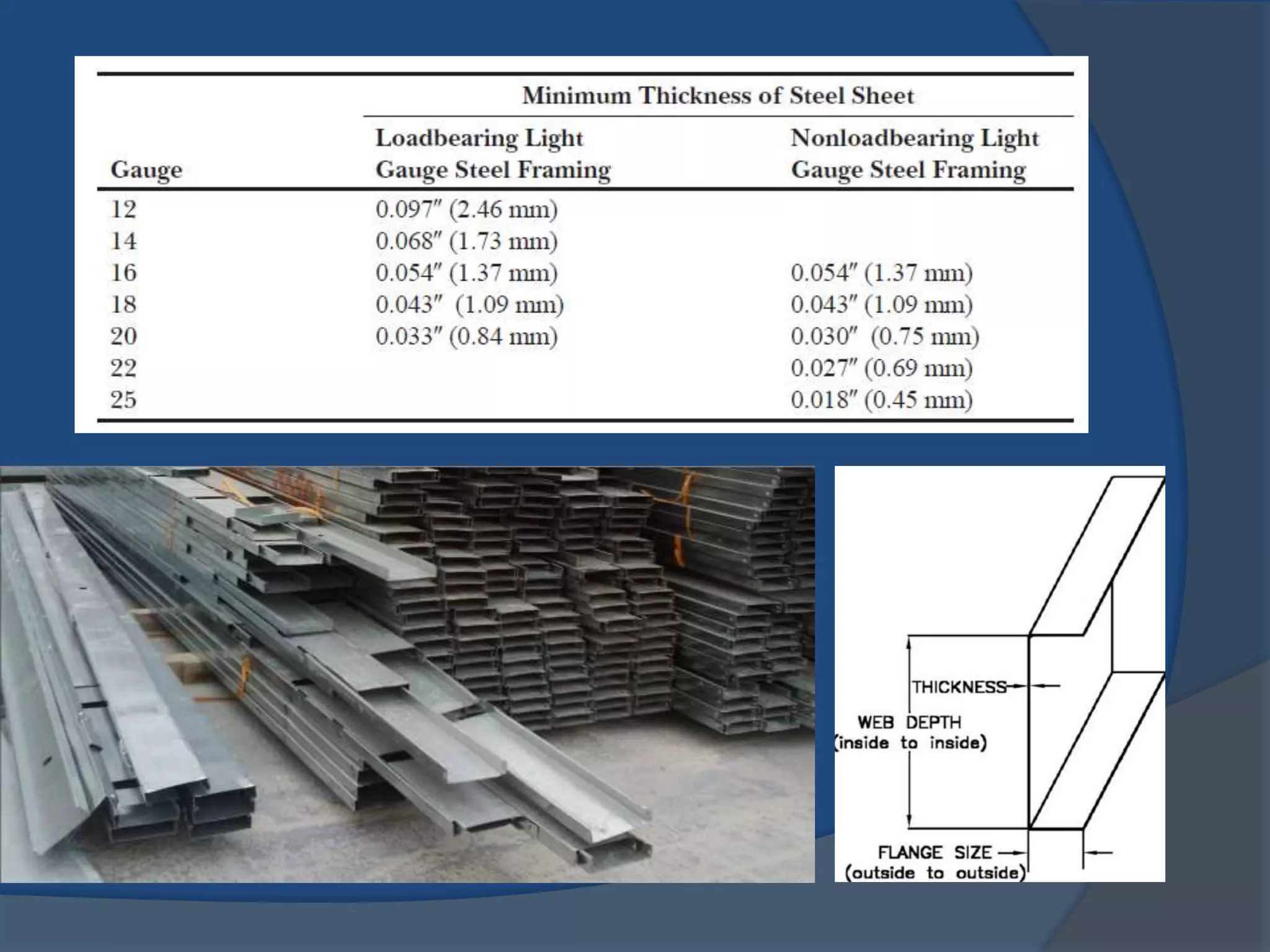
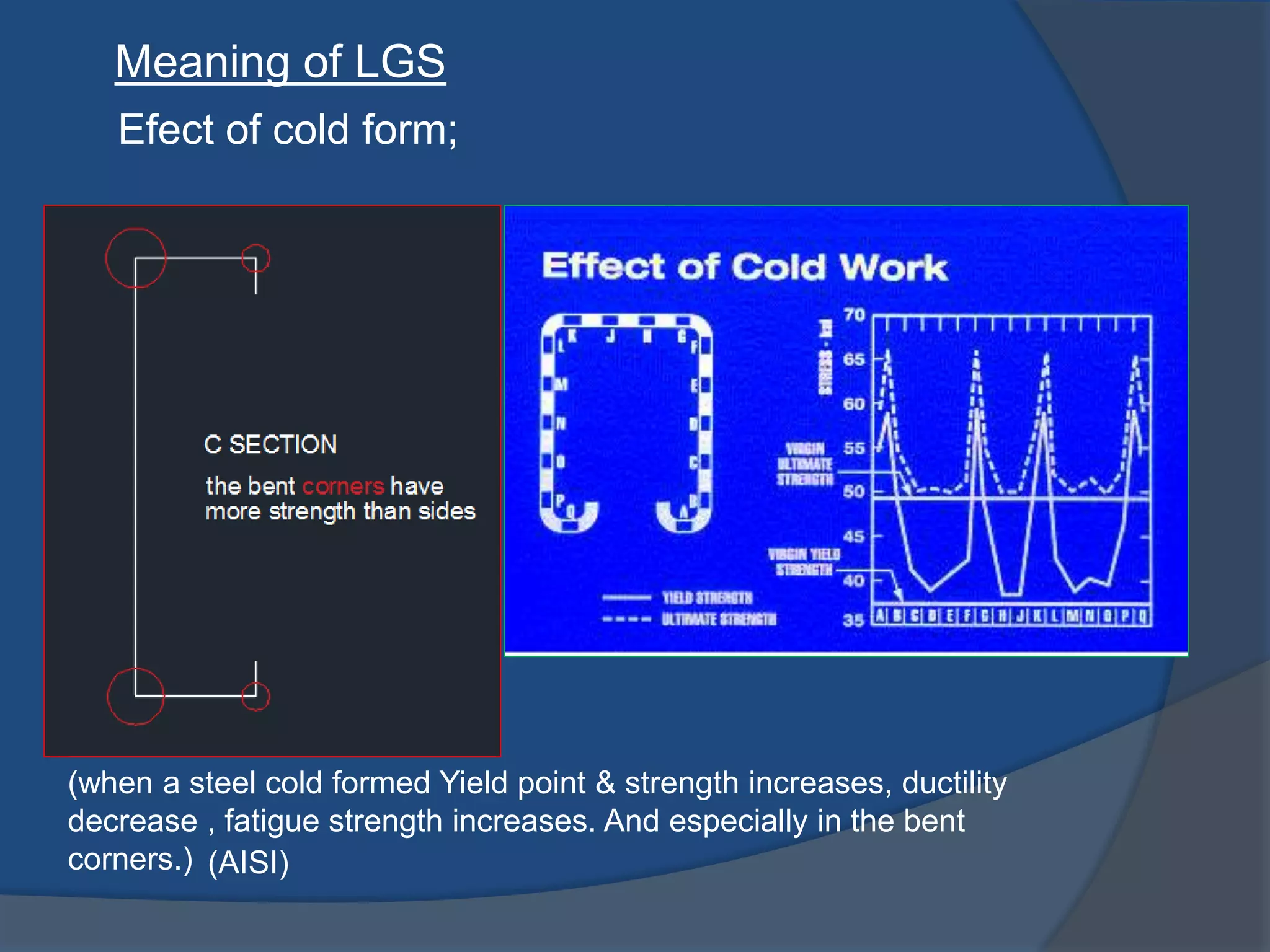
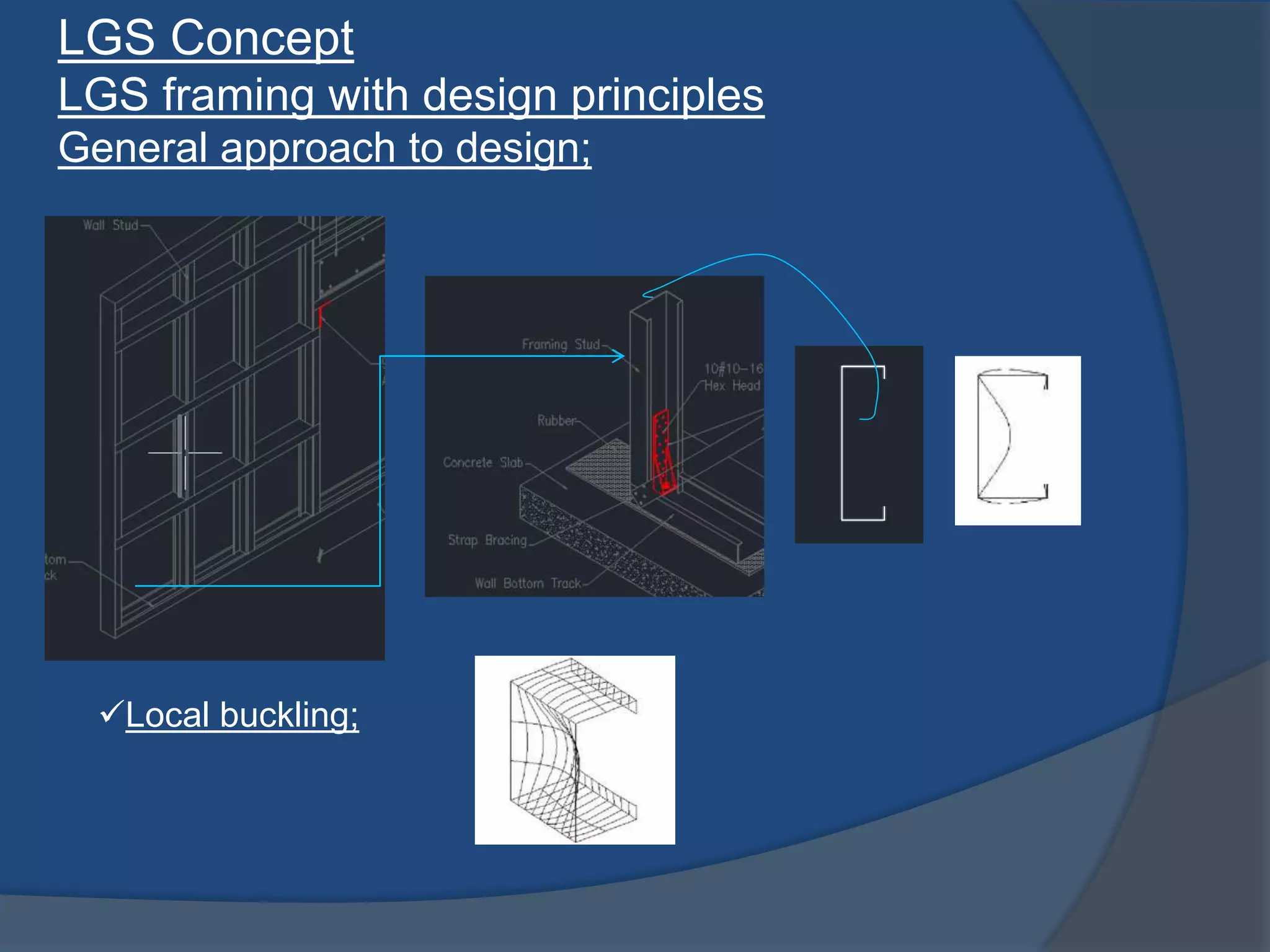
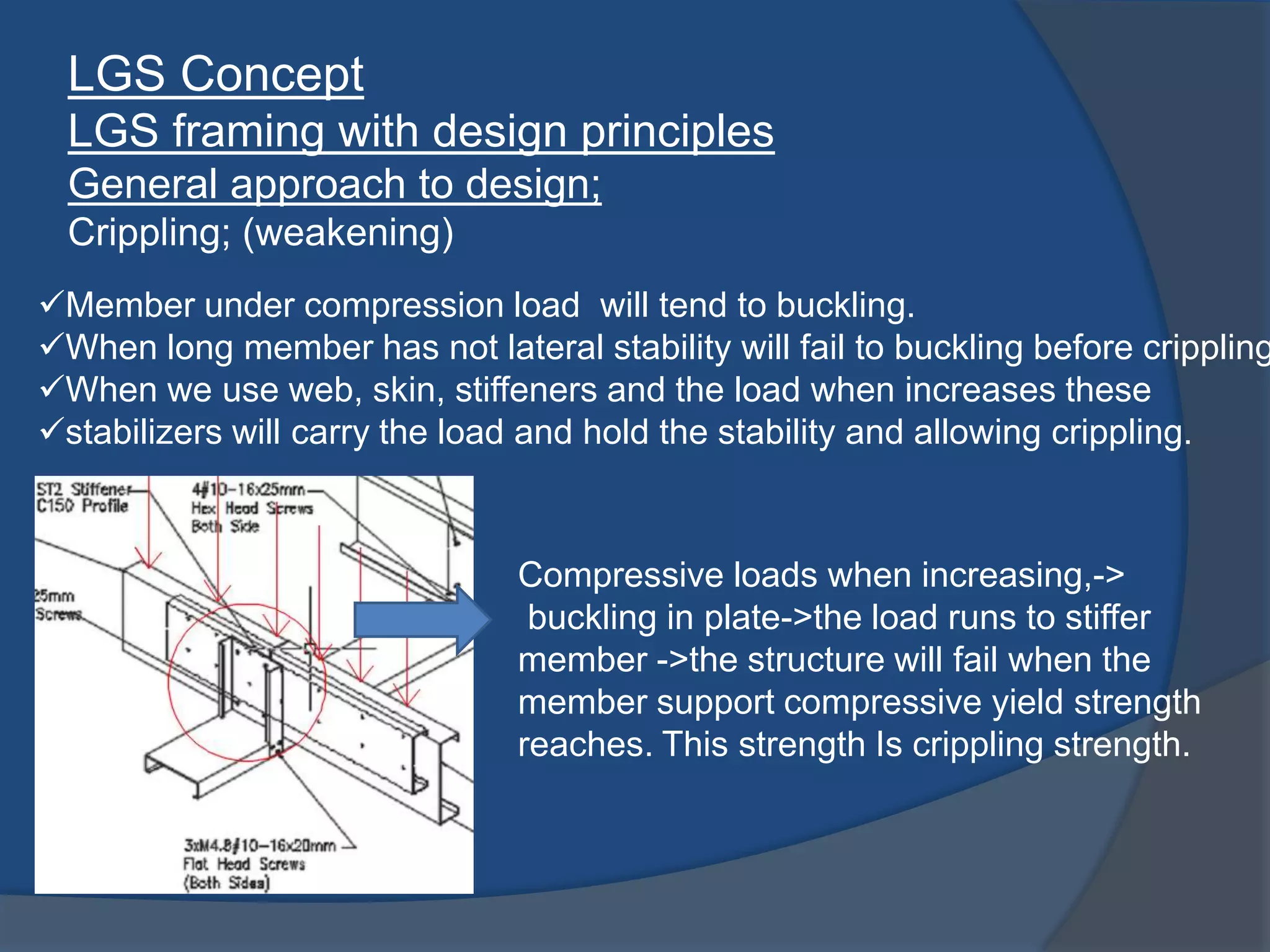
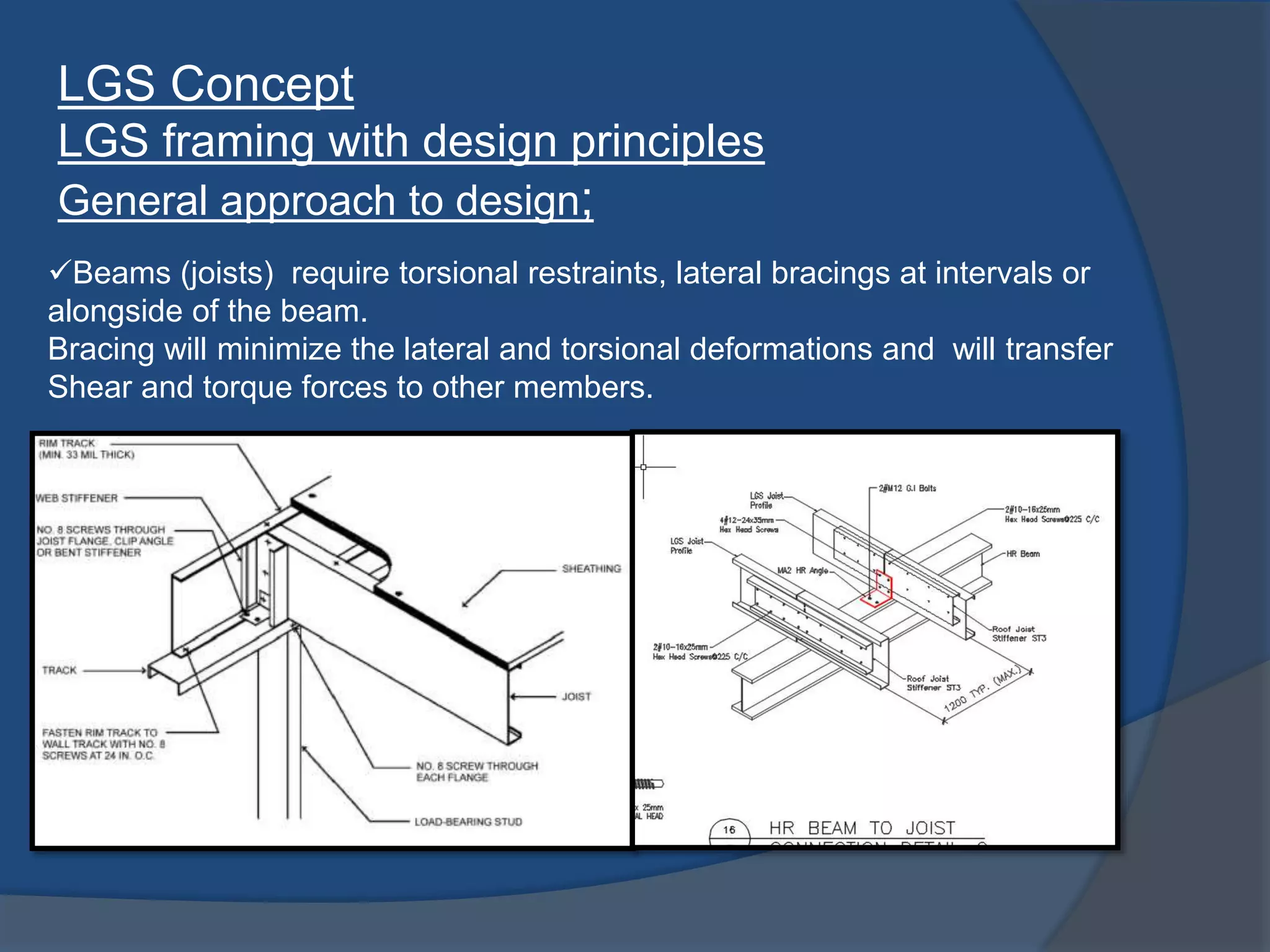
This document discusses light gauge steel (LGS), including its concept, manufacturing process, structural behavior, uses in framing, and construction methods. LGS is a thin sheet steel that is roll or brake formed into cross-sectional shapes. Compared to hot rolled steel, LGS is lighter but stronger. Its thin width-to-thickness ratio means it is susceptible to local buckling under compression loads. LGS framing uses C-sections for studs, joists, and beams. Construction involves erecting LGS wall panels, installing floor and roof joists, and finishing with cladding and insulation.