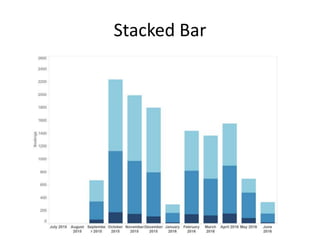
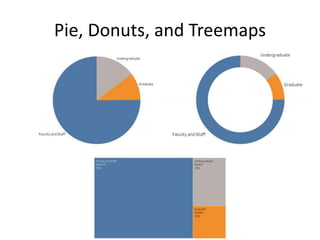
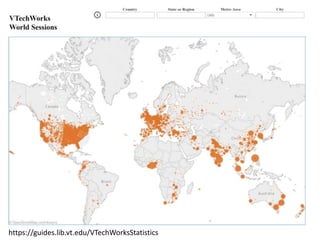
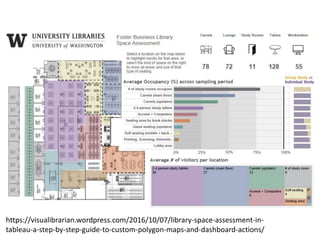
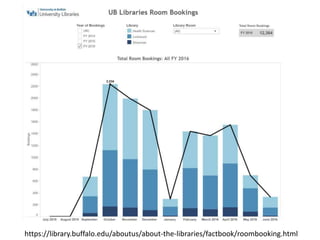
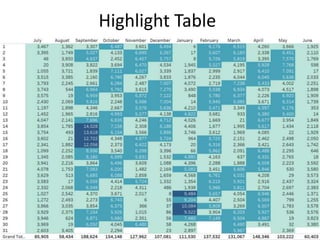
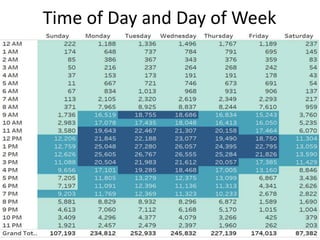
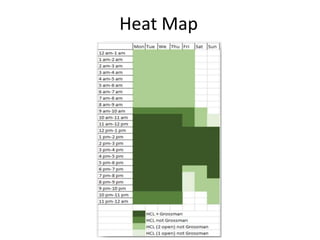
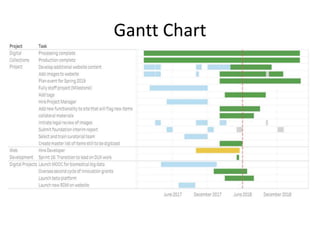
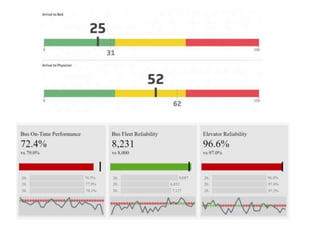
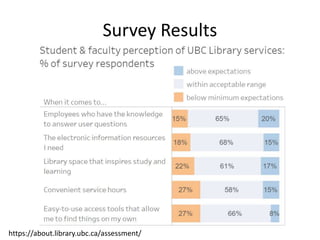
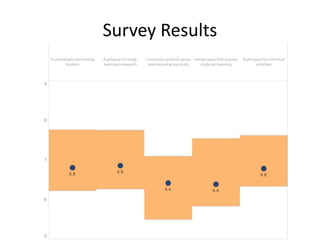
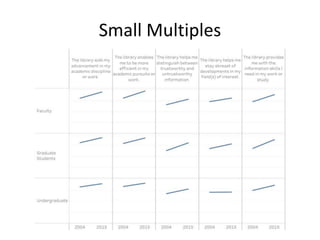
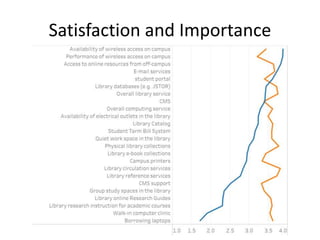
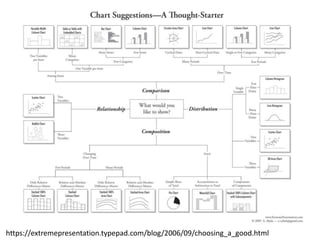
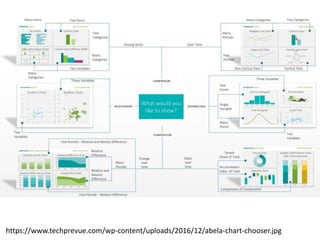
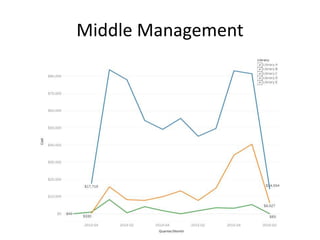
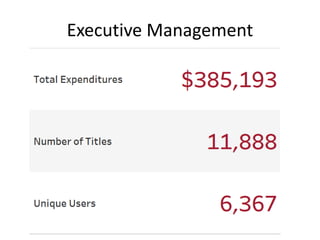
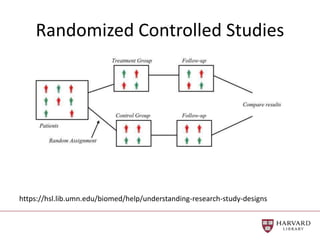
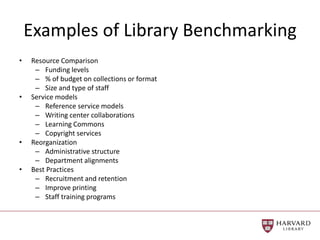
The document outlines best practices for data visualization, interpretation, and benchmarking in library assessment, emphasizing the importance of context and understanding audience demographics. It discusses methods for displaying various data types, correlation versus causation, and the significance of transparent data communication. Key elements include operational benchmarking strategies and fostering a culture of assessment within organizations.