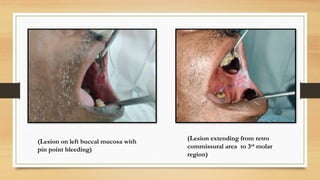
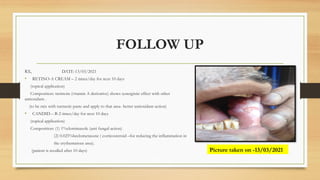
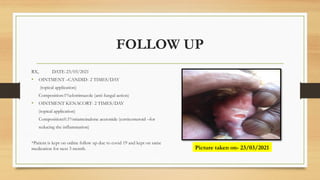
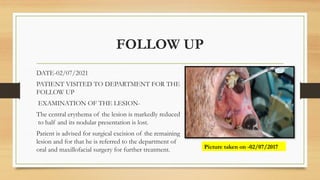
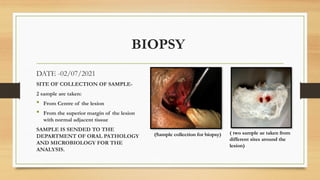
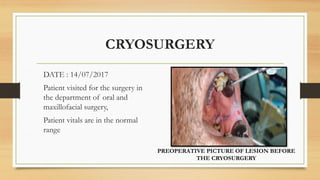
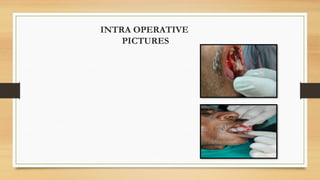
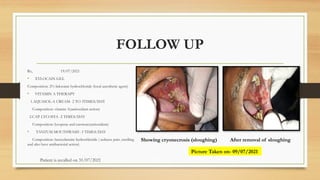
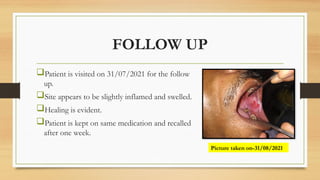
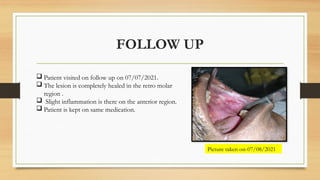
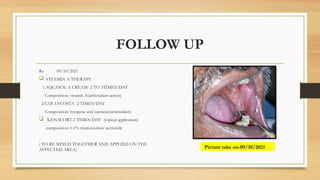
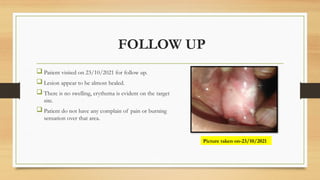
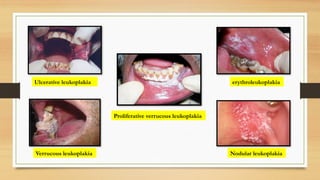
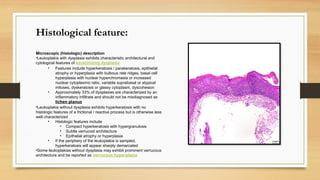
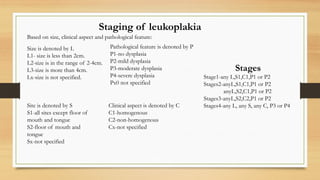
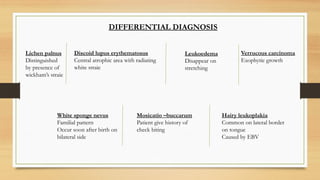
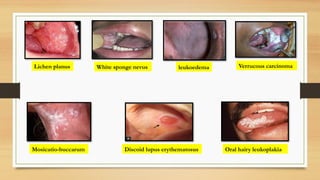
The document details a case report of leukoplakia presented by Ashutosh Yadav, highlighting patient history, clinical examination, provisional diagnosis, treatment plans, and follow-ups over time. Key findings include a nodulo-speckled leukoplakia in a 51-year-old male patient and a treatment regimen that involved non-surgical and surgical phases. The report also discusses the definition, epidemiology, and classification of leukoplakia, along with its histopathological features.