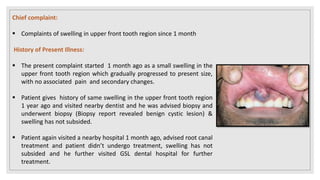
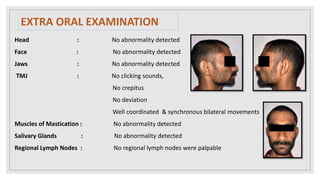
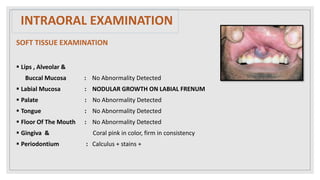
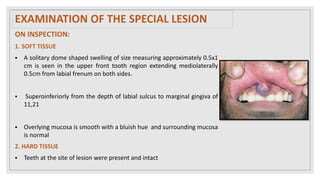
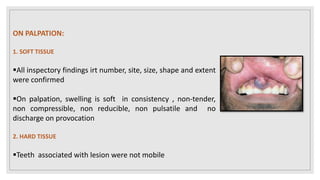
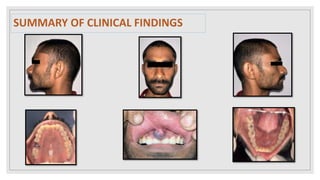
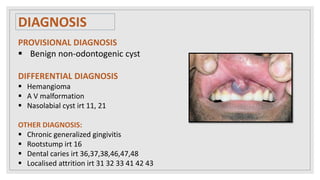
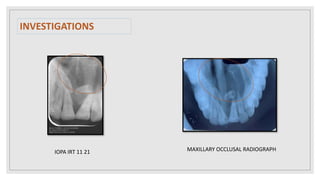
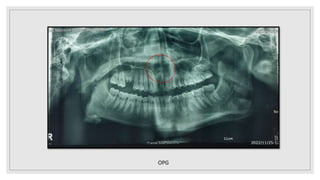
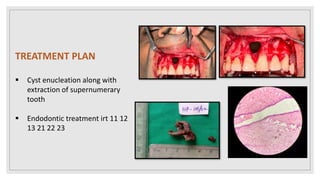
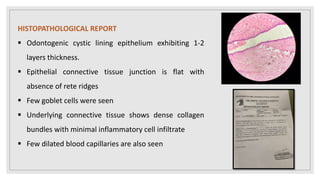
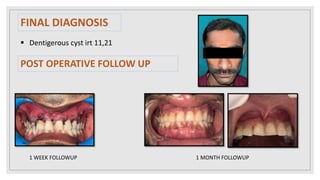
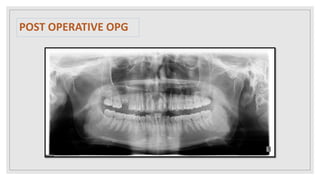
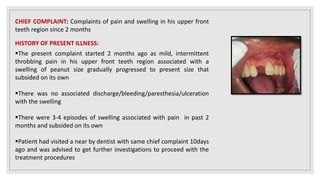
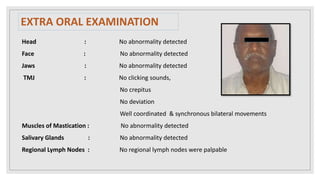
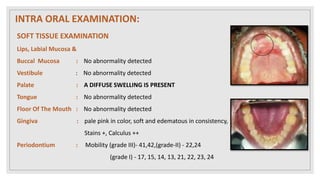
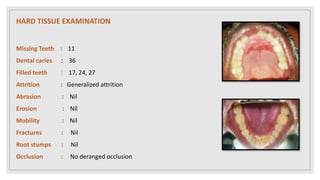
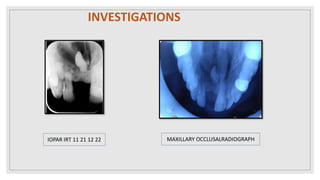
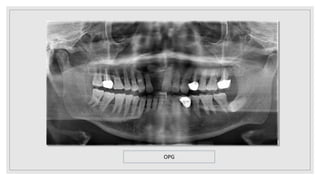
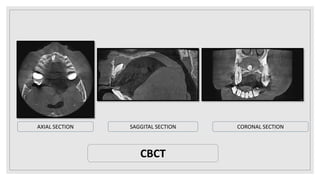
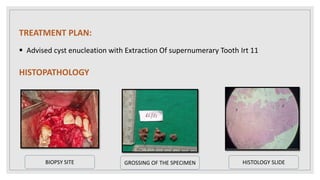
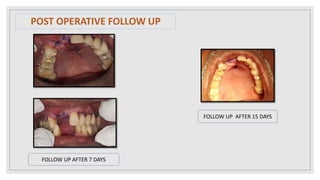
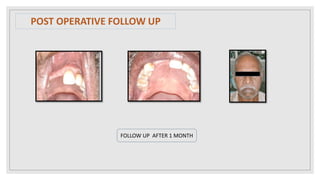
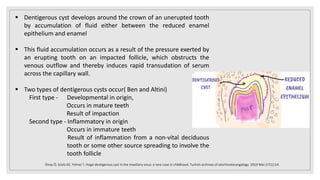
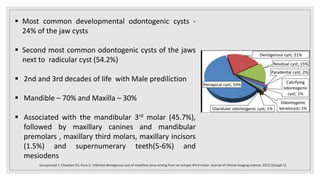
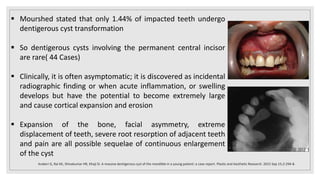
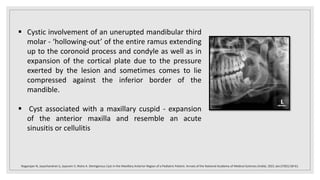
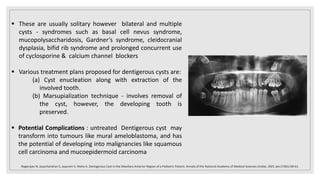
This document presents two case studies of patients with dentigerous cysts in the maxilla. The first case involves a 26-year-old male with a swelling in the upper front tooth region. Examination and radiographs revealed a dentigerous cyst associated with teeth 11 and 21. The cyst was enucleated and pathology confirmed the diagnosis. The second case involves a 73-year-old male with pain and swelling in the upper front teeth region. Examination found a diffuse palatal swelling and missing tooth 11. Radiographs showed a dentigerous cyst associated with teeth 11 and 12. The patient underwent cyst enucleation and extraction of the impacted tooth. Both patients recovered well post-operatively without