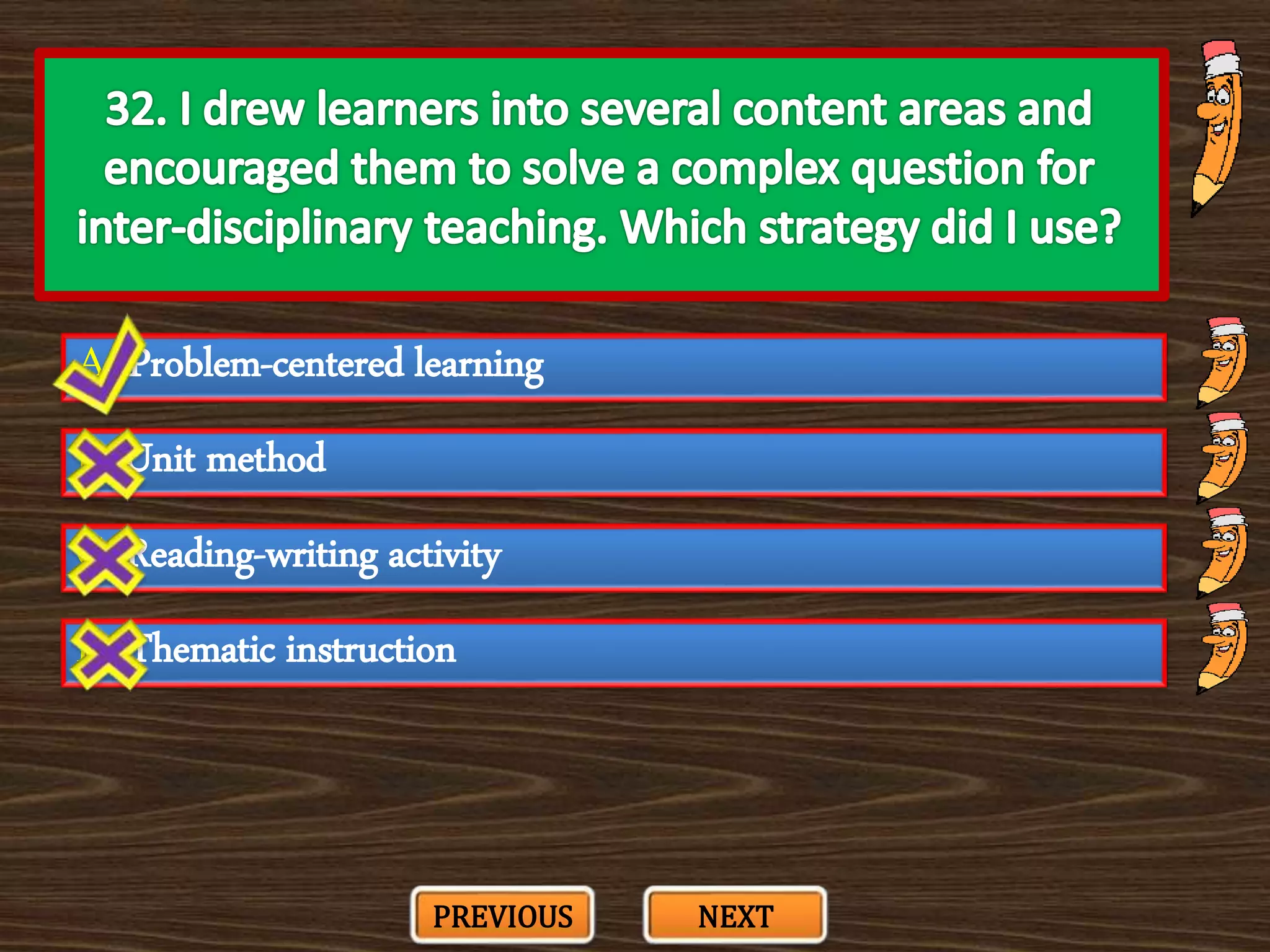
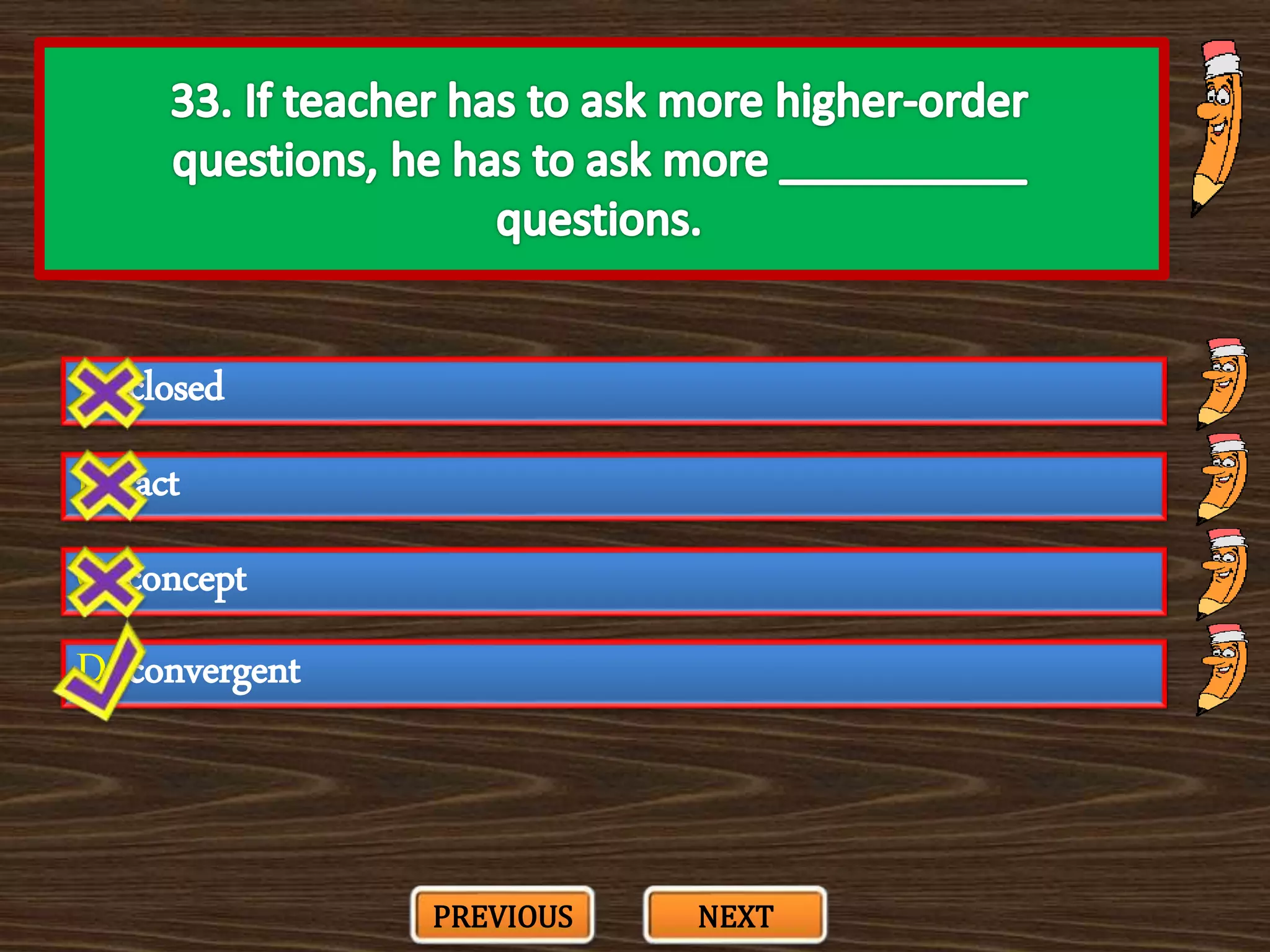
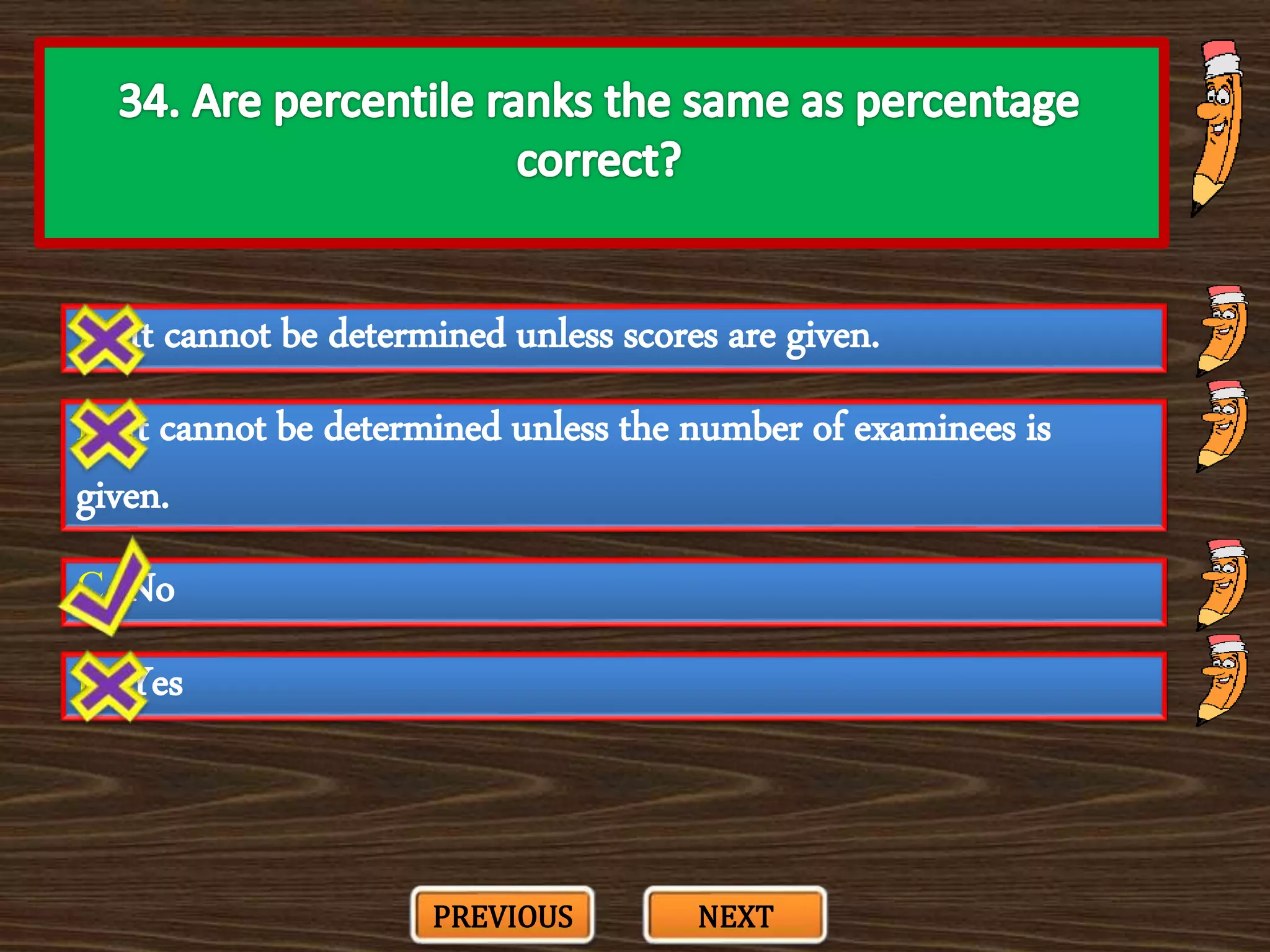
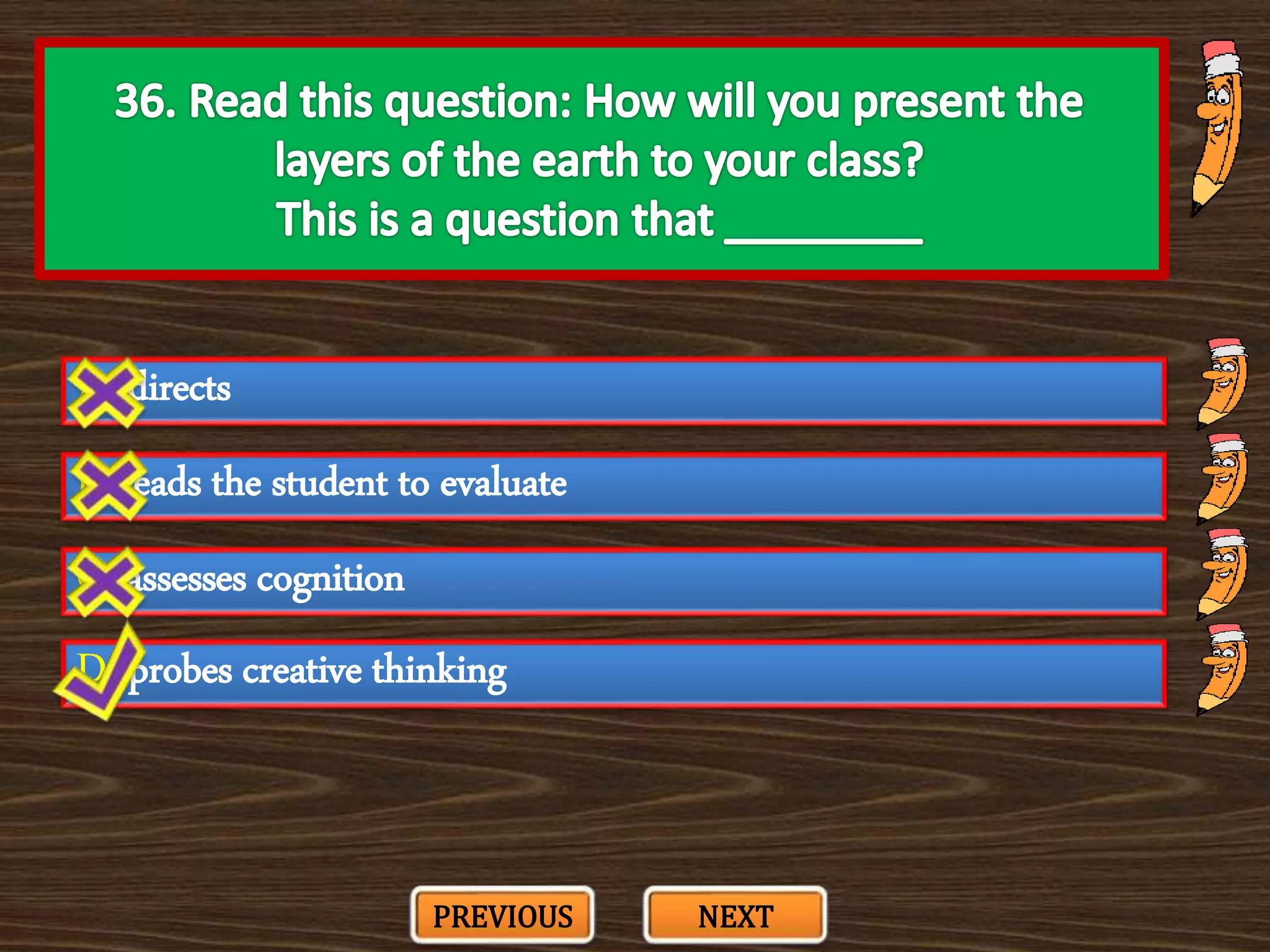
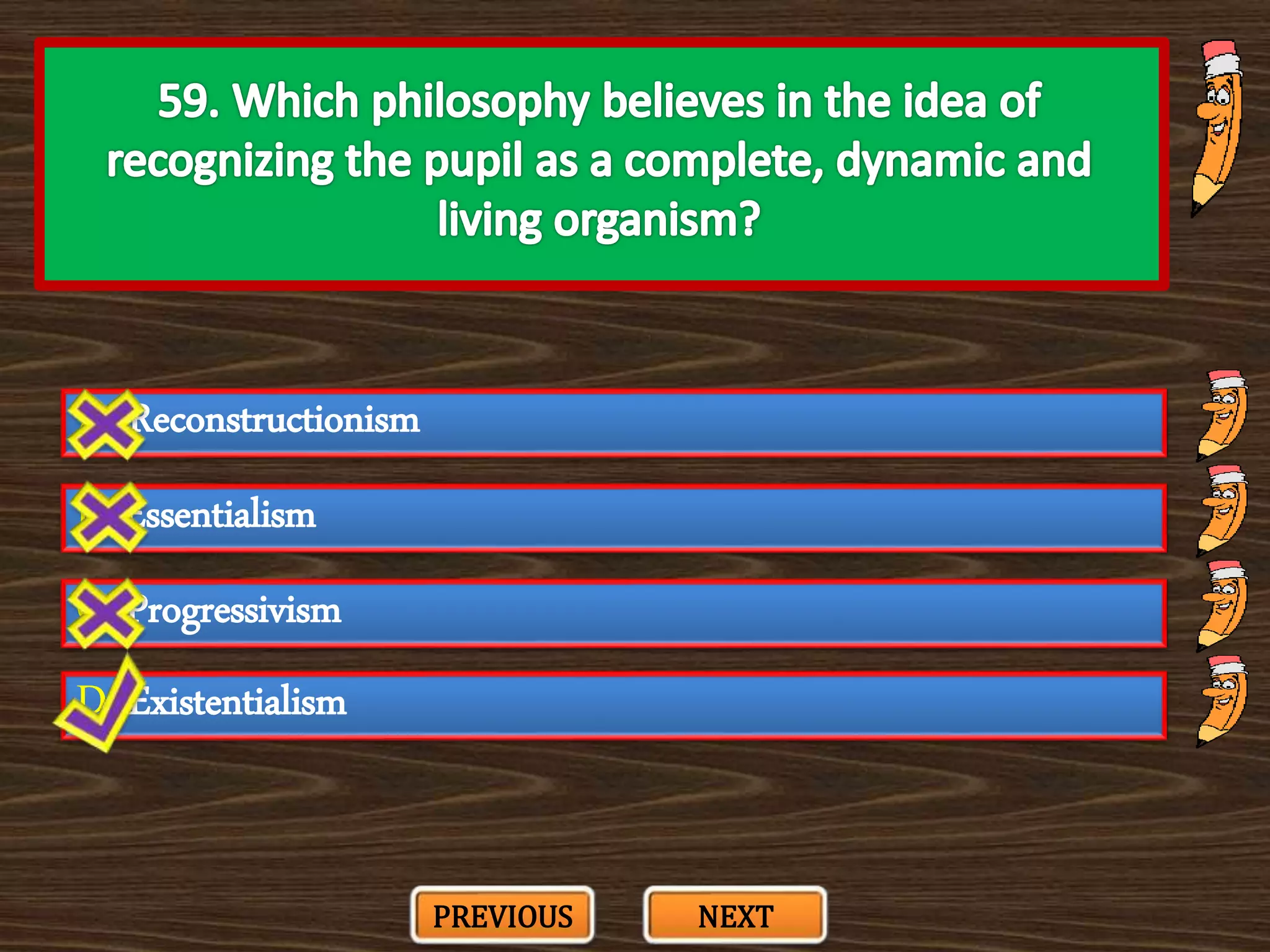
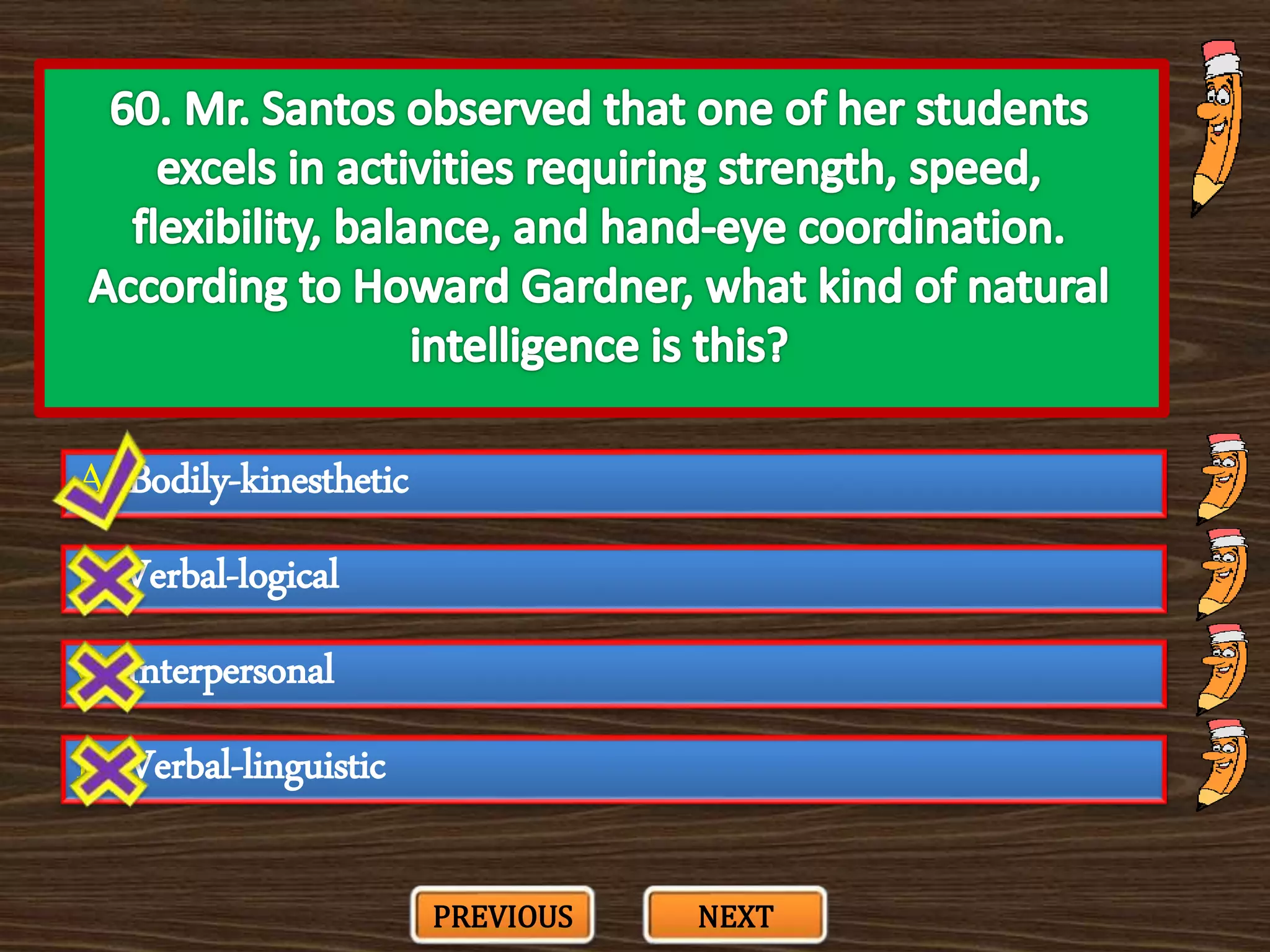
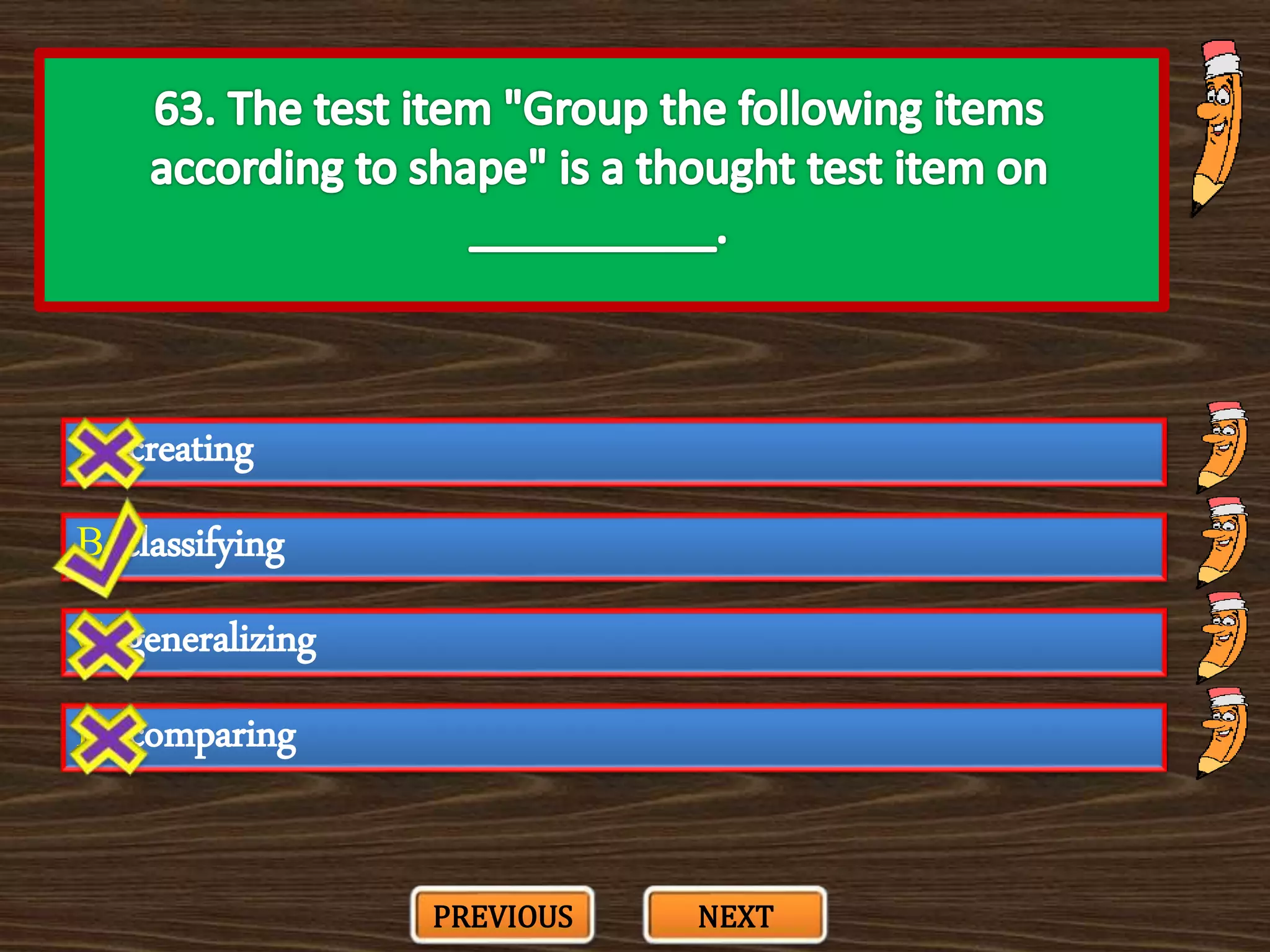
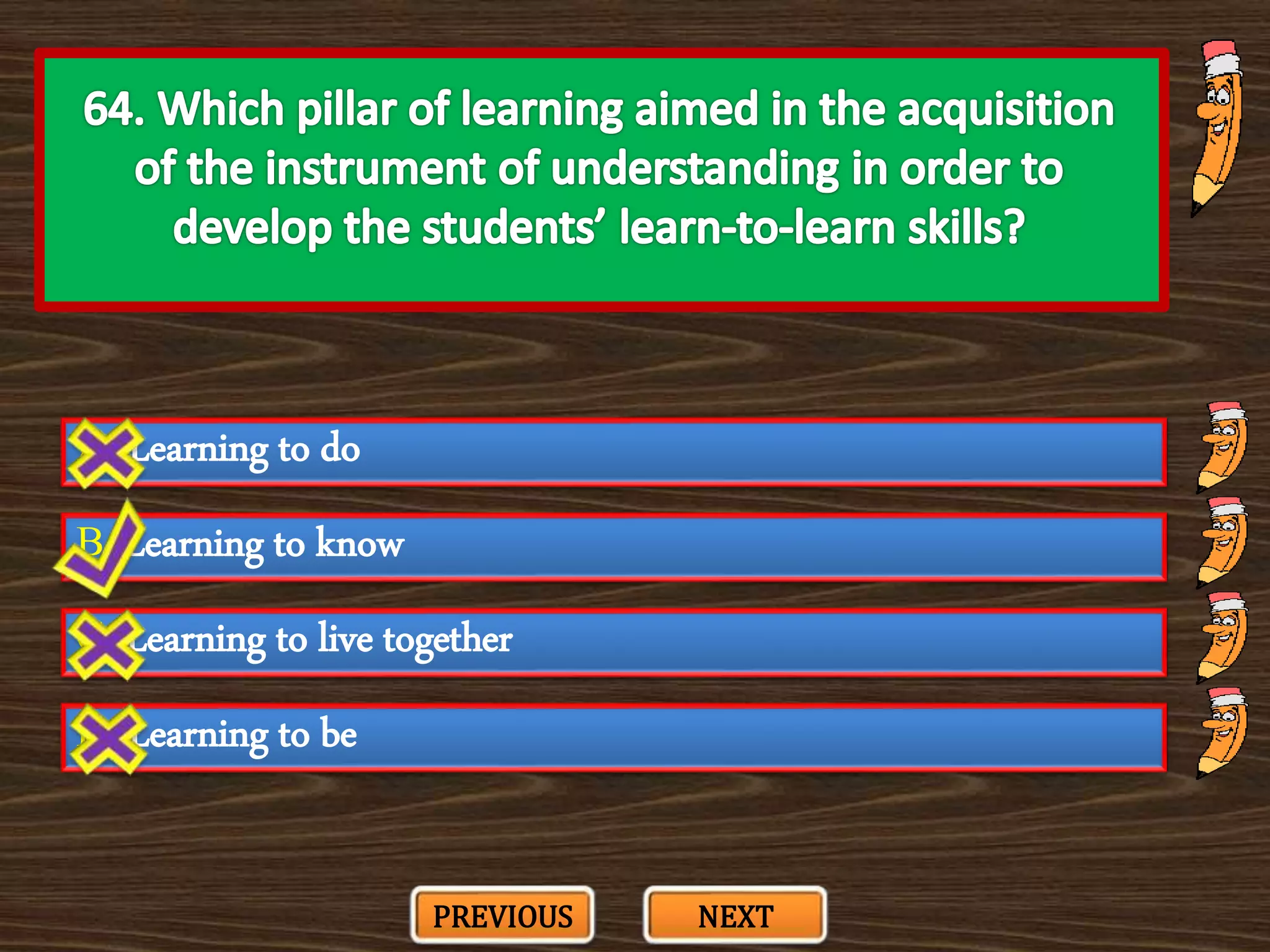
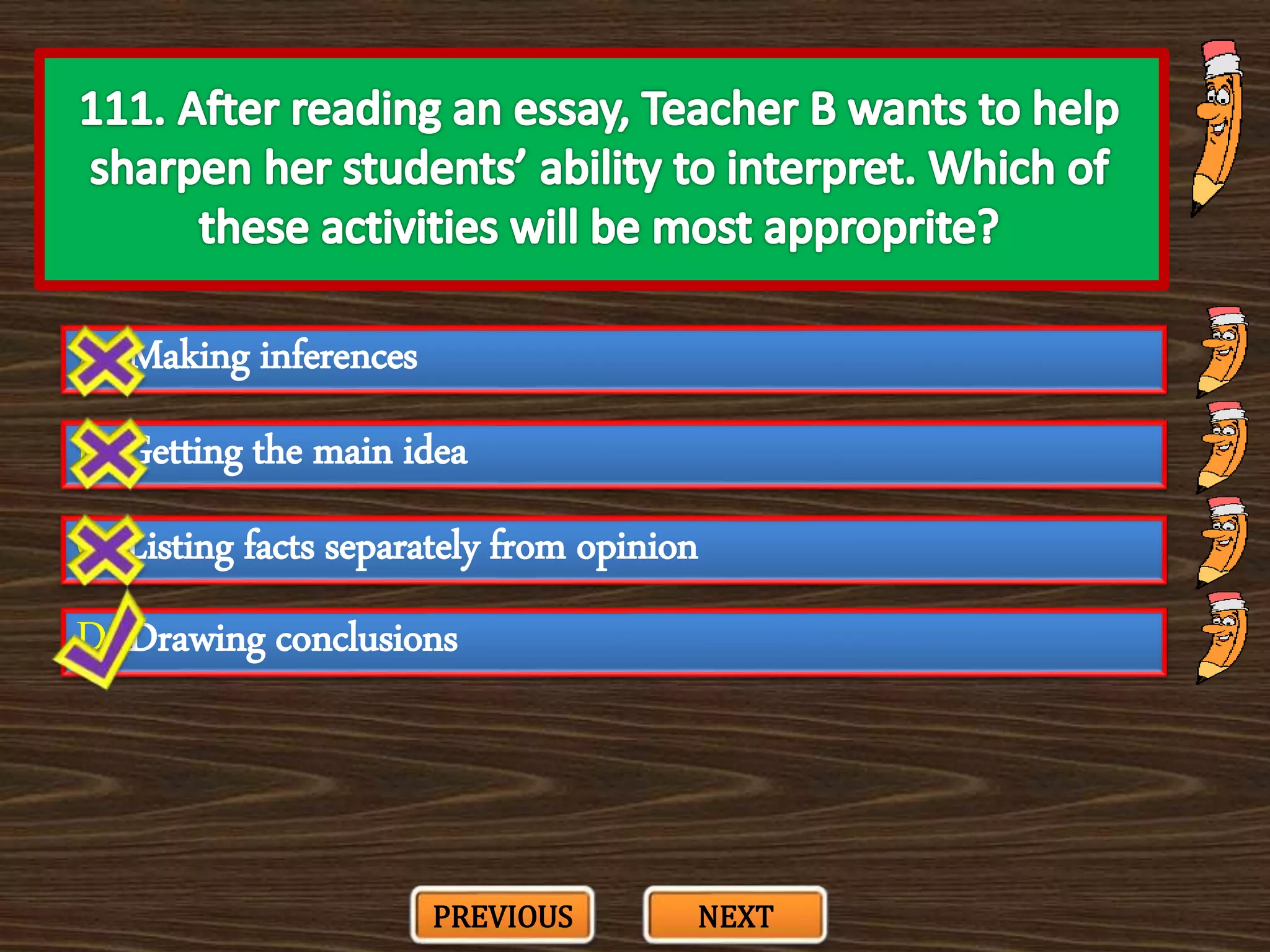
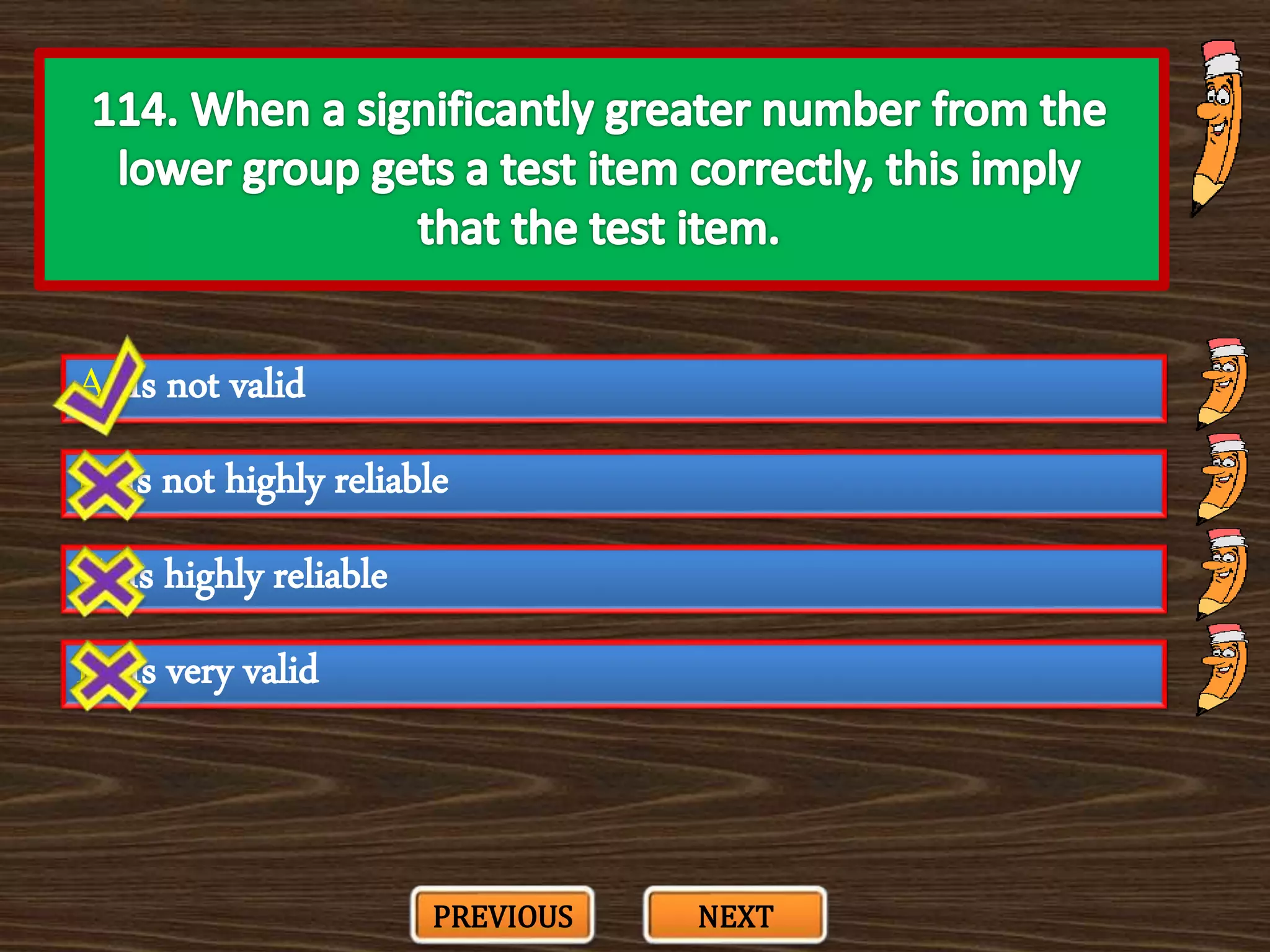
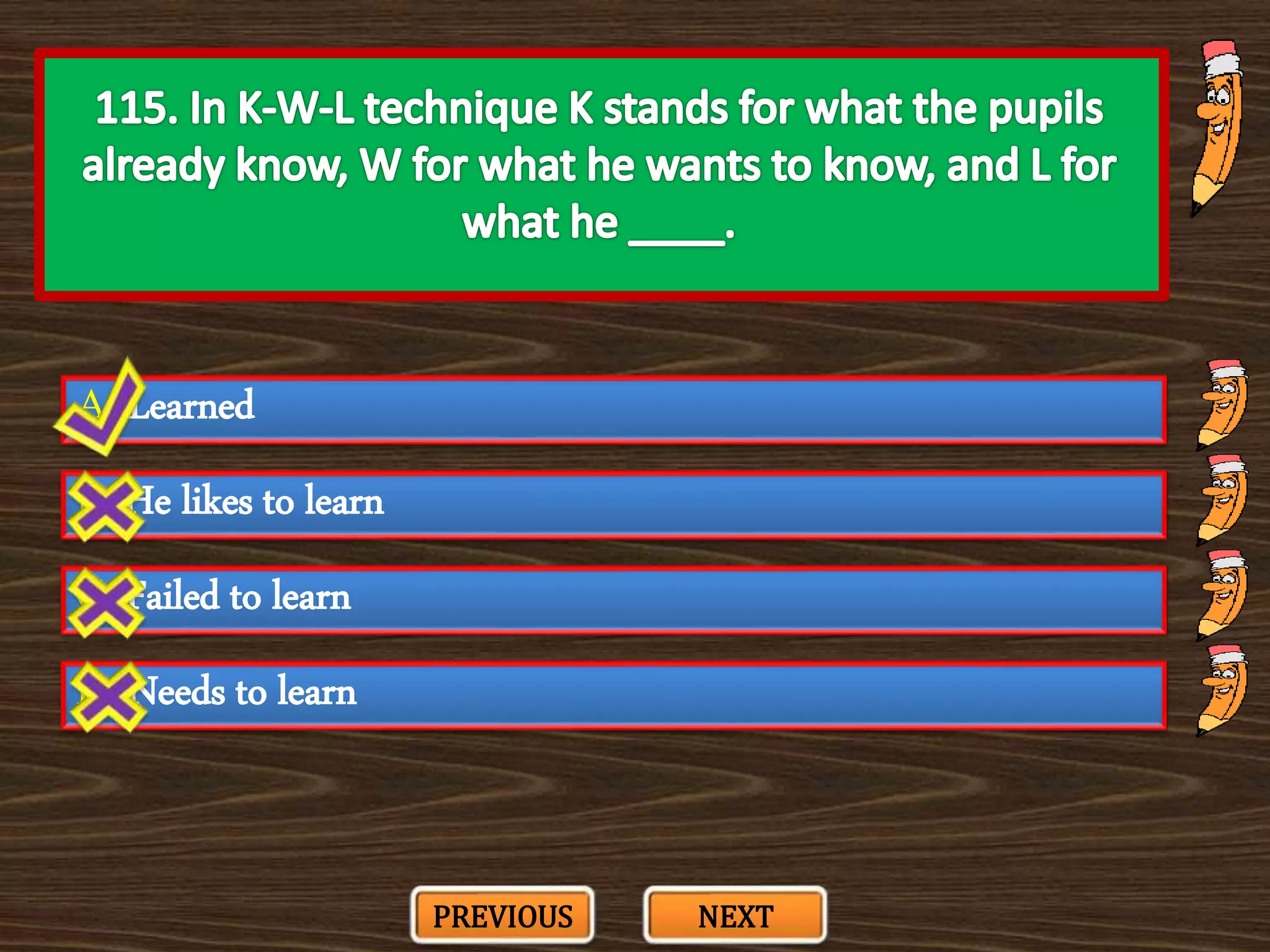
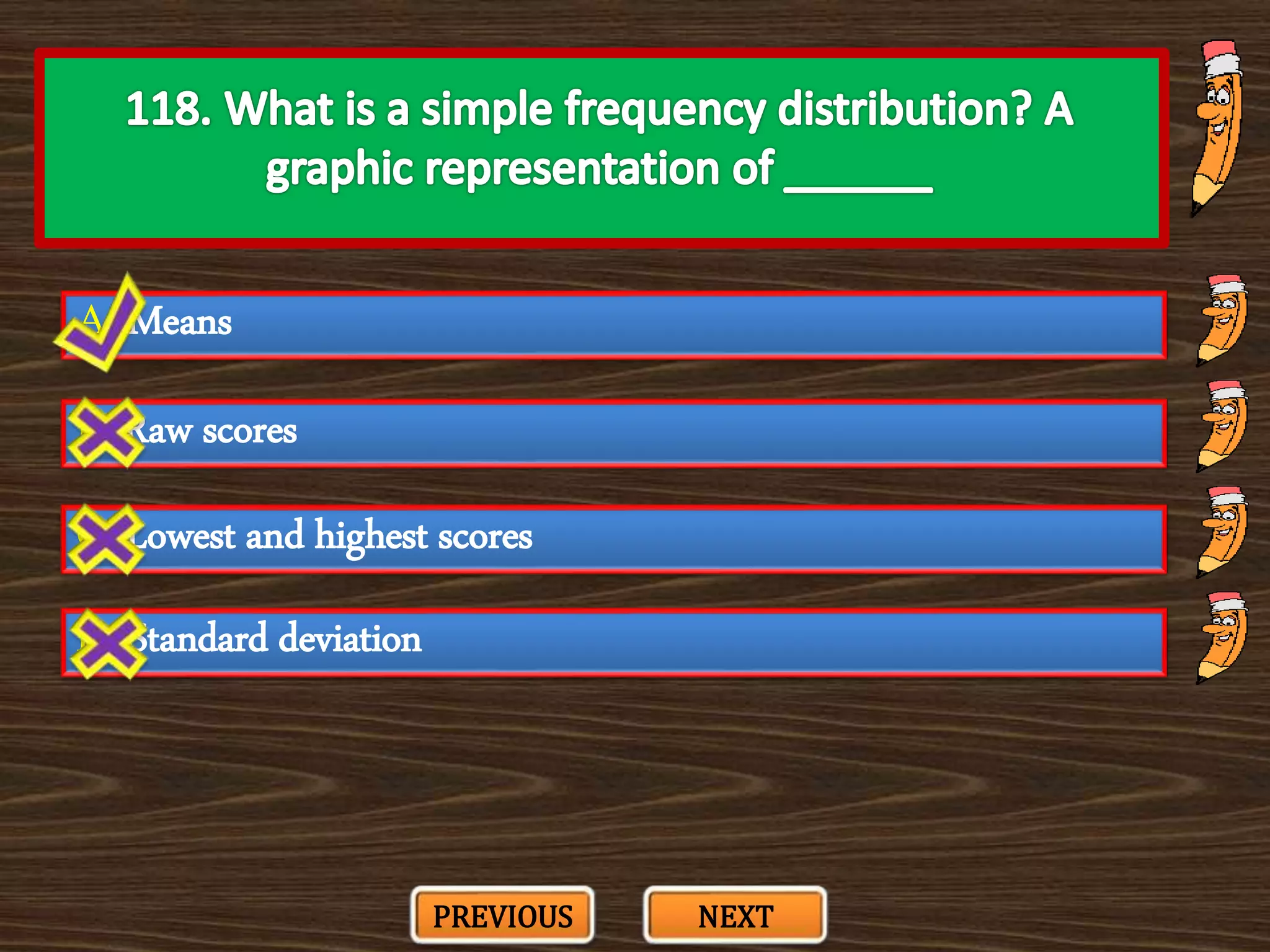
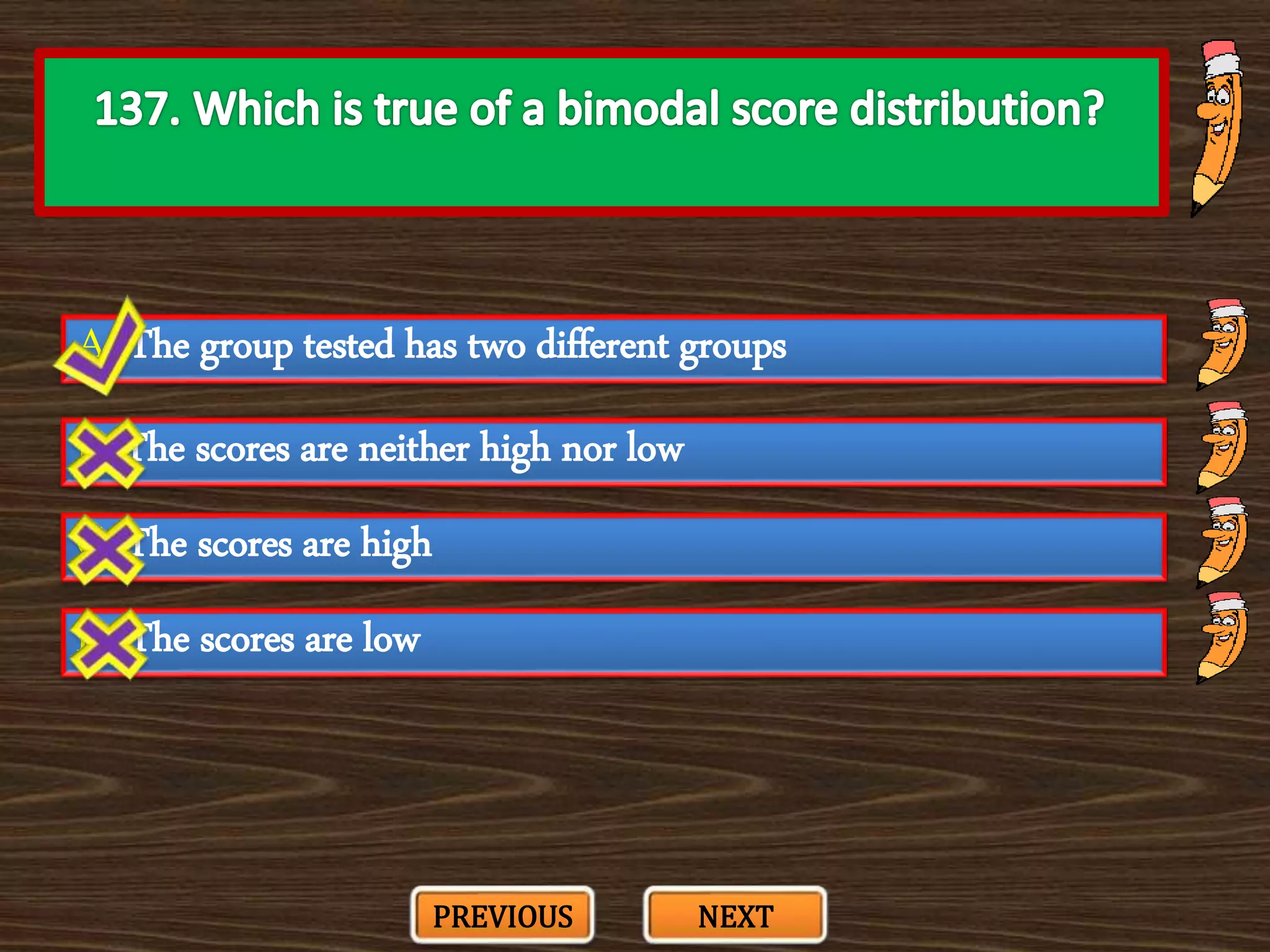
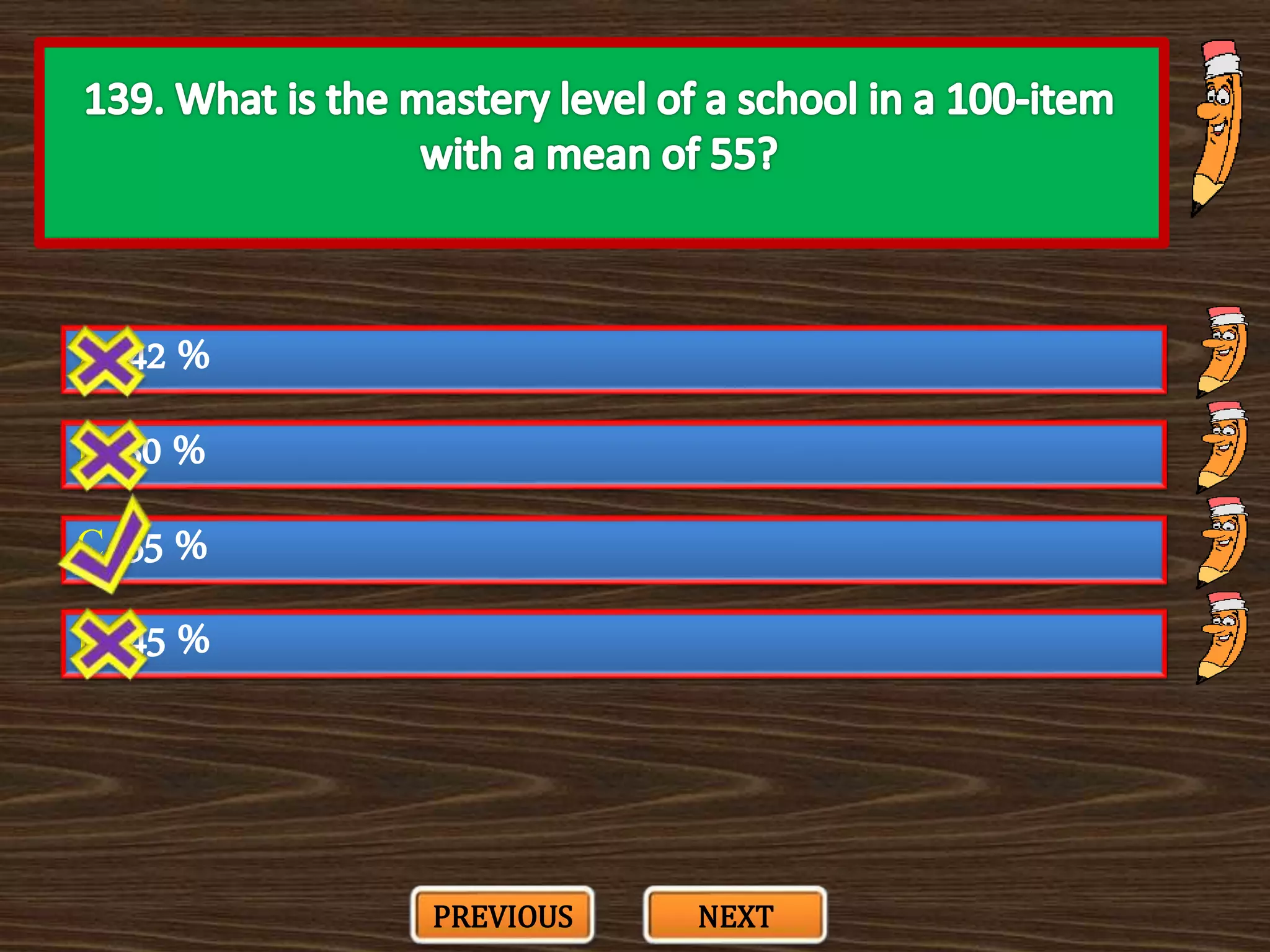
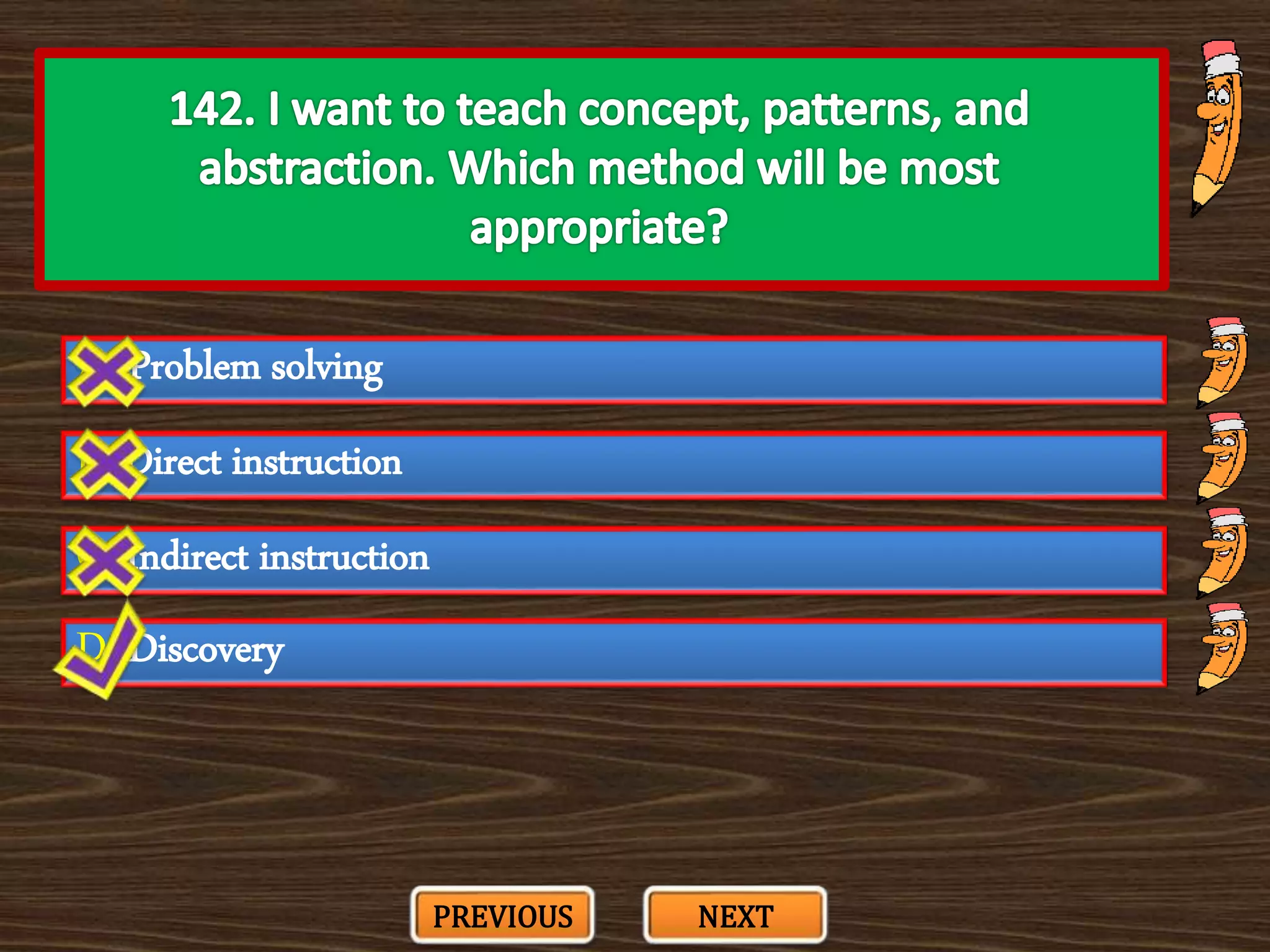
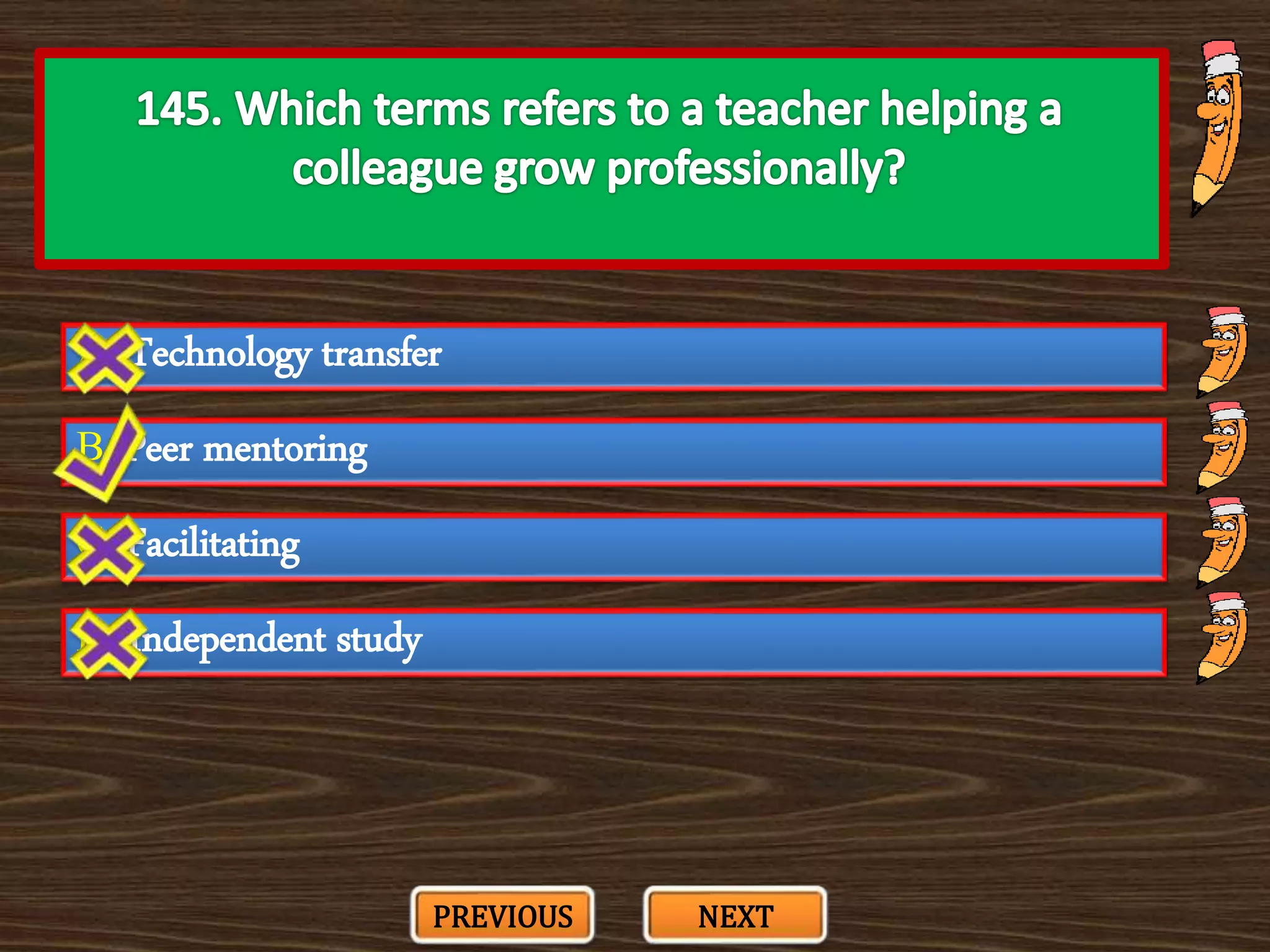
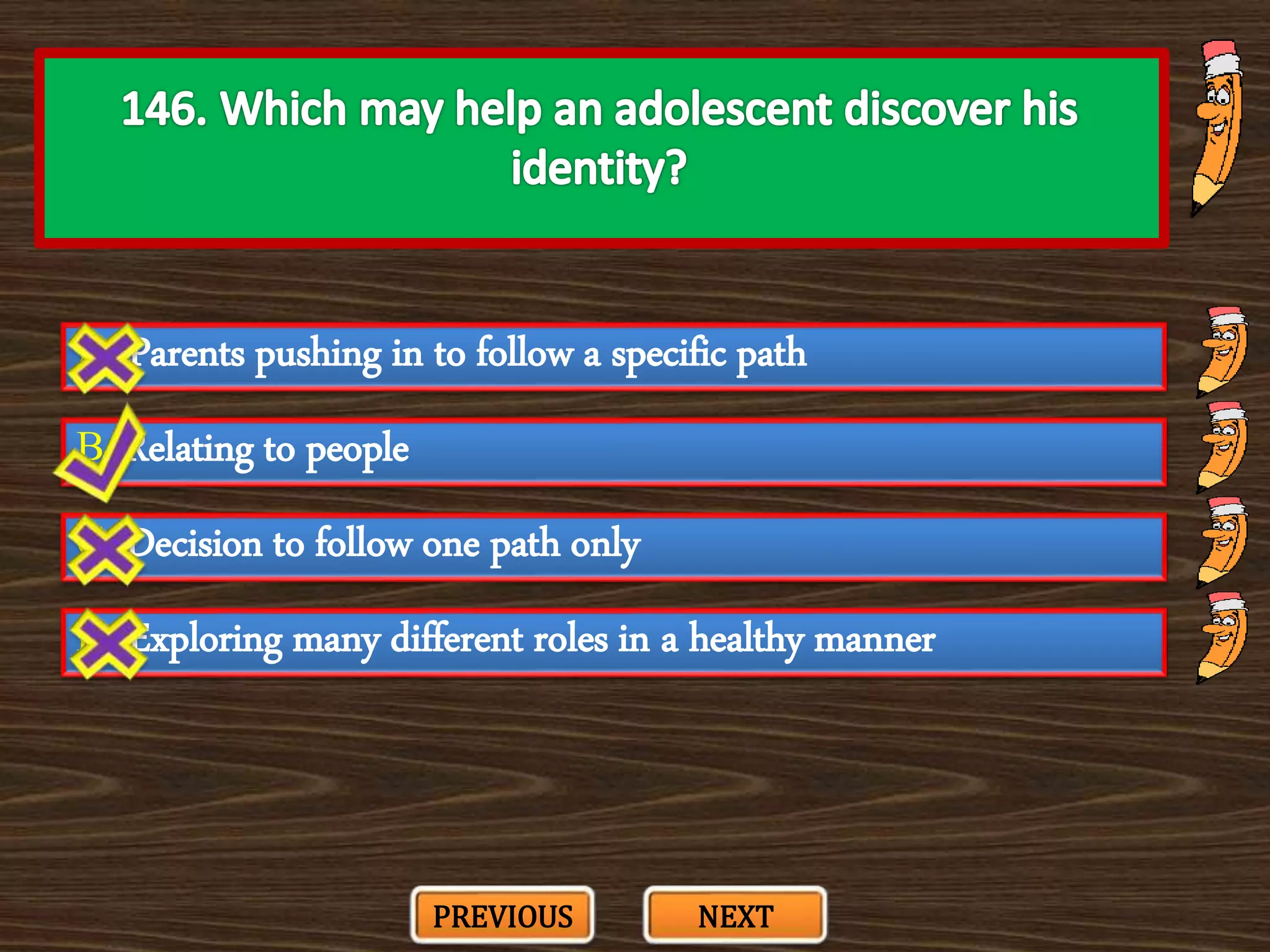
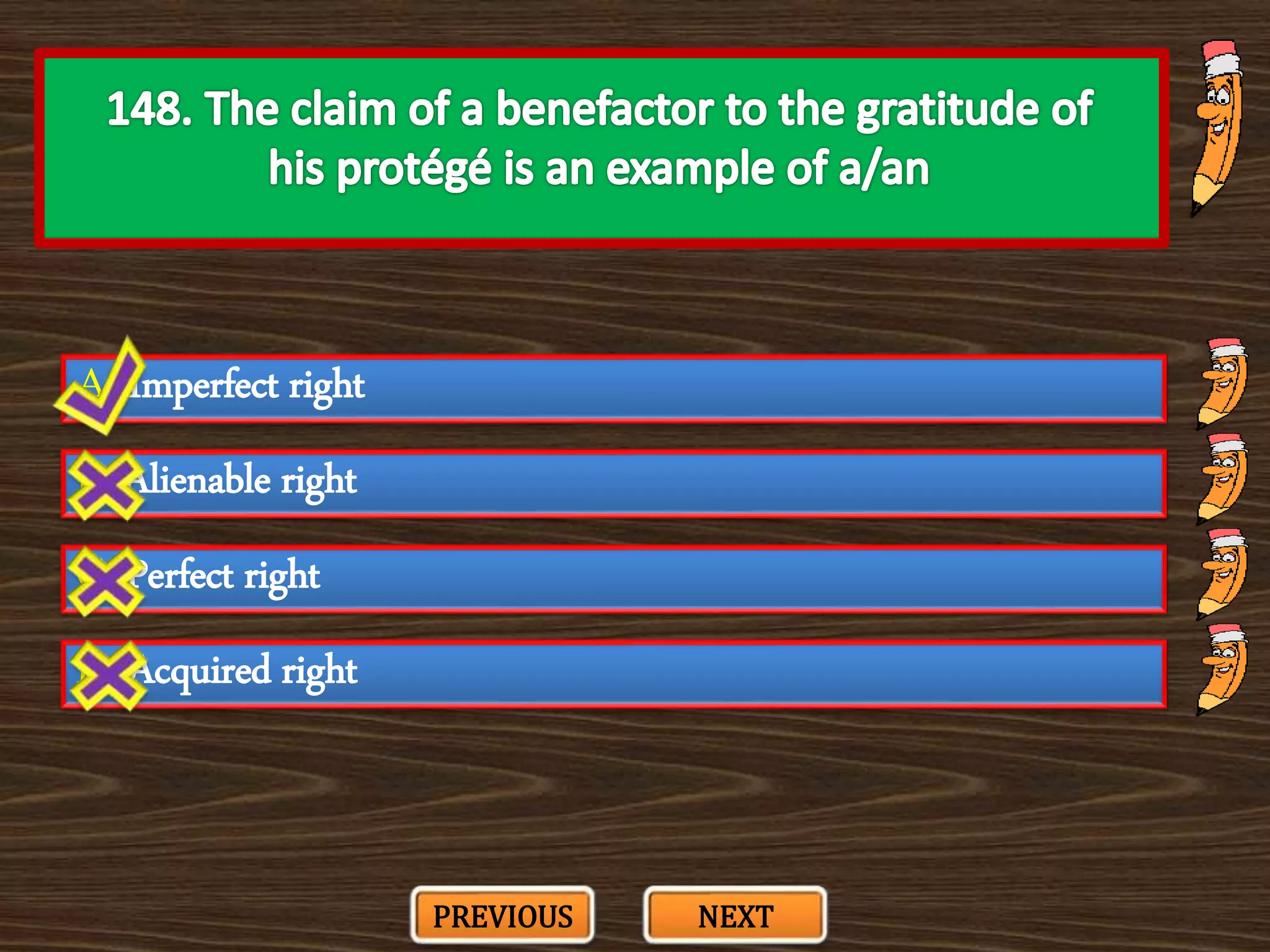
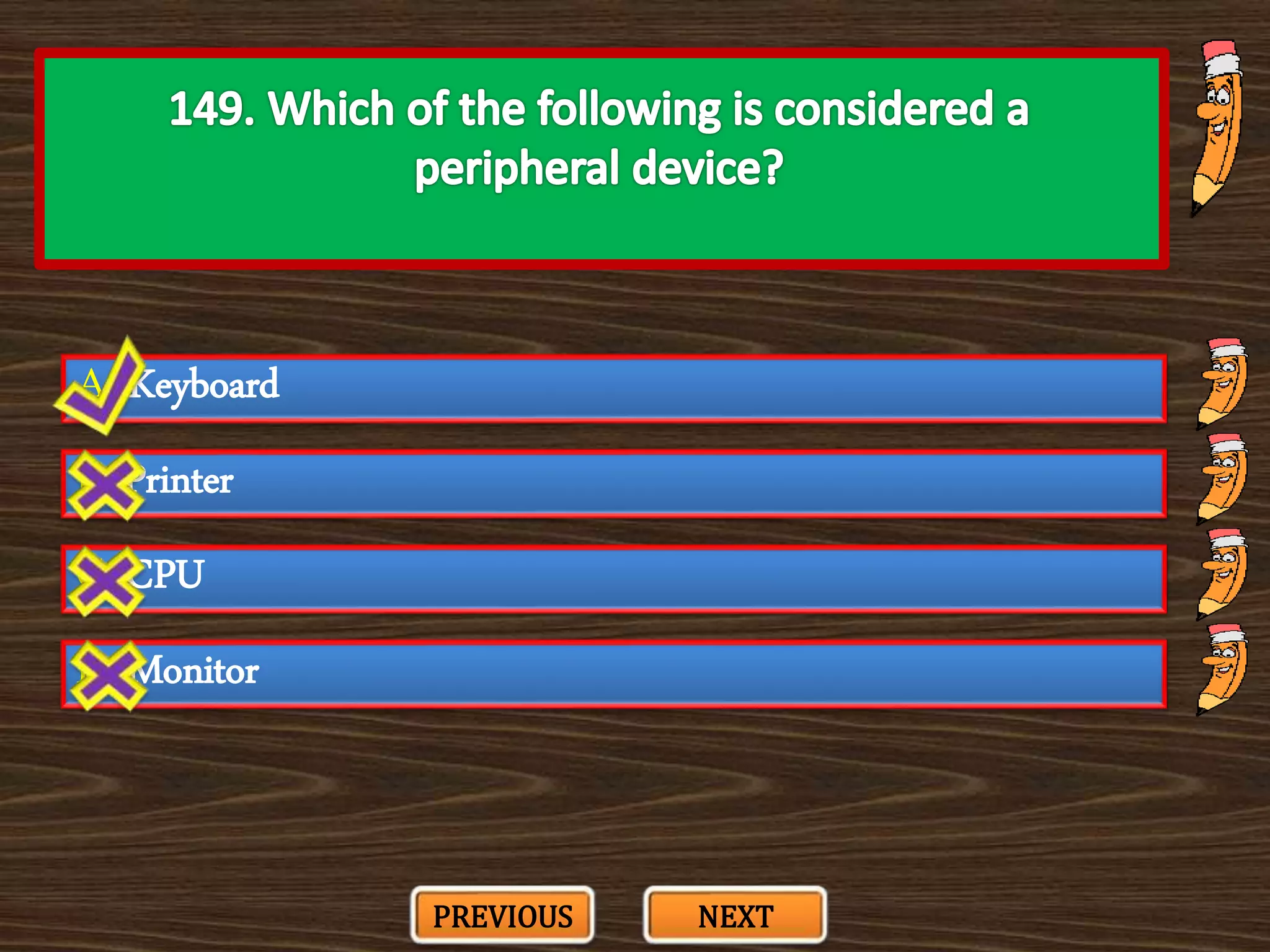
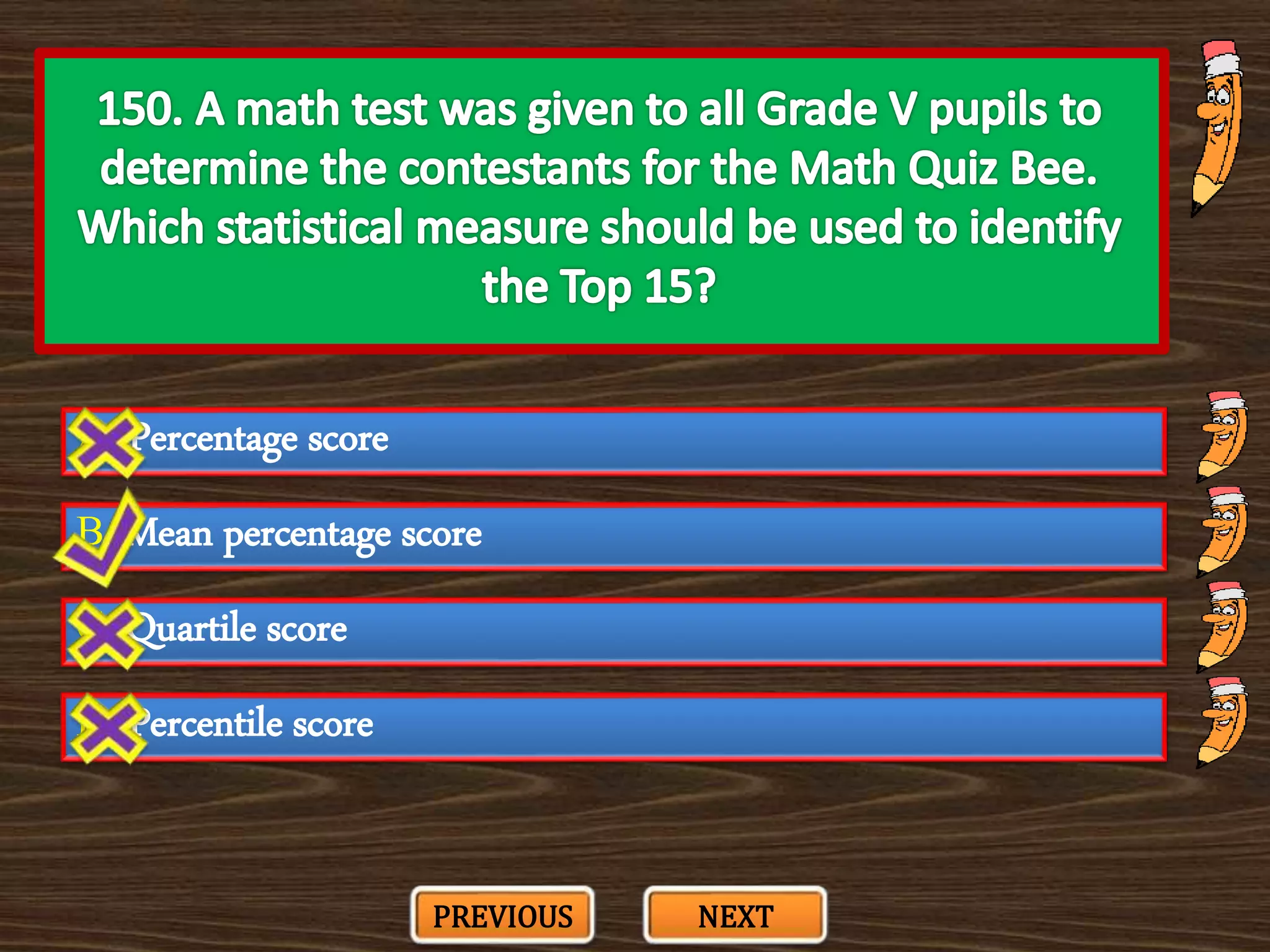
The document appears to be a series of multiple choice questions related to education, child development, and teaching. It covers topics like learning theories, curriculum approaches, assessment types, education laws and policies, and classroom management strategies. The questions are presented one at a time for the user to select the best answer from the given options.