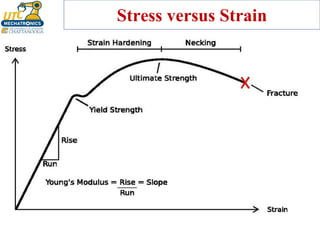
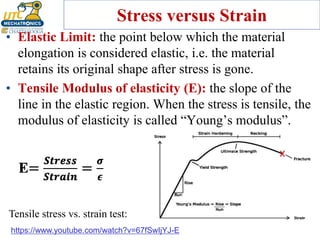
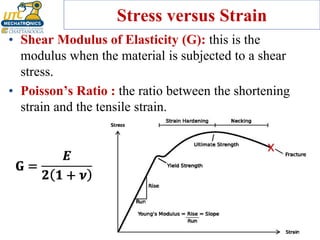
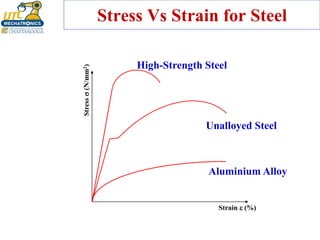
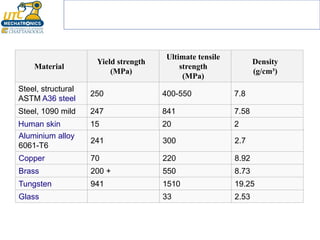
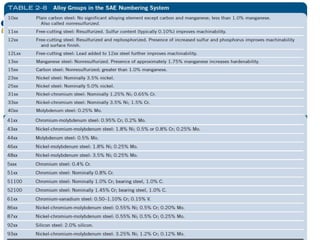
This document discusses various types of materials used in maintenance and their properties. It covers metals like steel, aluminum, and alloys; polymers; ceramics; and composites. Key material properties discussed include stress-strain behavior, modulus of elasticity, hardness, toughness, fatigue strength, and effects of temperature. Several destructive tests are summarized that are used to characterize these properties, such as tensile, impact, creep, and fatigue testing.