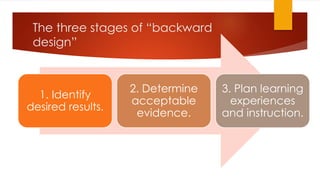
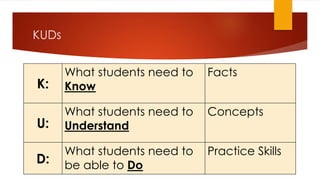
This document provides an overview of lesson planning using a backward design approach. It discusses identifying desired learning objectives and outcomes, determining assessments, and planning learning experiences to help students achieve objectives. Key aspects covered include establishing clear student roles, using understanding, knowledge and skills (KUDs) to guide objective setting, and employing a two-column lesson plan design to clarify teacher and student responsibilities. Additional tips focus on pacing, materials, activities, and reflection to improve lessons. The presentation aims to help educators understand backward design and apply its principles to make objectives clear and drive instruction.