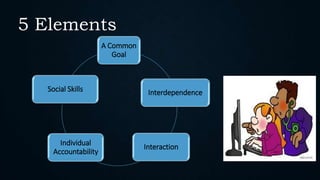
The document discusses cooperative or collaborative learning, which involves students working together in small groups on common tasks. It identifies five key elements of cooperative learning: common goal, interdependence, interaction, individual accountability, and social skills. Not all group work qualifies as cooperative learning; it requires these specific elements. Research shows cooperative learning can improve academic performance, literacy, language skills, and teacher effectiveness while also enhancing personal development and social relations among students. When computers are used for cooperative learning tasks, students interact and help each other, contradicting fears that computers isolate students. For cooperative learning to be effective using computers, teachers must mix student abilities, establish interdependence, teach social skills, ensure accountability, and help groups process information. The ideal