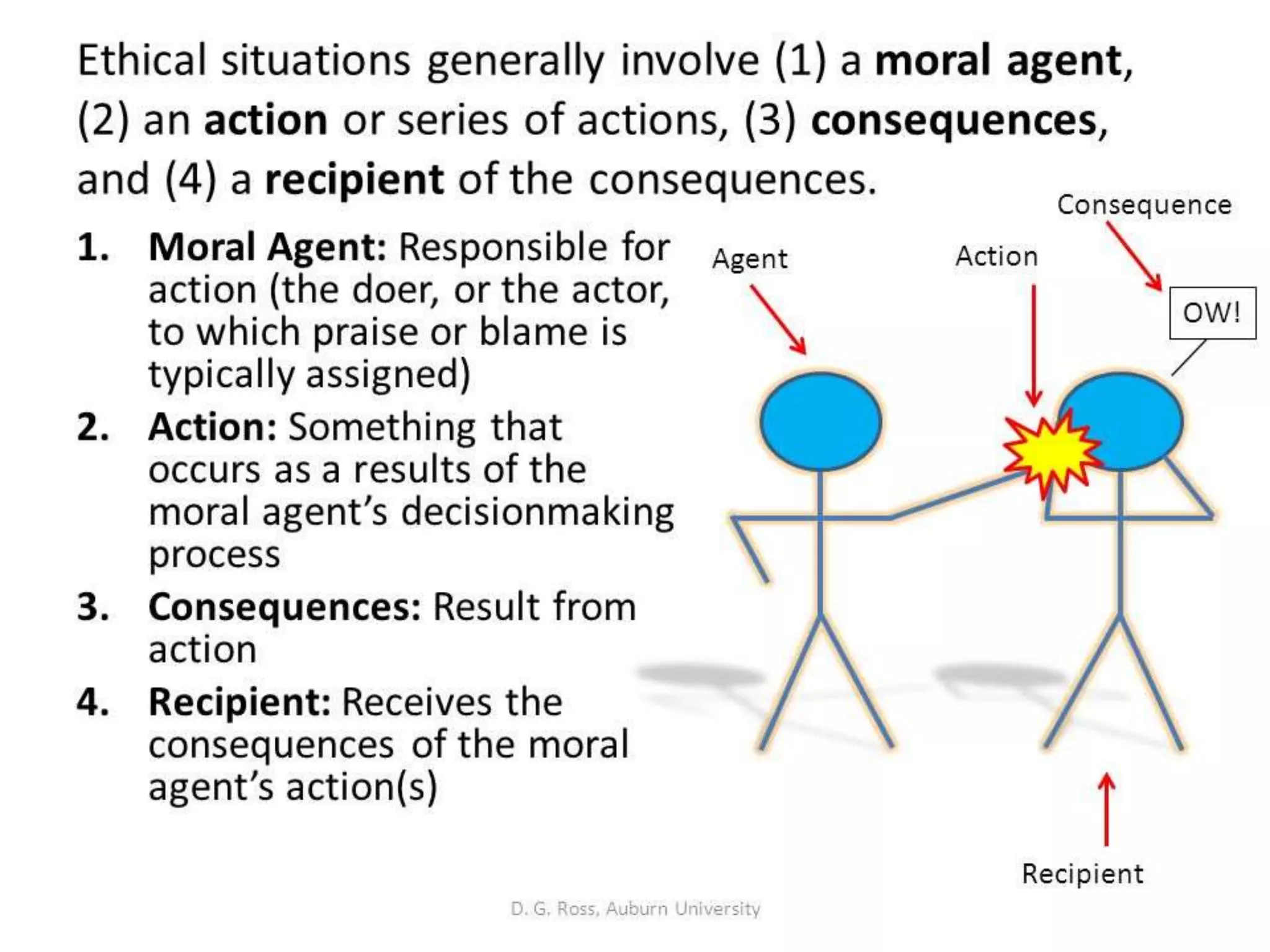
The document discusses the fundamentals of ethics, including its origins in ancient Greece and definitions. It describes ethics as the study of distinguishing between right and wrong actions based on customs and habits. Two key assumptions of ethics are that humans are rational beings who can act with purpose and that humans have free will. The objects of ethics are moral agents (people and institutions) and their actions, which can be involuntary natural acts, voluntary natural acts, or intentional human acts that can be moral or immoral. The document outlines different forms of ethical analysis including descriptive ethics, normative ethics, consequentialist versus nonconsequentialist theories, and practical versus theoretical ethics.