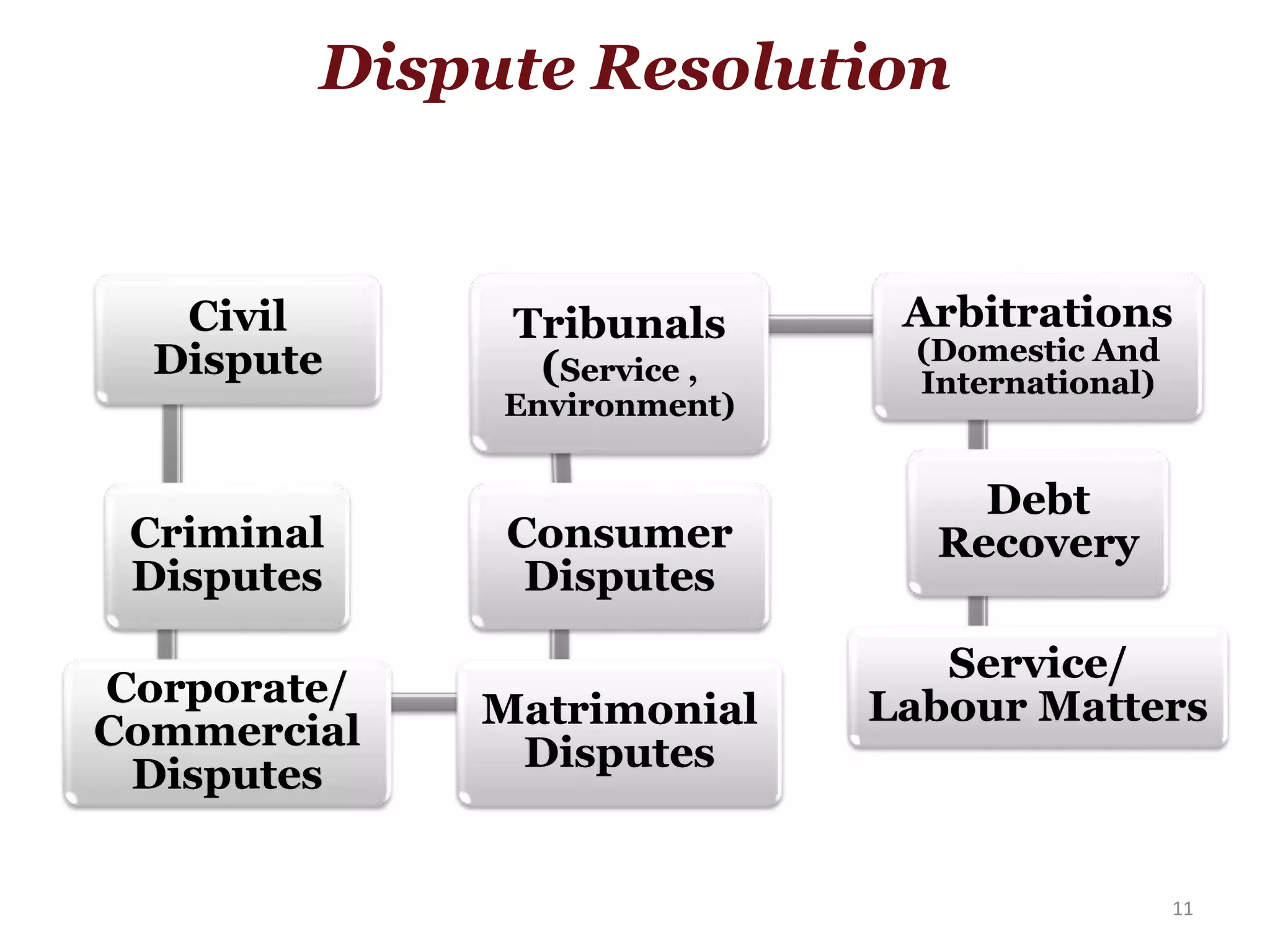
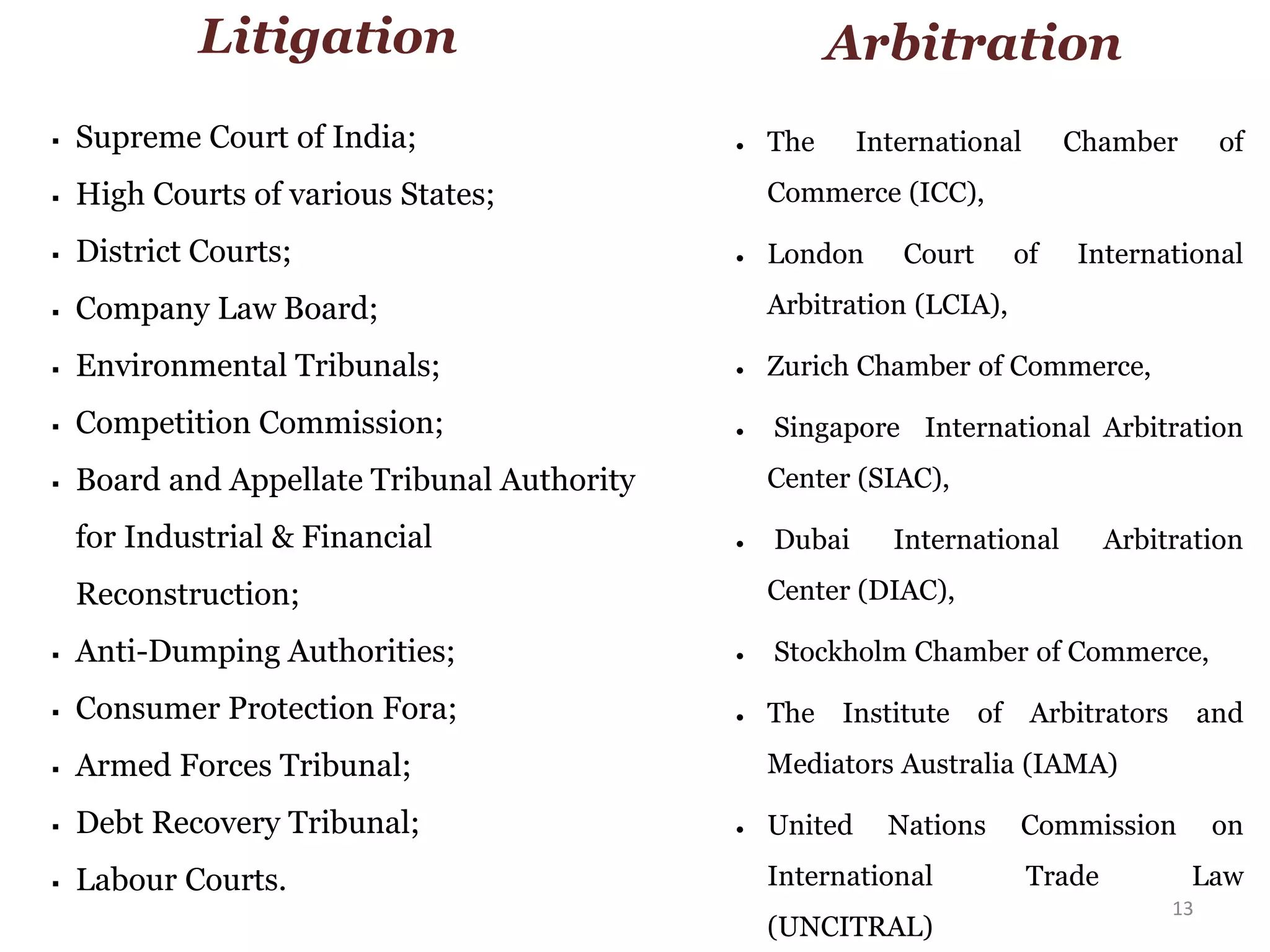
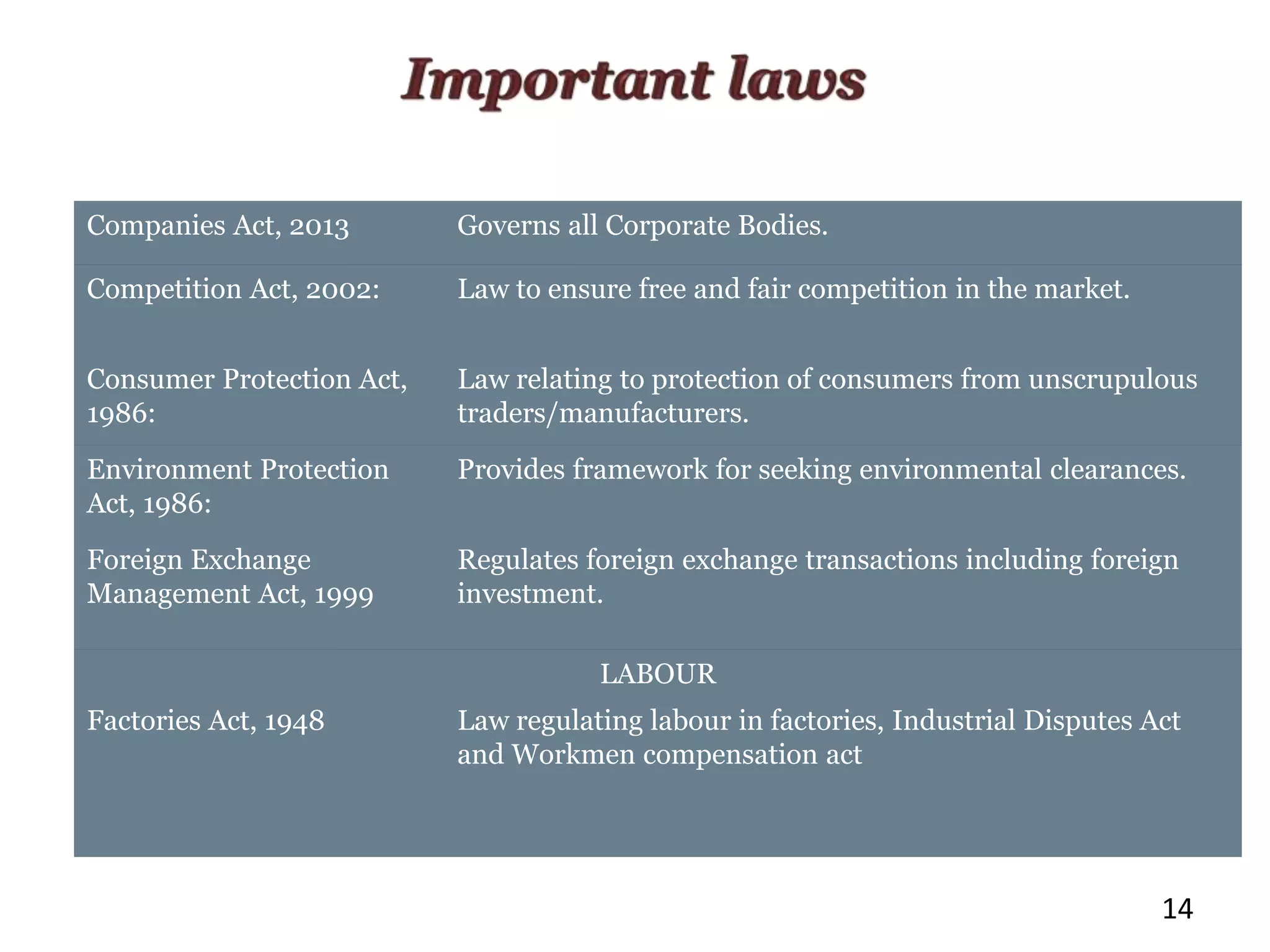
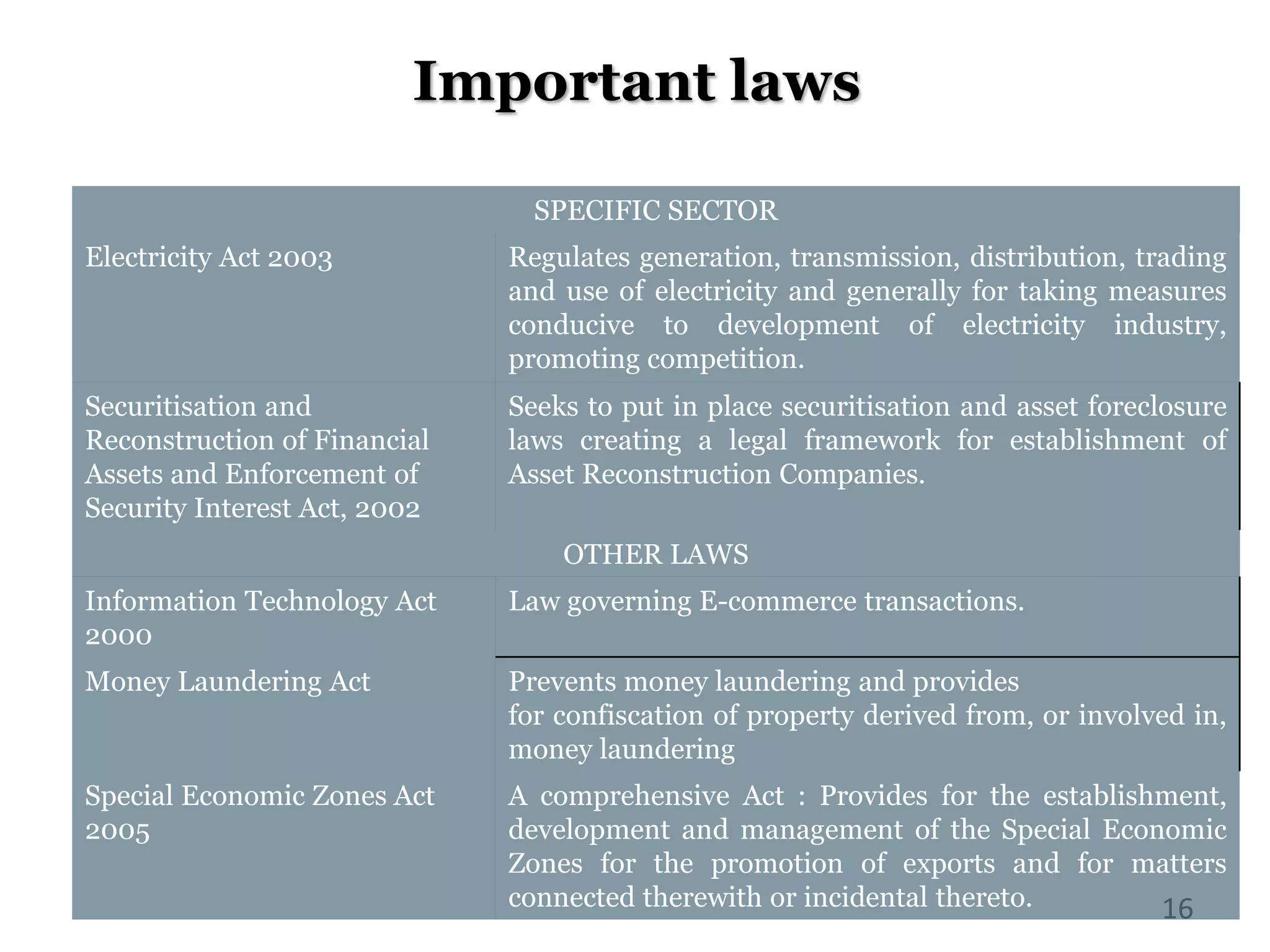
The document outlines various legal issues faced by startups, including essential incorporation documents and crucial clauses in contracts. It covers important laws governing corporate bodies, competition, consumer protection, environmental regulations, and labor laws, as well as specific laws relevant to various industries. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of dispute resolution mechanisms like litigation and arbitration in the Indian legal context.