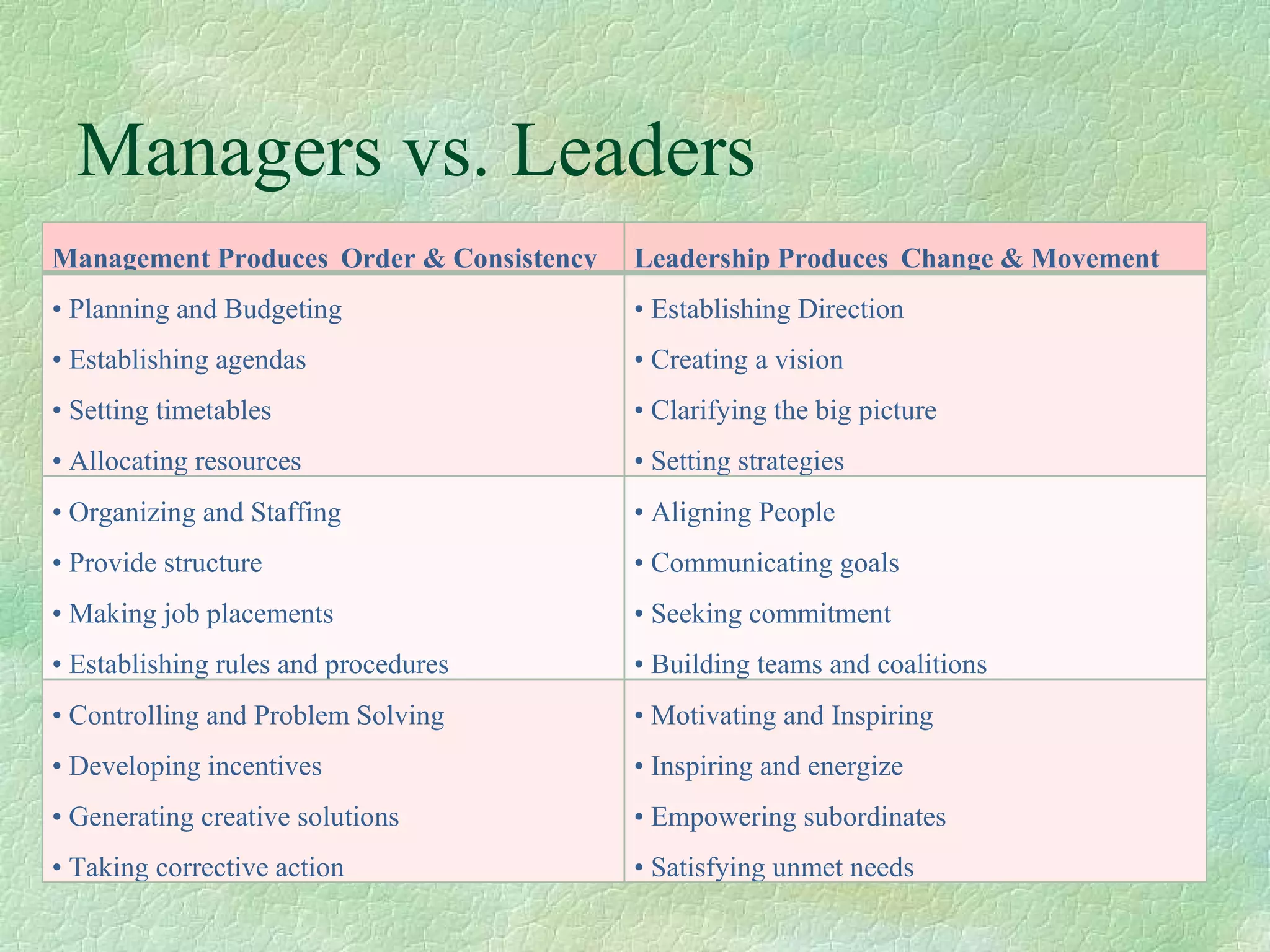
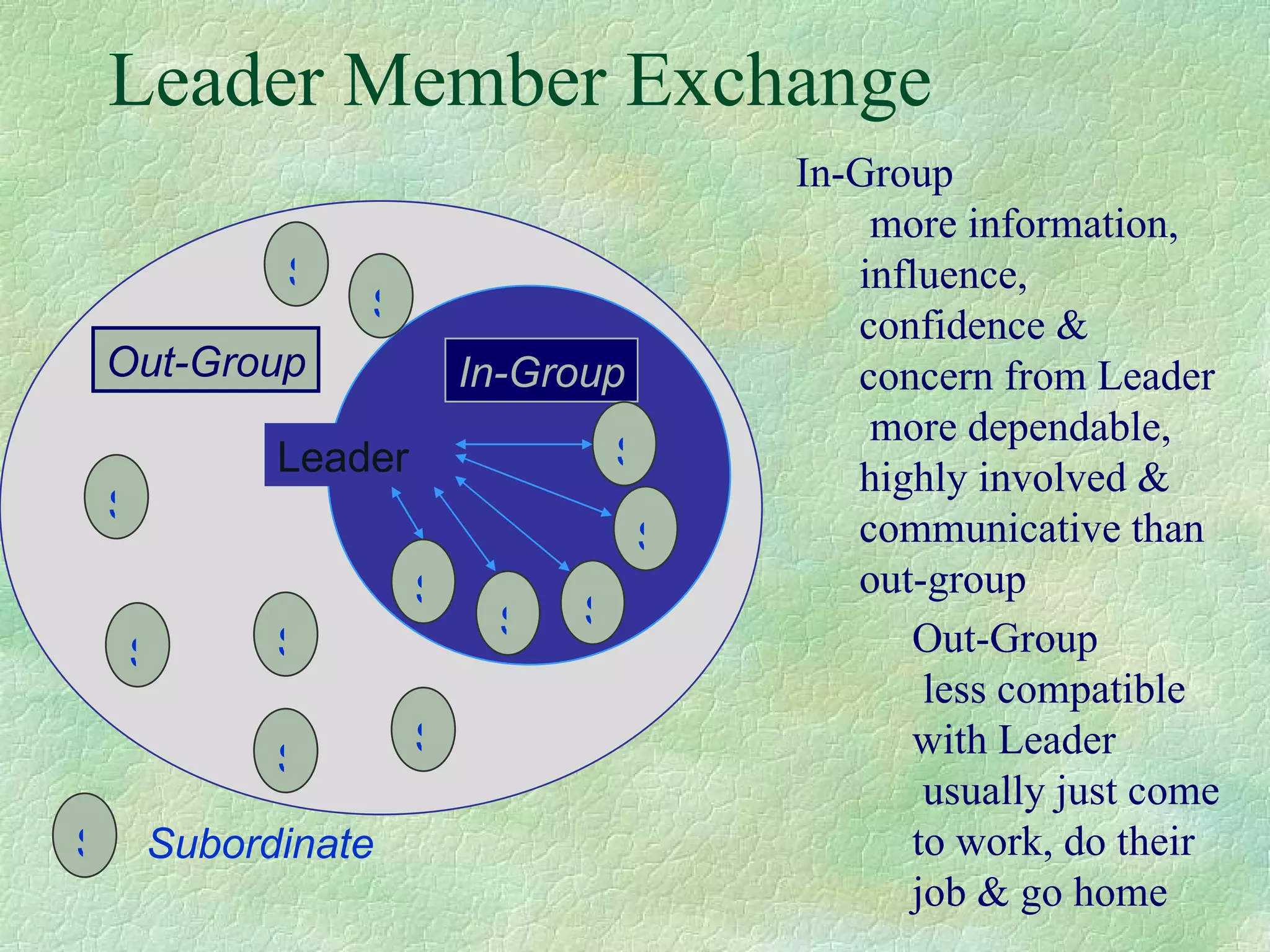
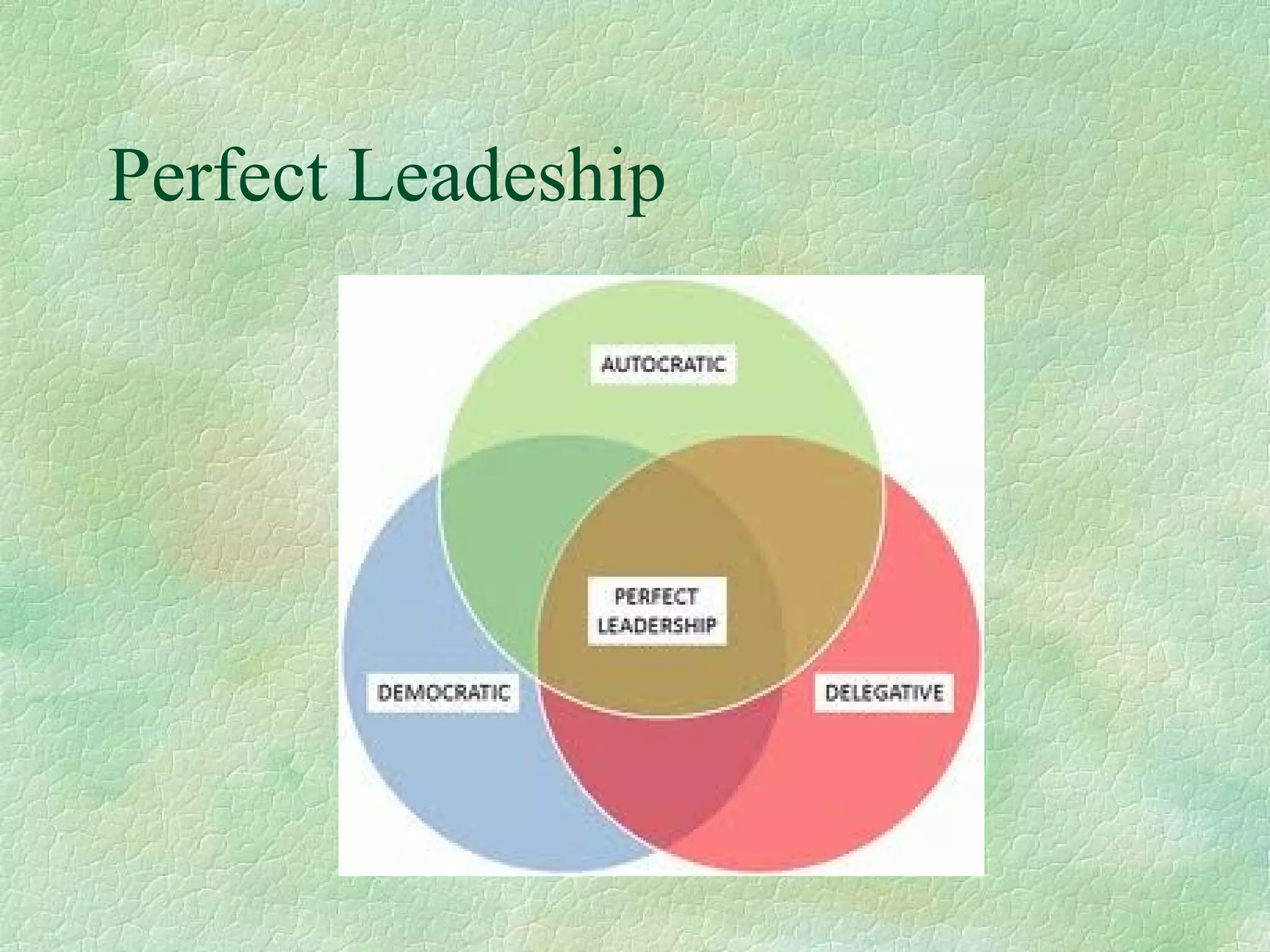
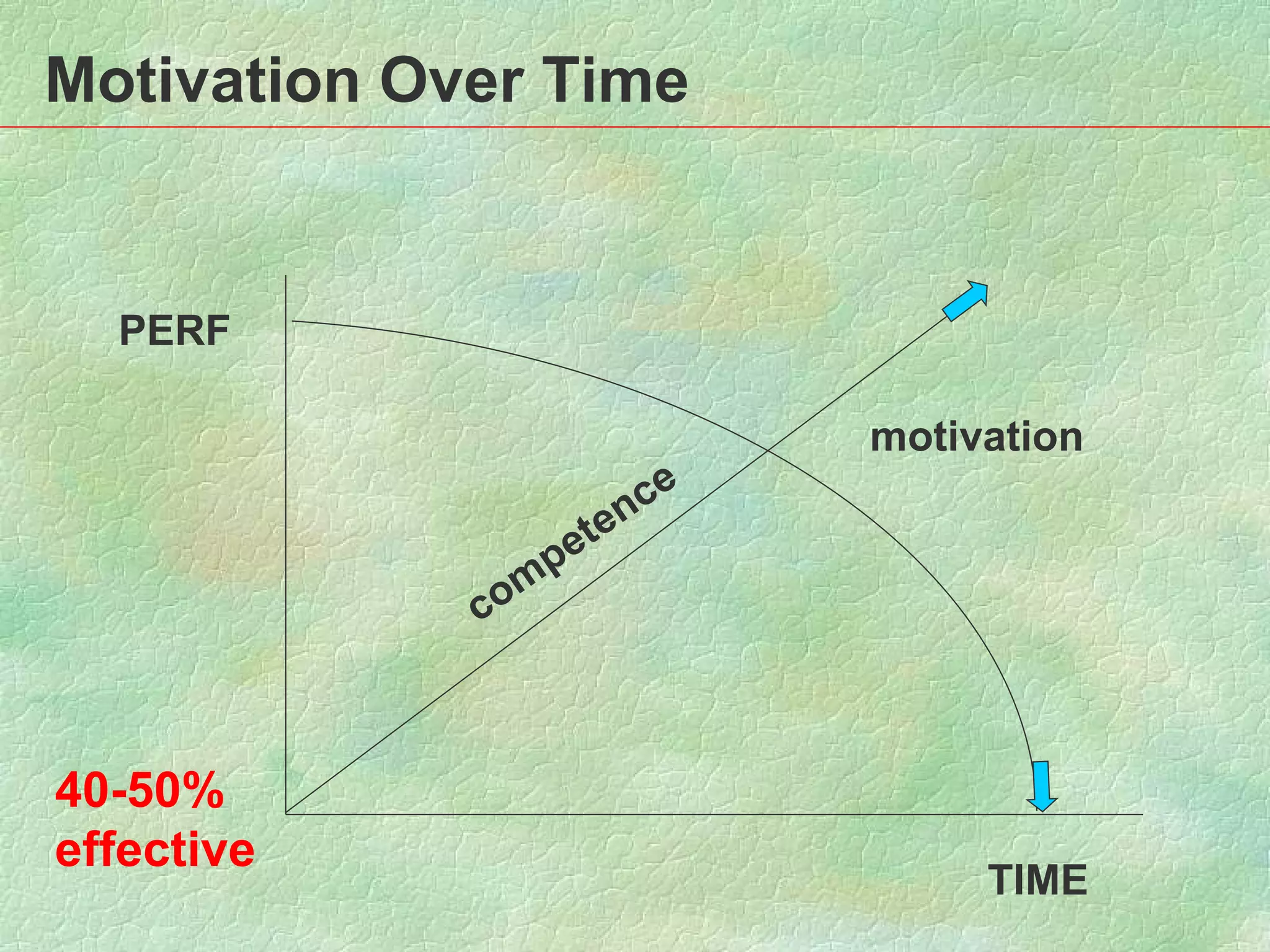
This document summarizes and compares the leadership styles of two hospitals in Sri Lanka: National Hospital Sri Lanka and Lanka Hospital PLC. It discusses different leadership styles (autocratic, democratic, delegative), goals of leadership, and factors that influence leadership style. Data was collected from managers and employees on characteristics like decision making, delegation, customer relations, teamwork, motivation and efficiency. The analysis found Lanka Hospital PLC had stronger traits in these areas. The document concludes with recommendations for leadership.