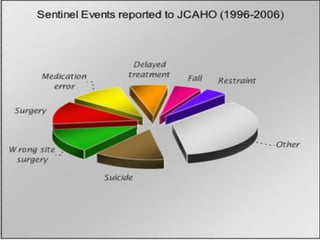
The document outlines the policies and procedures of a hospital's patient safety plan. It establishes a patient safety committee to identify risks, prevent medical errors, and improve patient outcomes. Key parts of the plan include defining terms like medical errors and sentinel events, establishing safety standard policies in various areas of care, and forming teams to address specific safety issues like surgery, medication management, infections, and environmental safety. The goal is to institutionalize patient safety as a fundamental part of healthcare delivery.