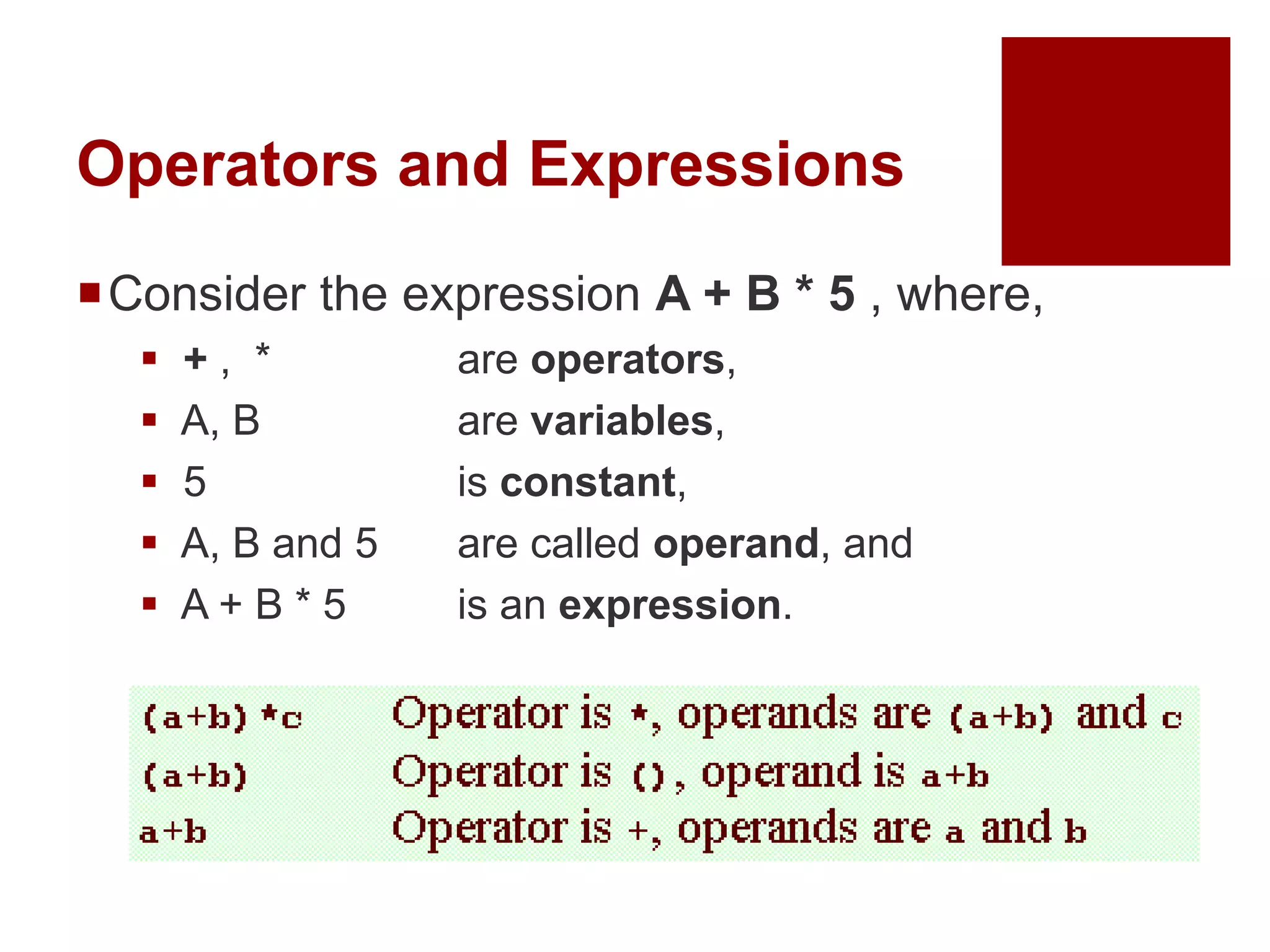
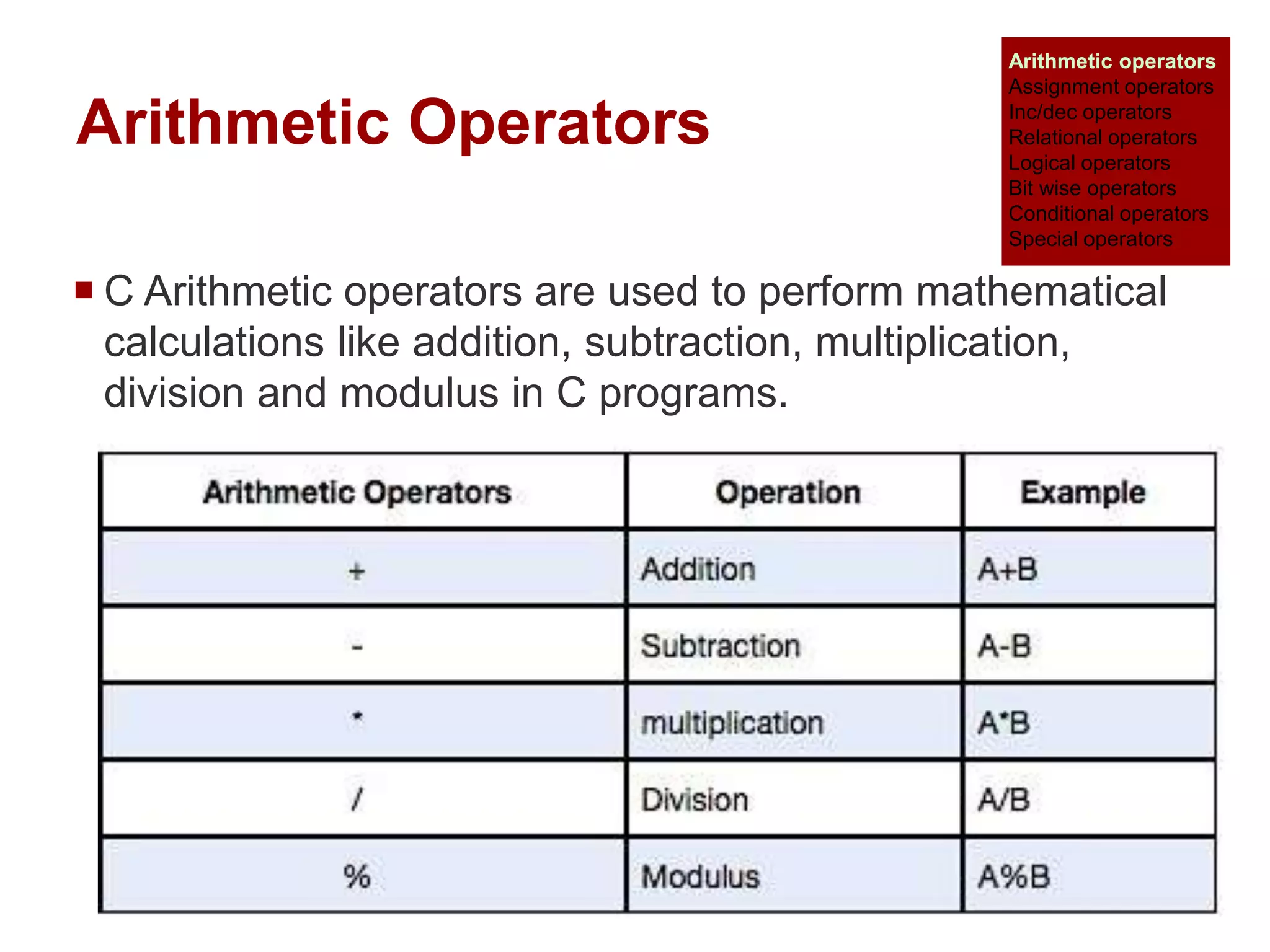
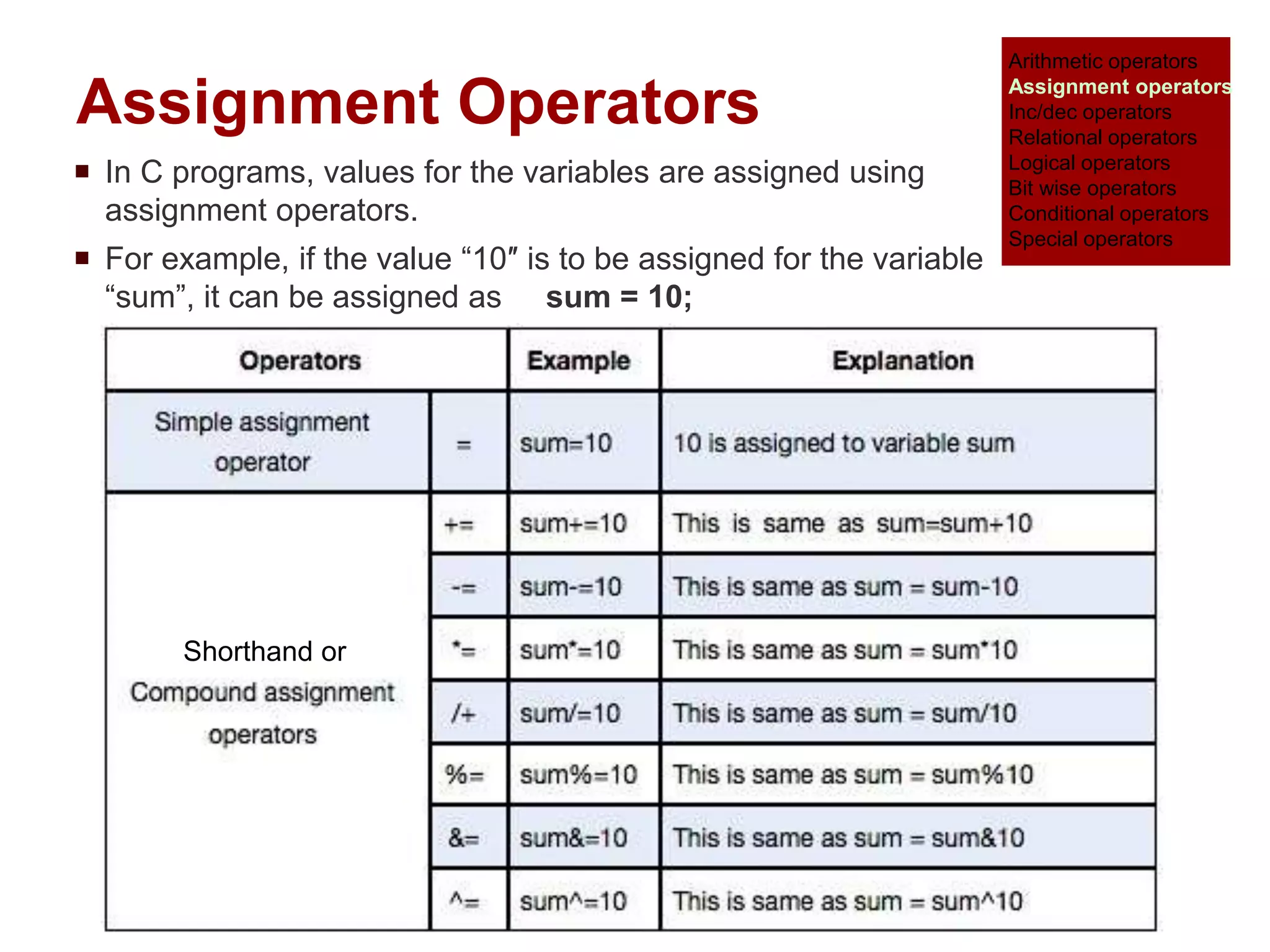
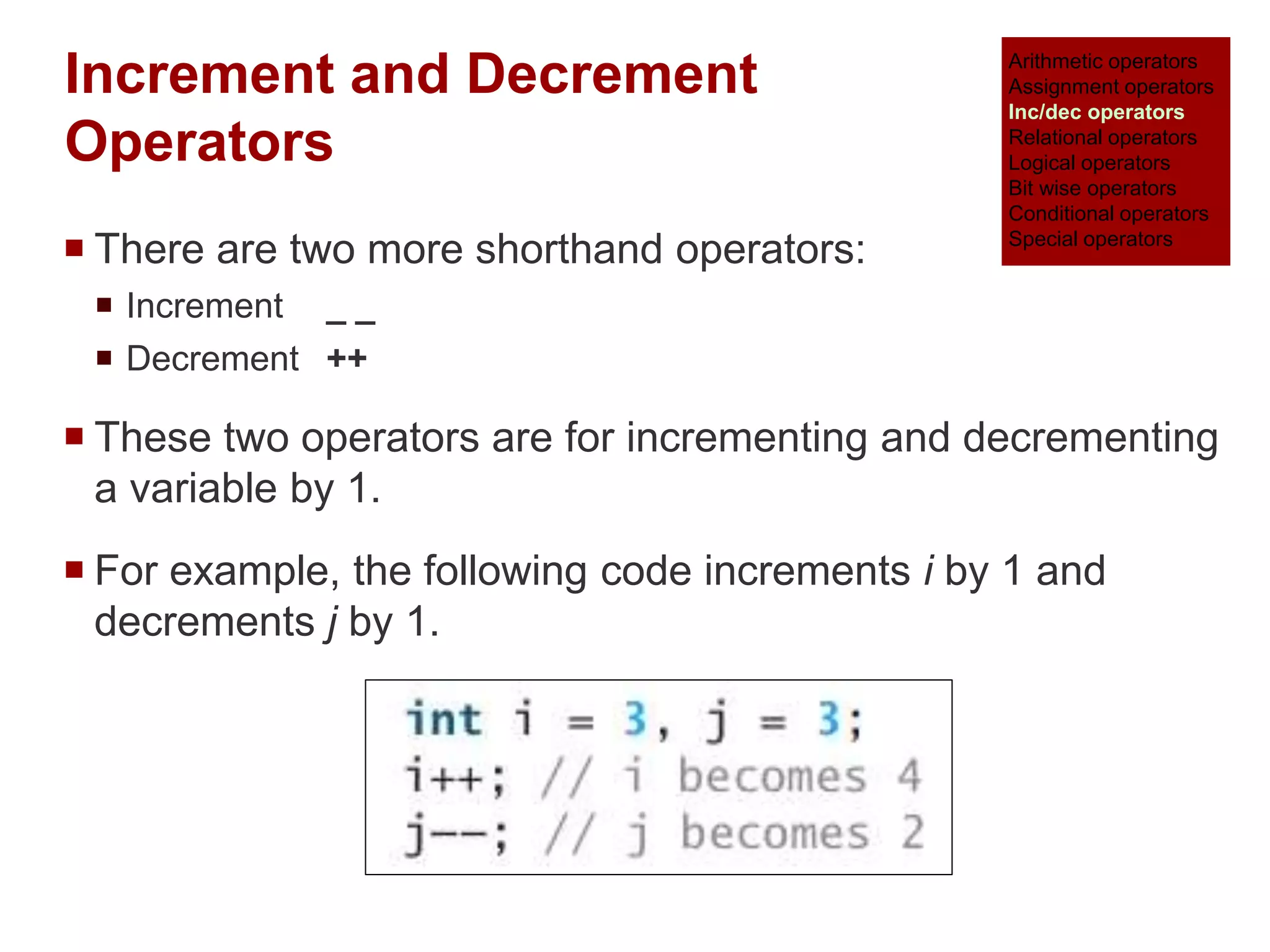
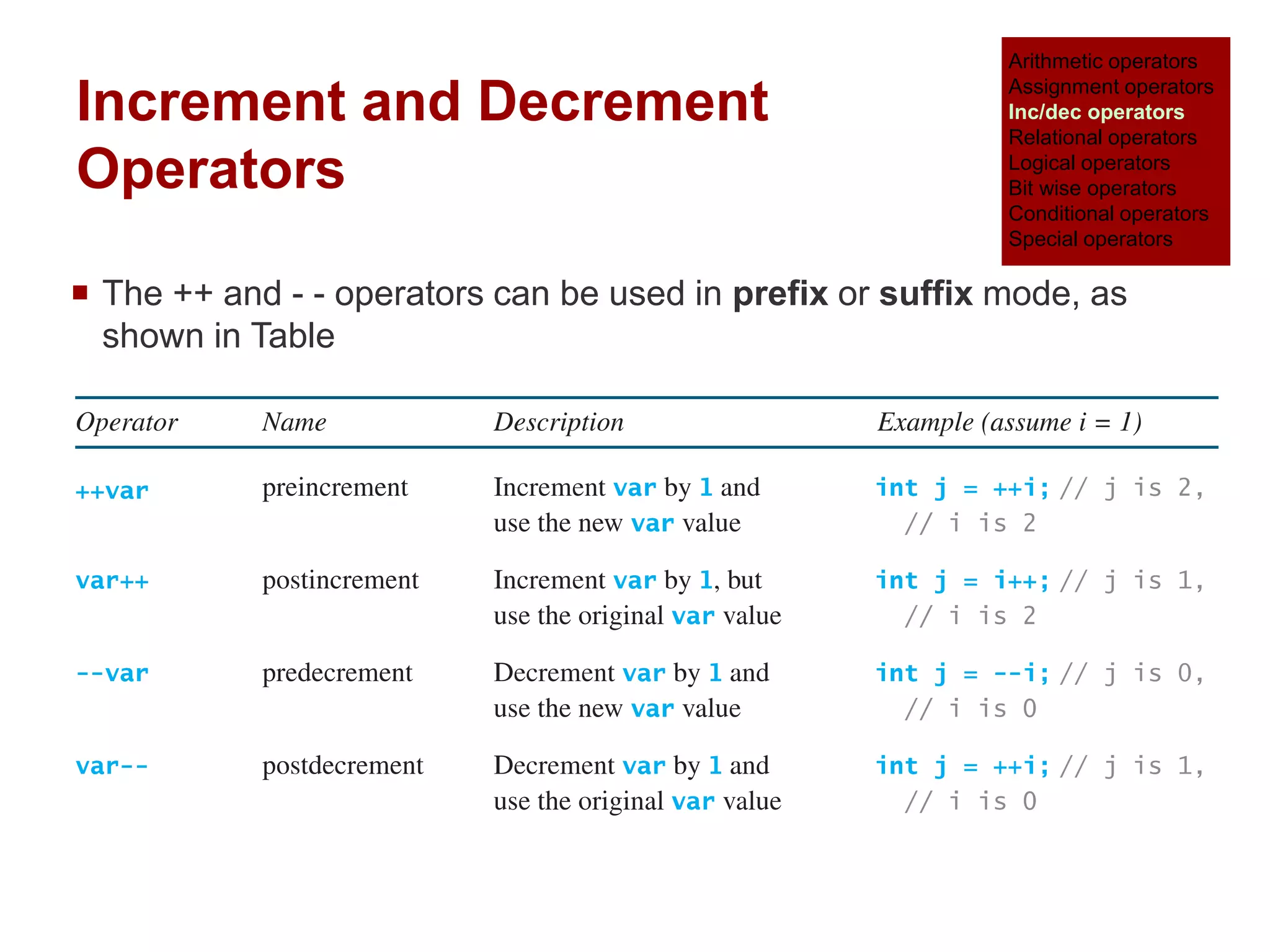
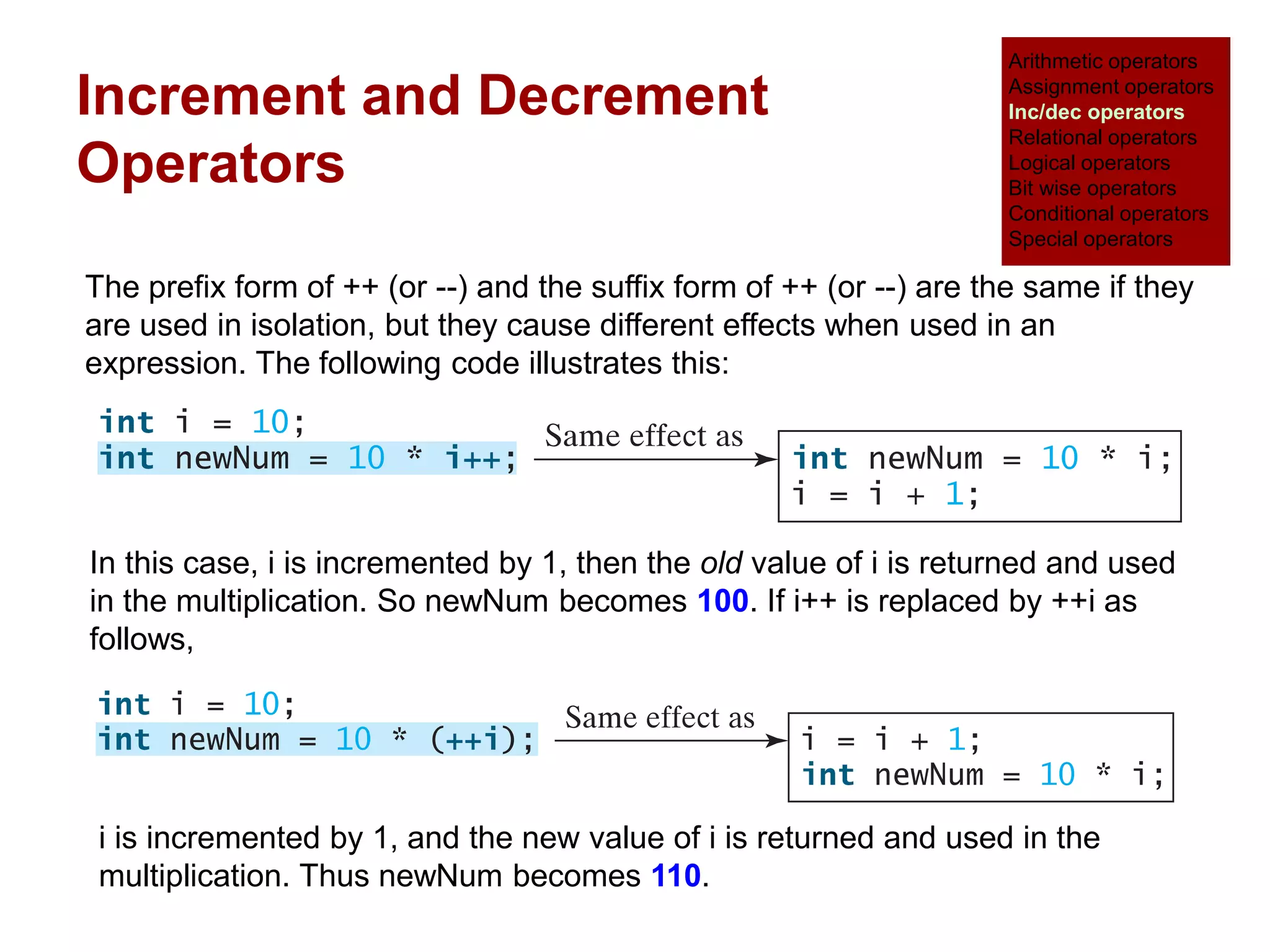
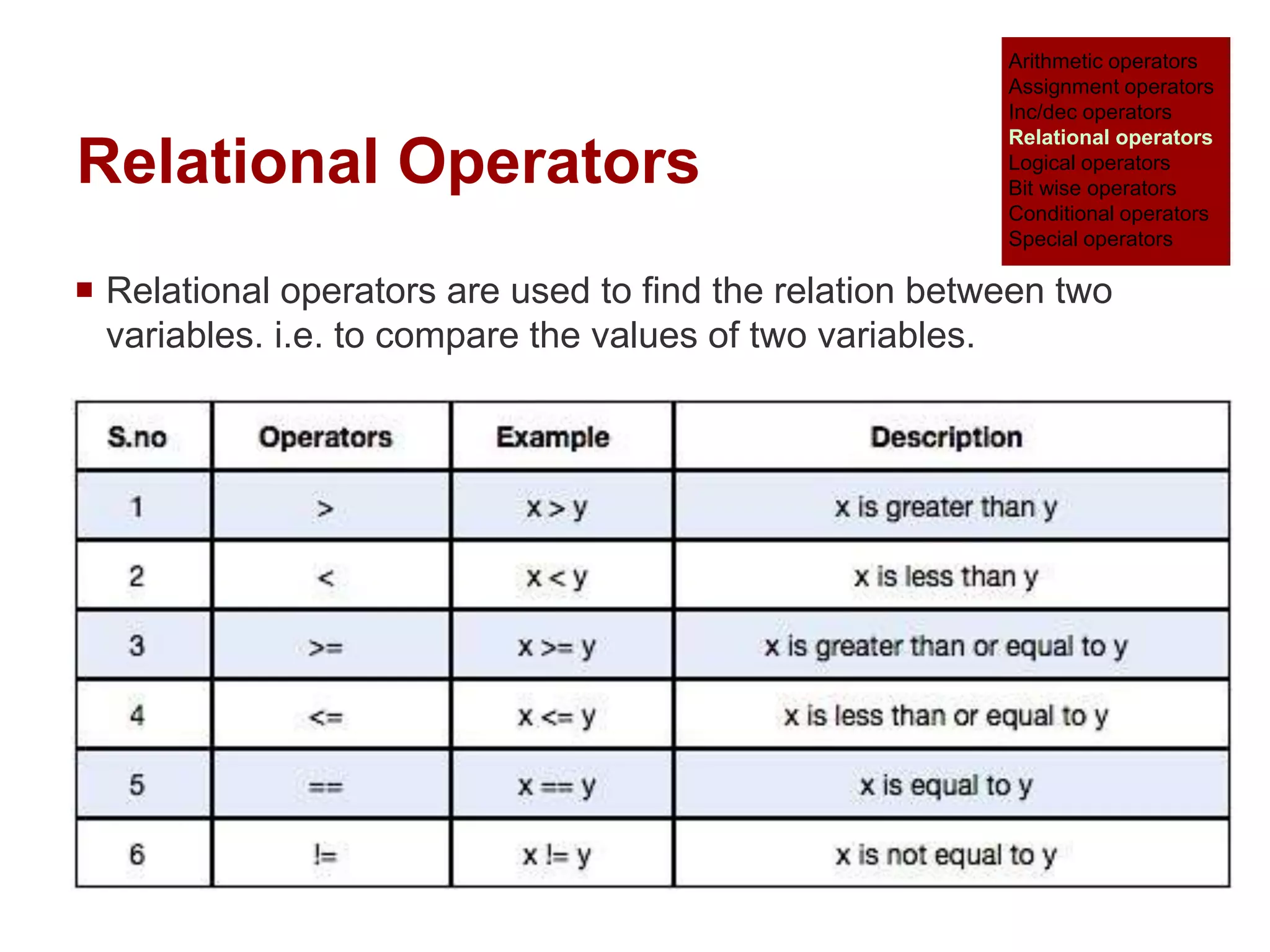
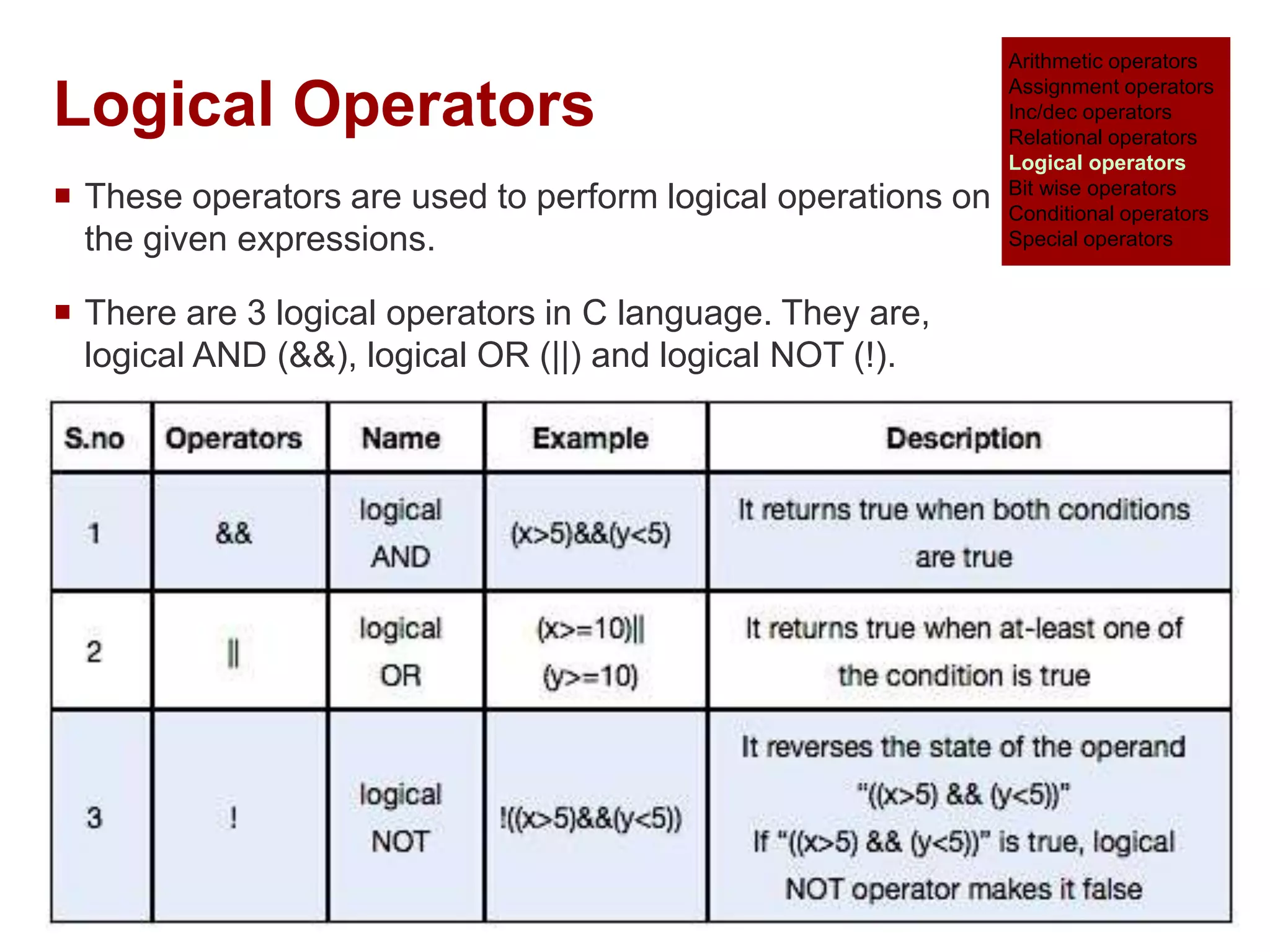
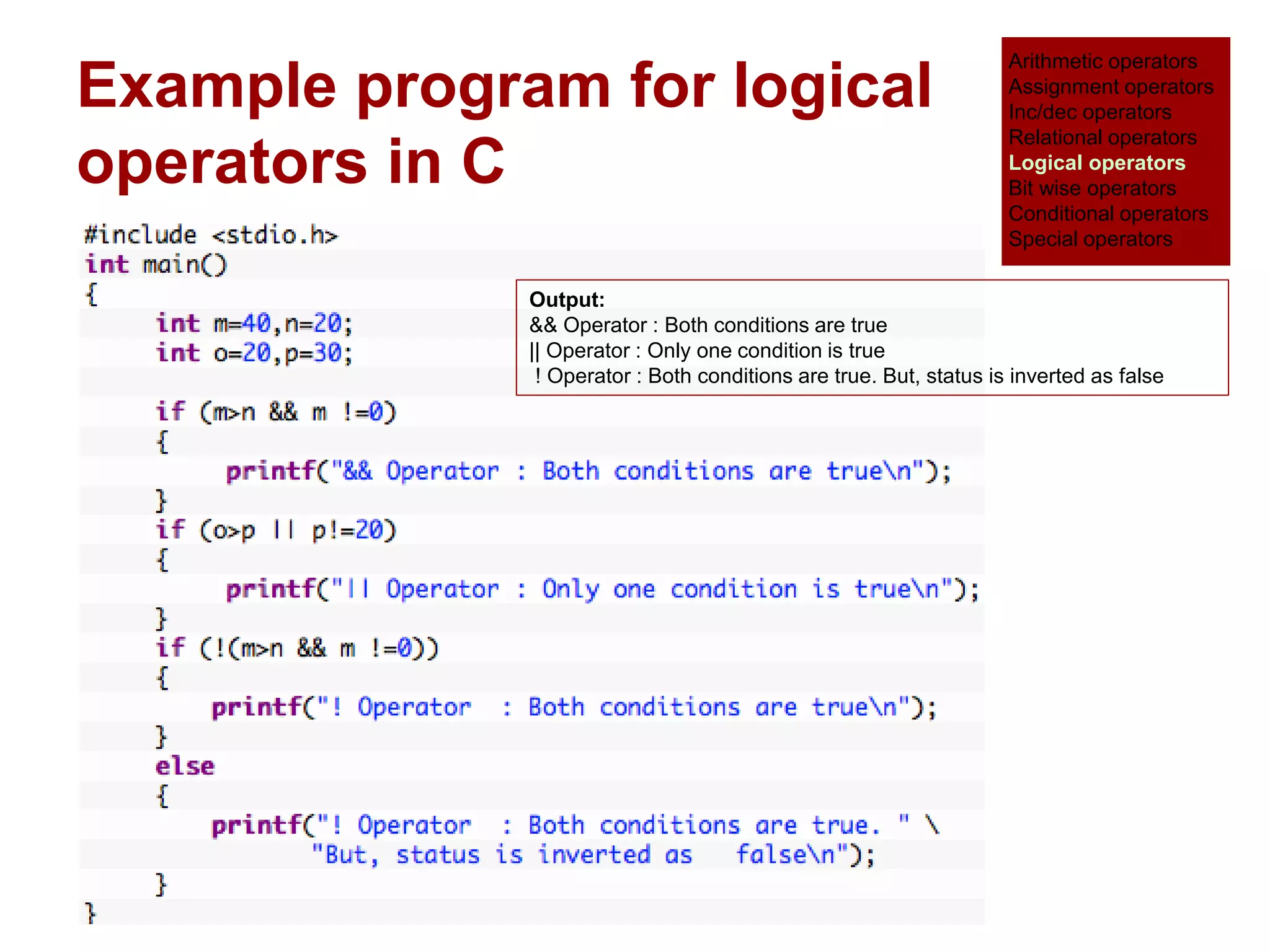
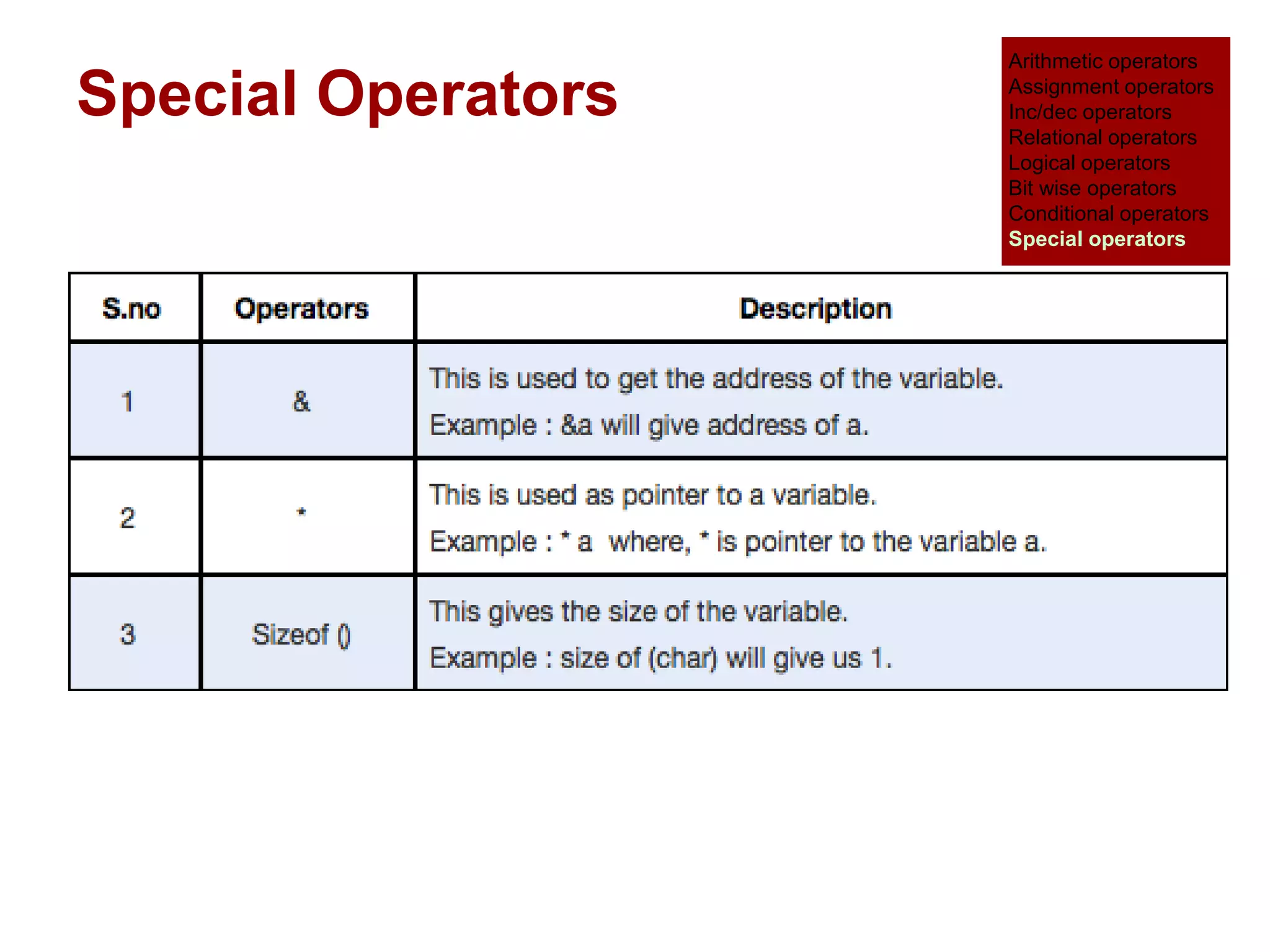
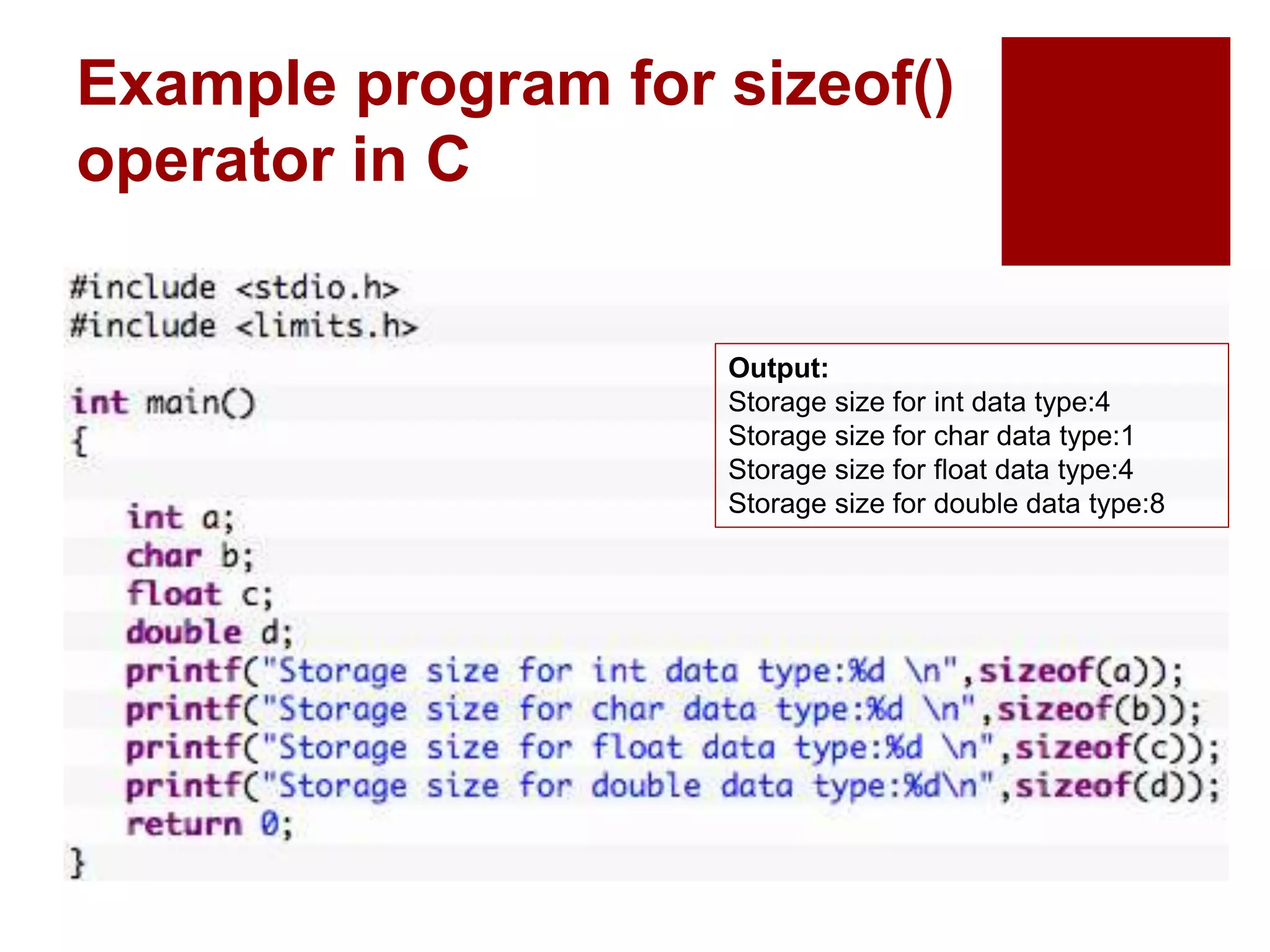
The document provides an overview of operators and expressions in the C programming language, including various types of operators such as arithmetic, assignment, increment/decrement, relational, logical, bitwise, and conditional operators. It explains how arithmetic operations can be performed on integer, real, and mixed mode operands, and highlights the usage and differences of increment and decrement operators in both prefix and suffix forms. Additionally, it covers relational and logical operators, as well as special operators like sizeof(), used to determine the storage size of data types.