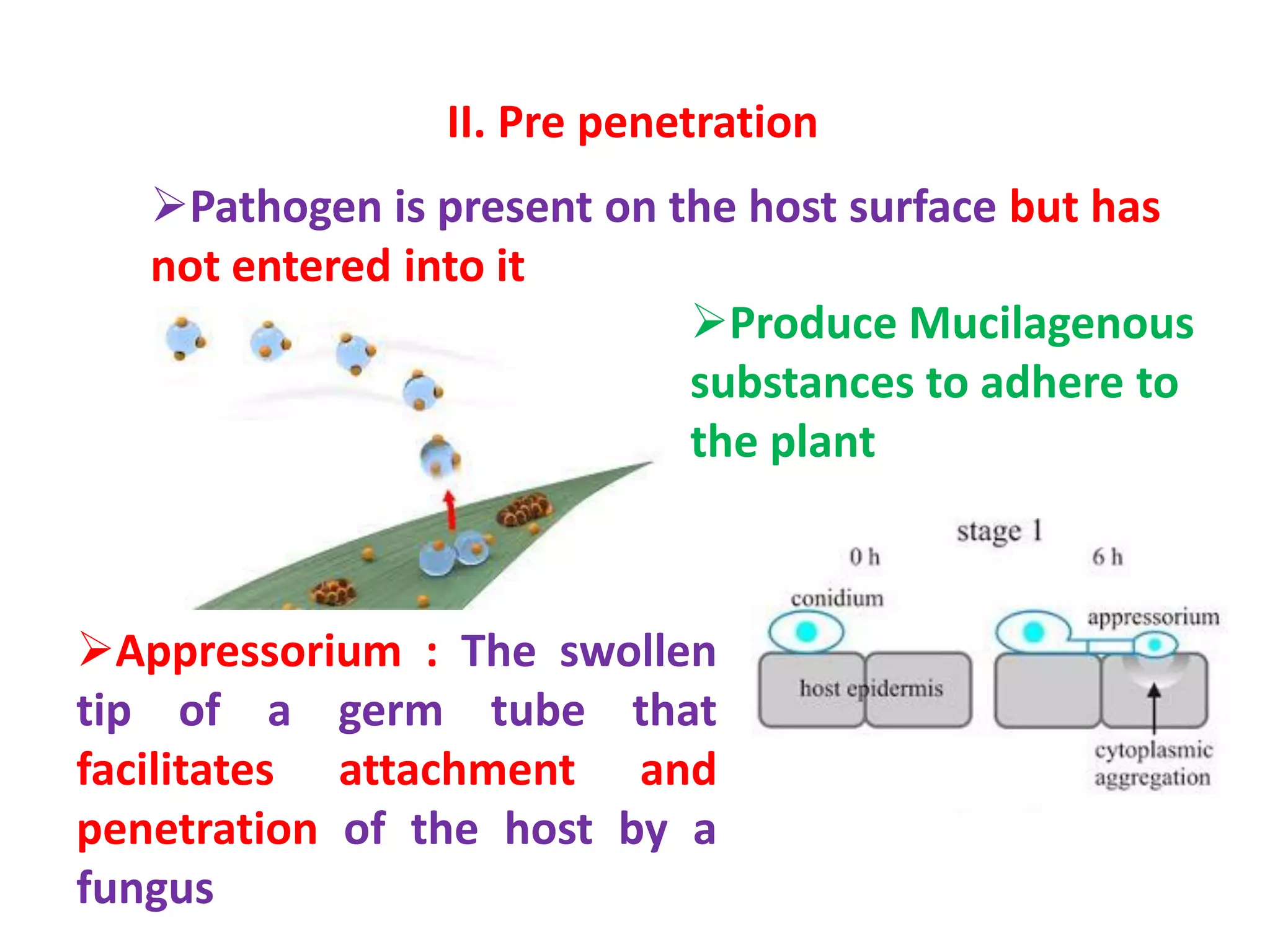
This document discusses the pathogenesis or disease cycle of pathogens. It defines pathogenesis as the series of events leading to disease development and perpetuation. Pathogens can have monocyclic, polycyclic, or polyetic disease cycles. Monocyclic pathogens complete one cycle per year, while polycyclic pathogens have multiple cycles per growing season, increasing inoculum levels. Polyetic pathogens take over one year to complete a cycle. The stages of pathogenesis discussed are inoculation, pre-penetration, penetration, infection, dissemination, and overwintering/survival. Primary inoculum initiates infections while secondary inoculum spreads disease epidemically. Pathogens penetrate directly or through natural openings and colonize hosts systemically or locally.