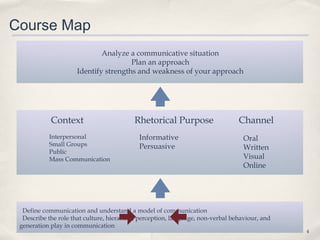
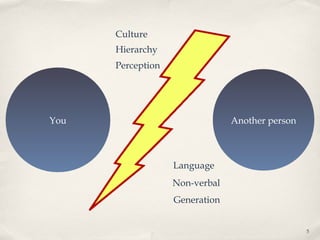
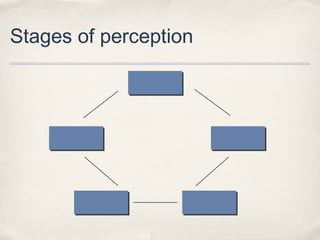
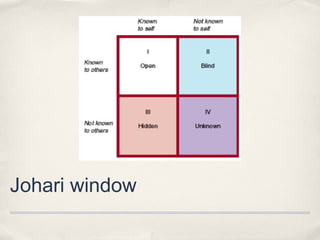
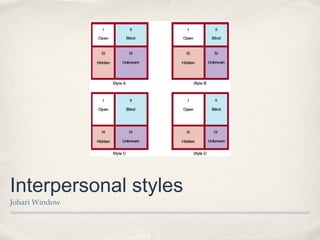
This document summarizes a lecture on perception. It discusses the stages of perception including figure-ground principle, perceptual schemata, closure, and selective perception. It also addresses how we perceive ourselves through self-concept and the Johari window model, and how we perceive others through first impressions, stereotypes, self-serving bias, and empathy. The lecture highlights how memory and experiences influence our perceptions and the "dark side" of perception through biases.