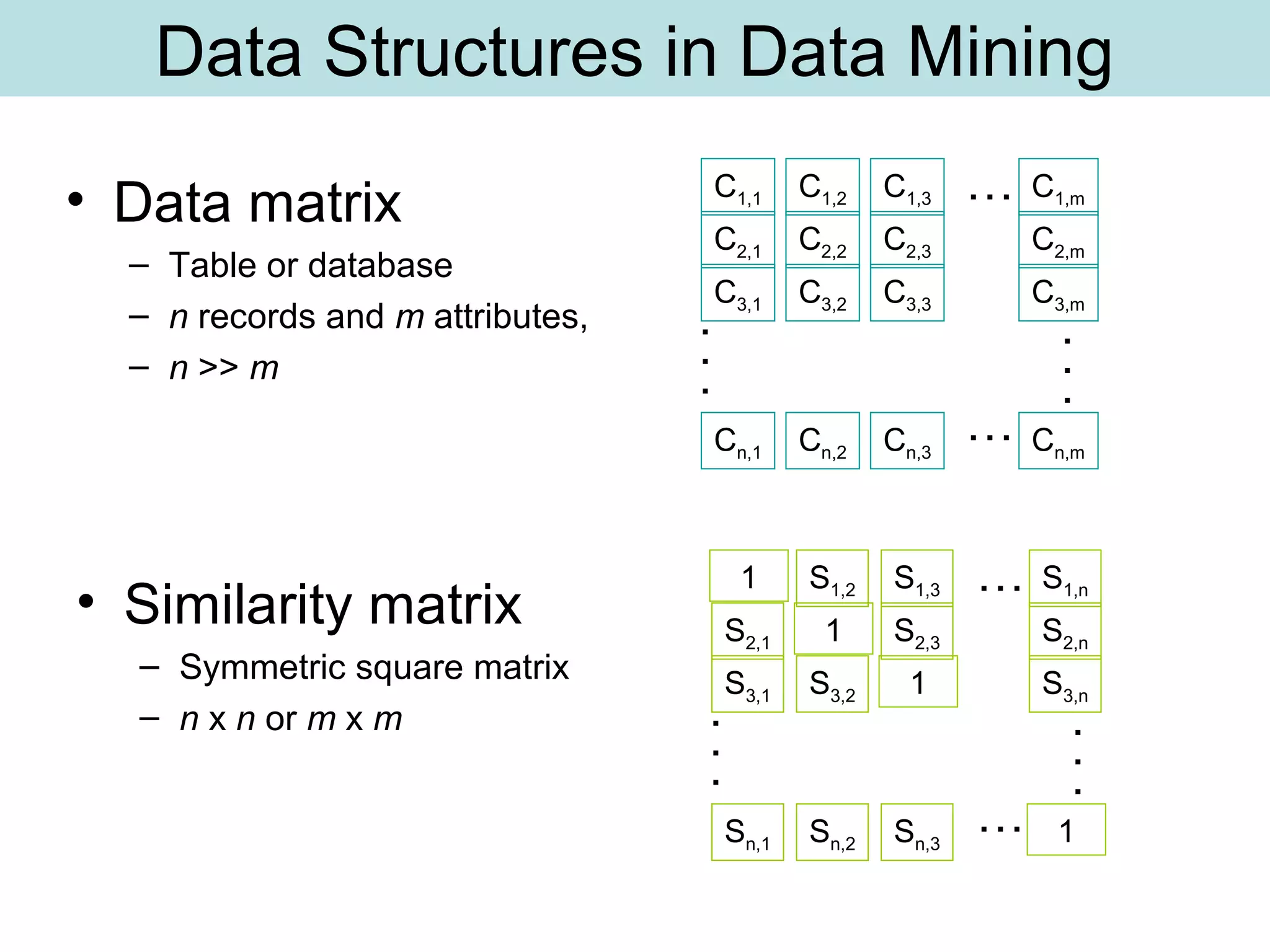
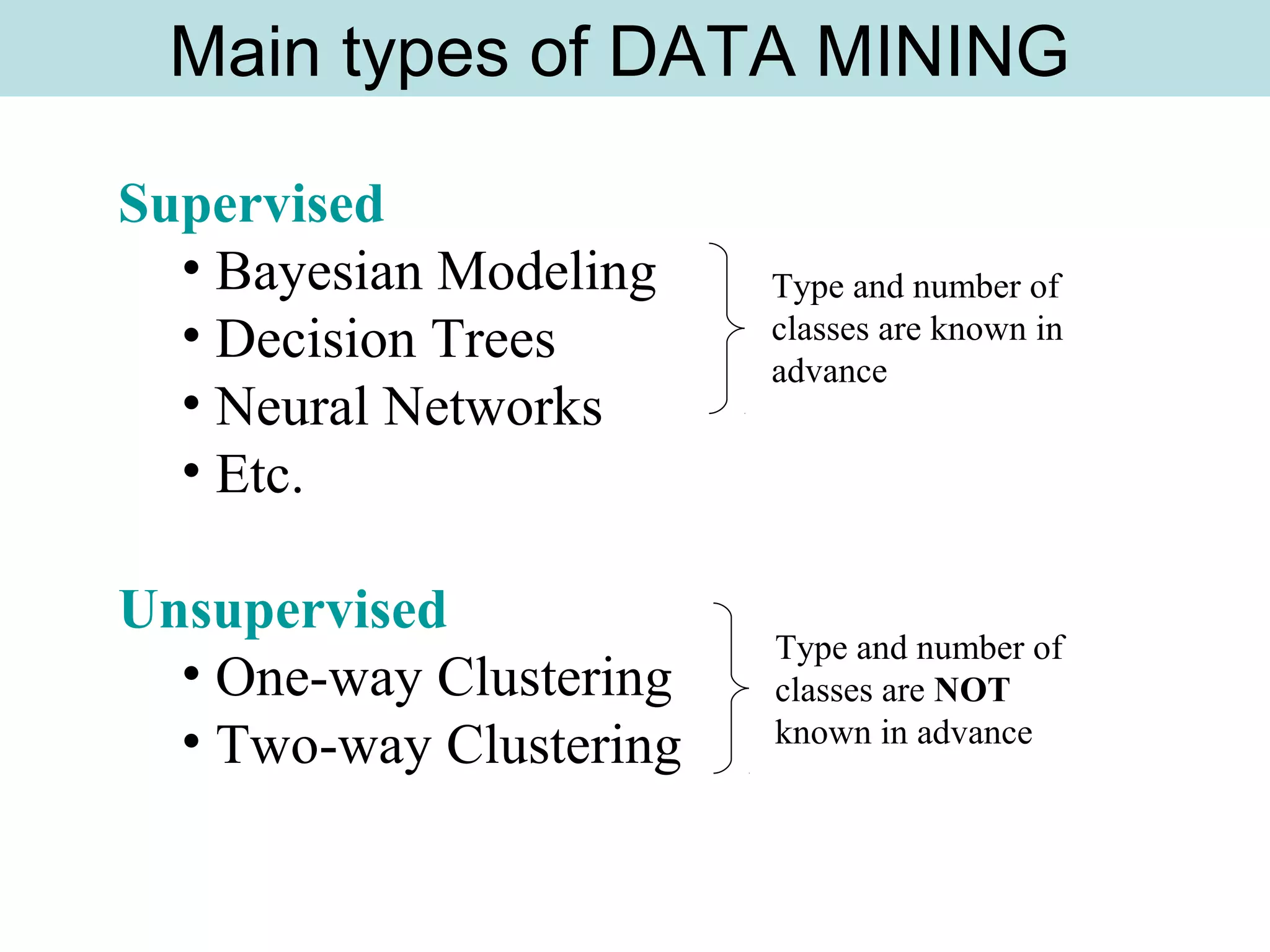
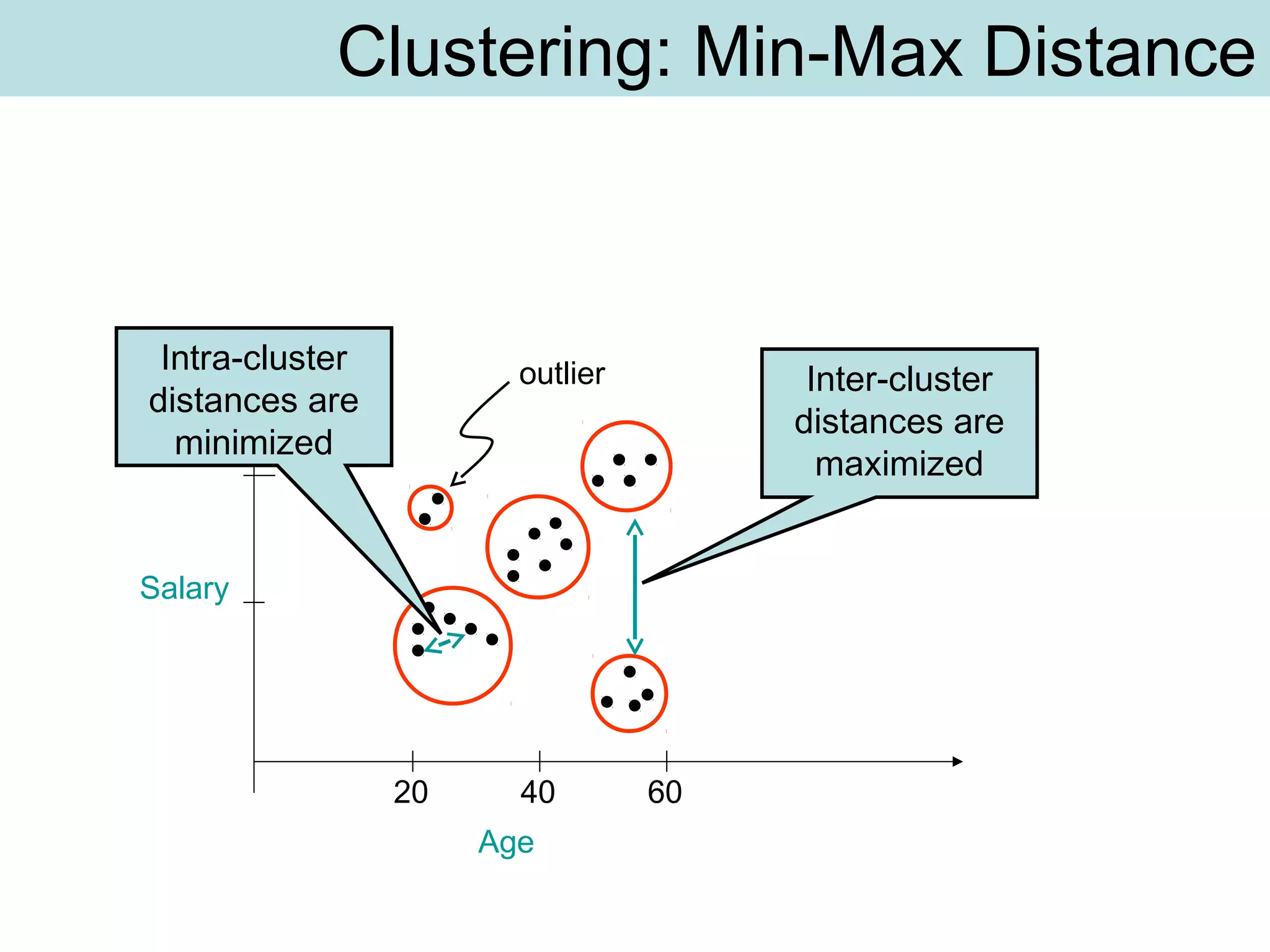
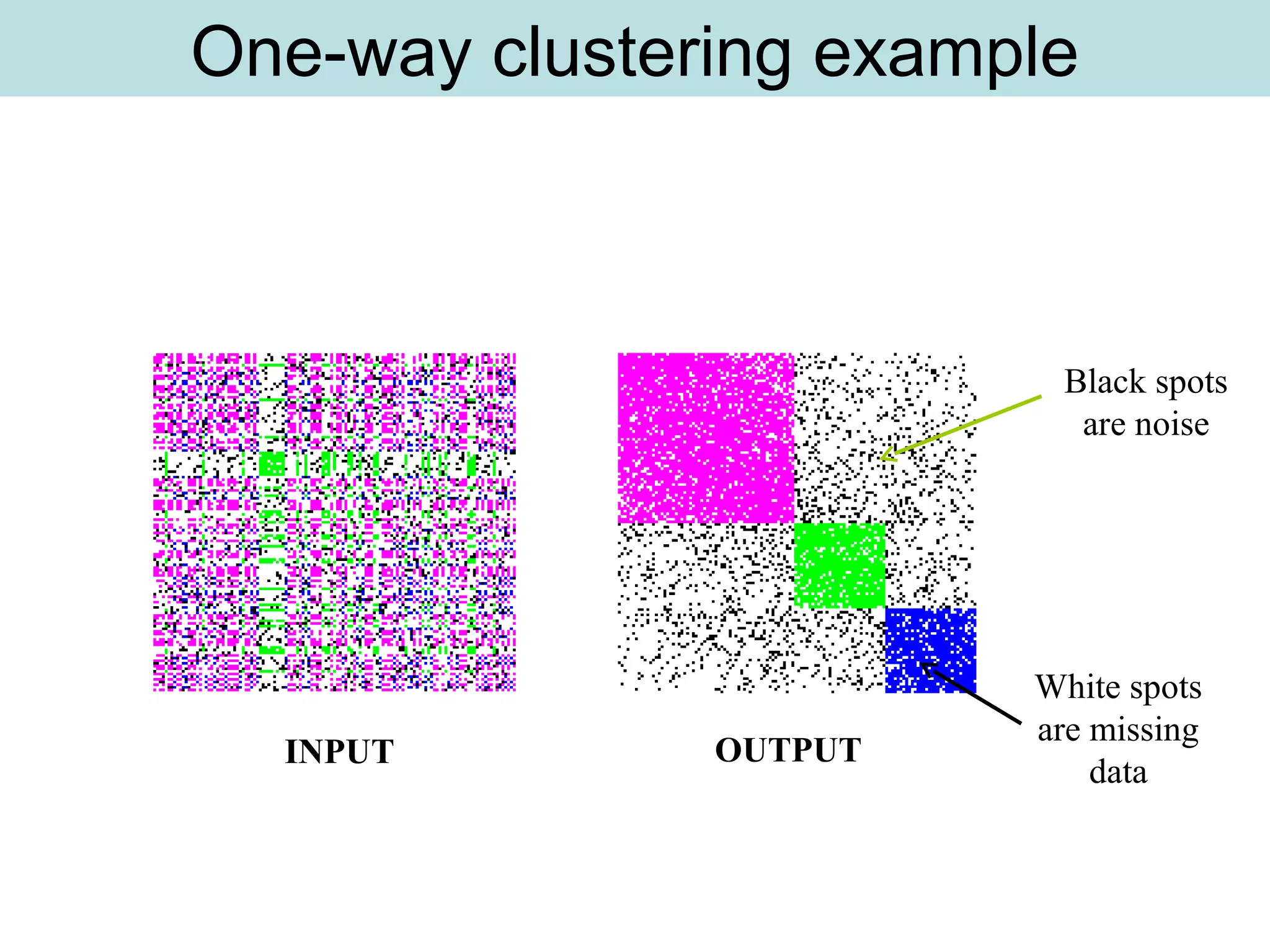
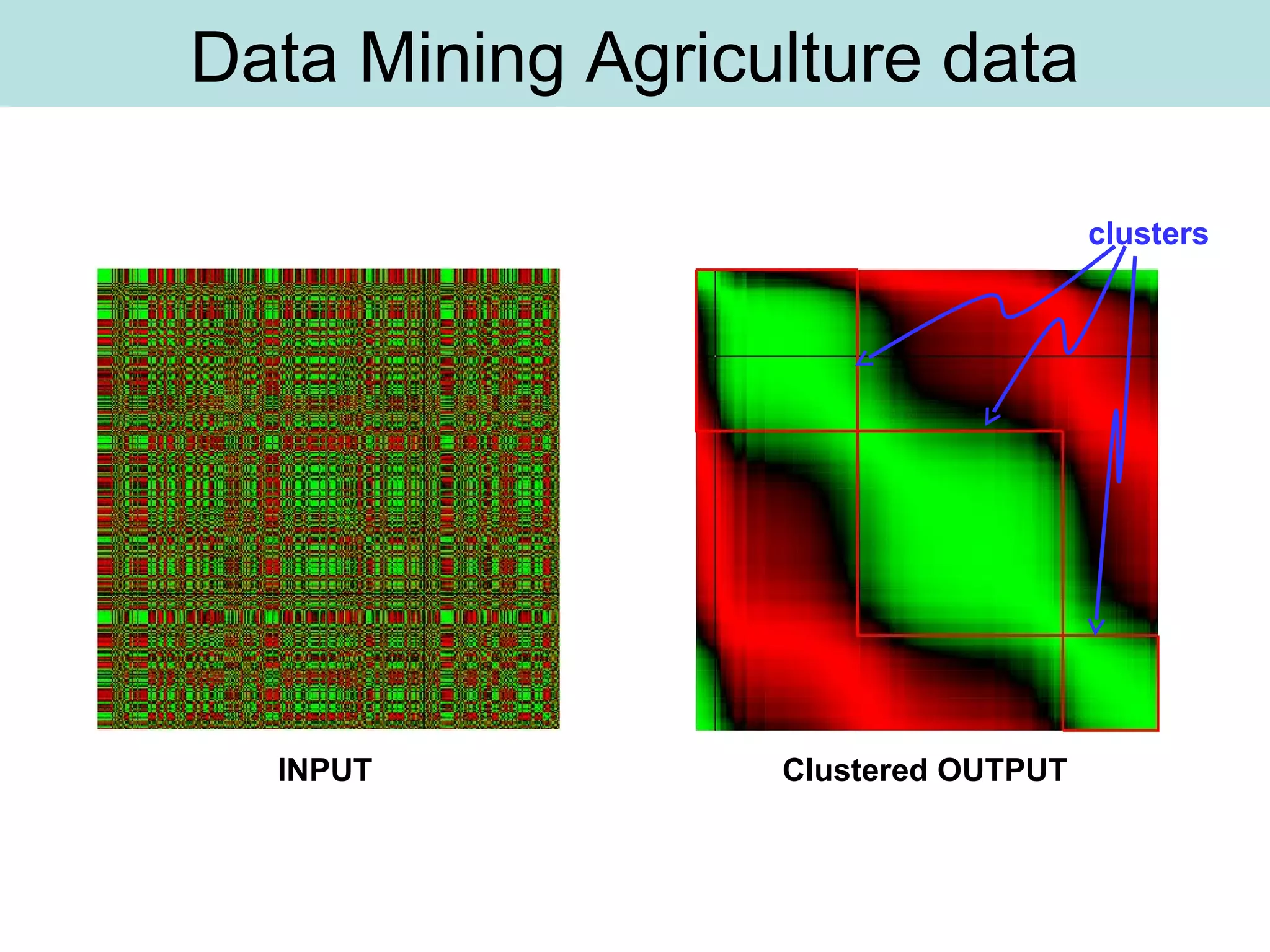
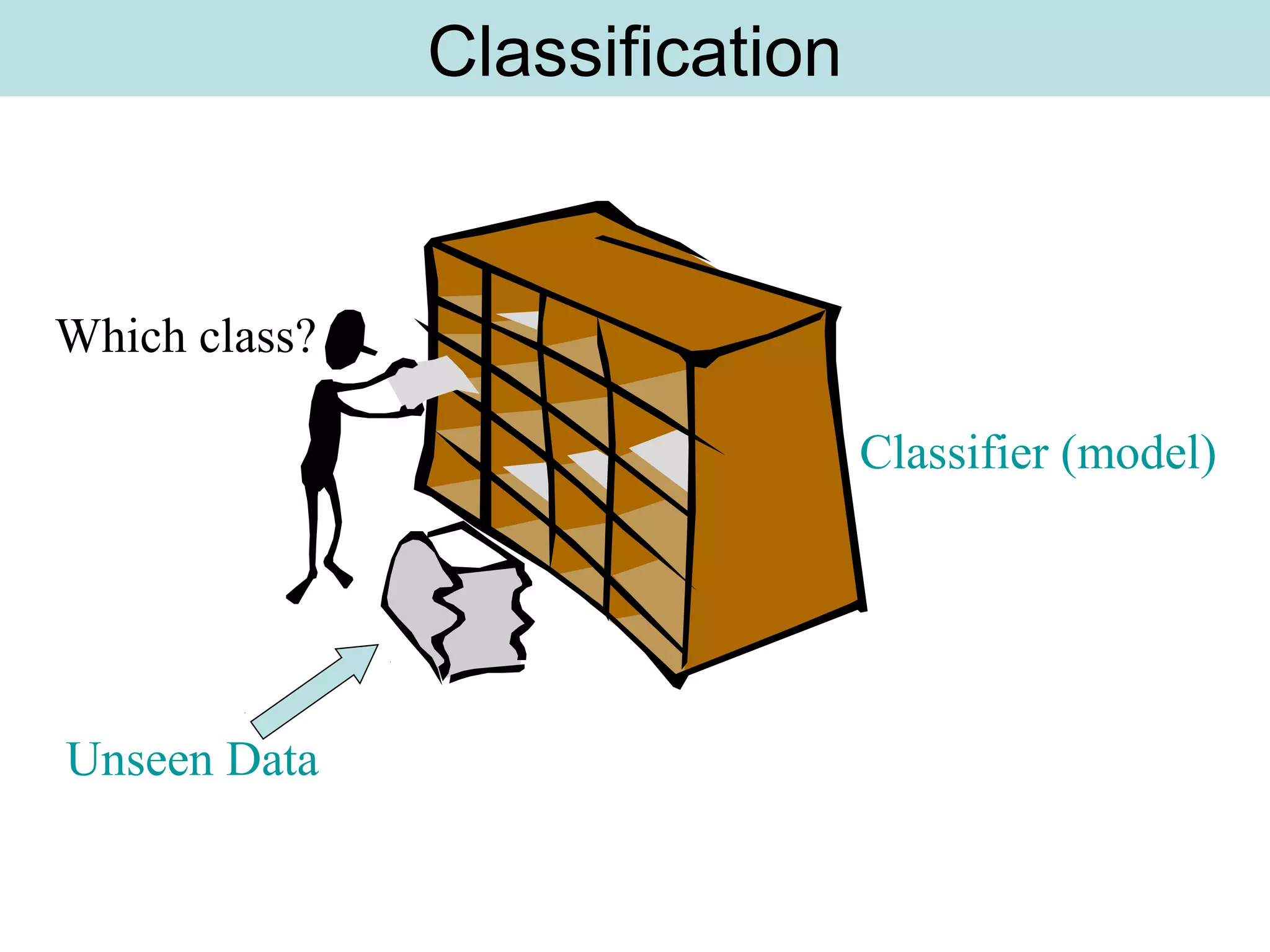
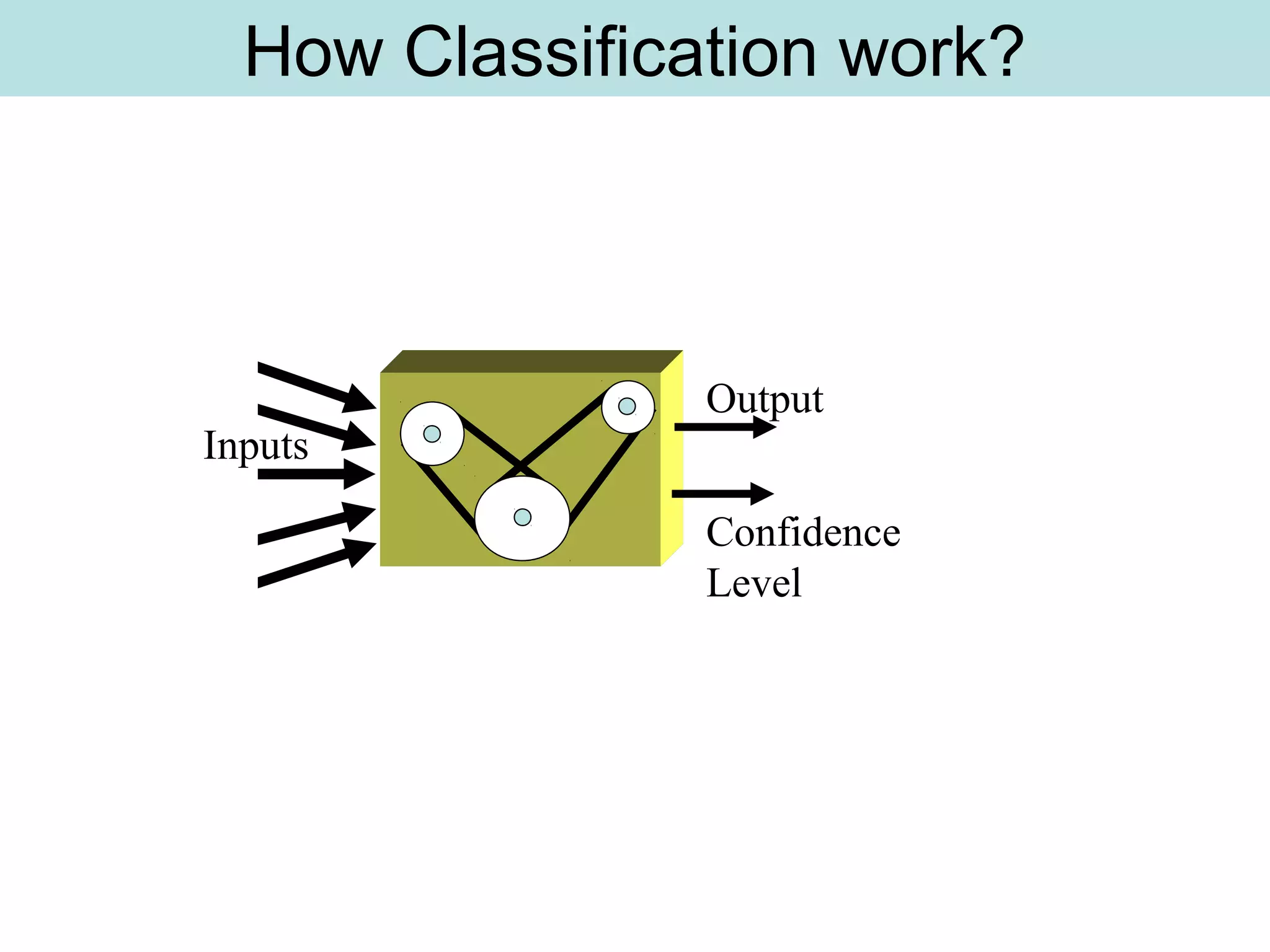
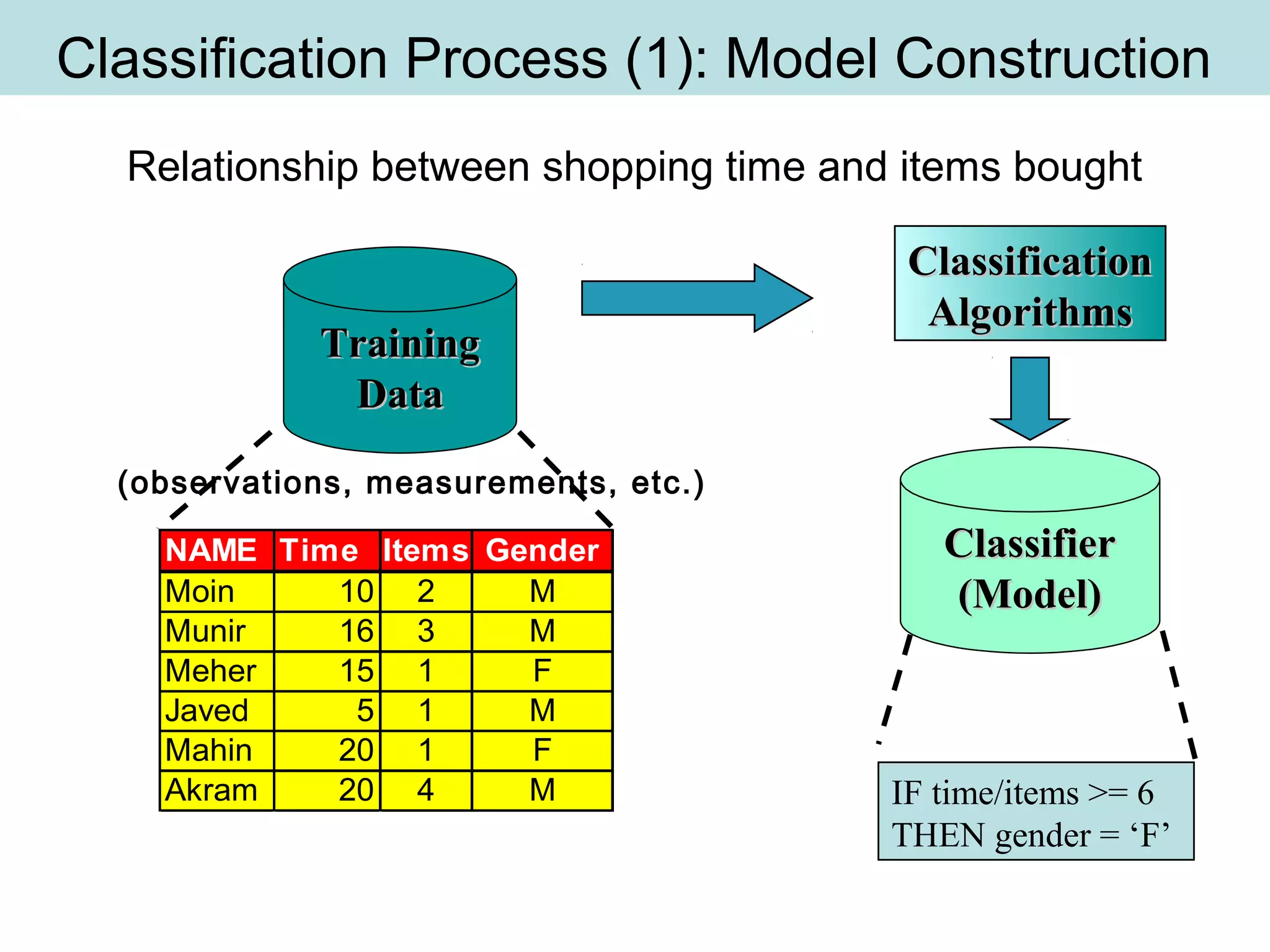
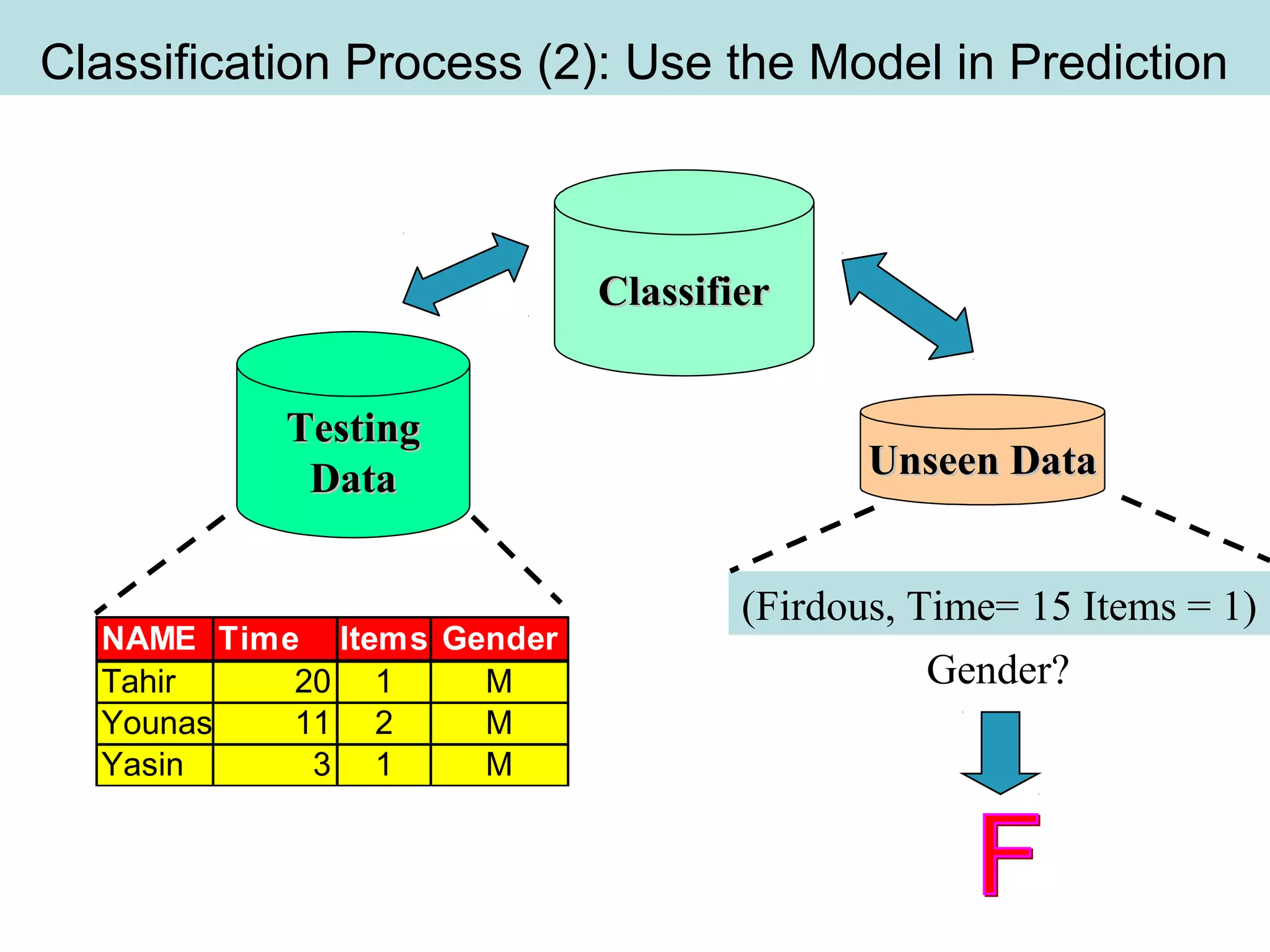
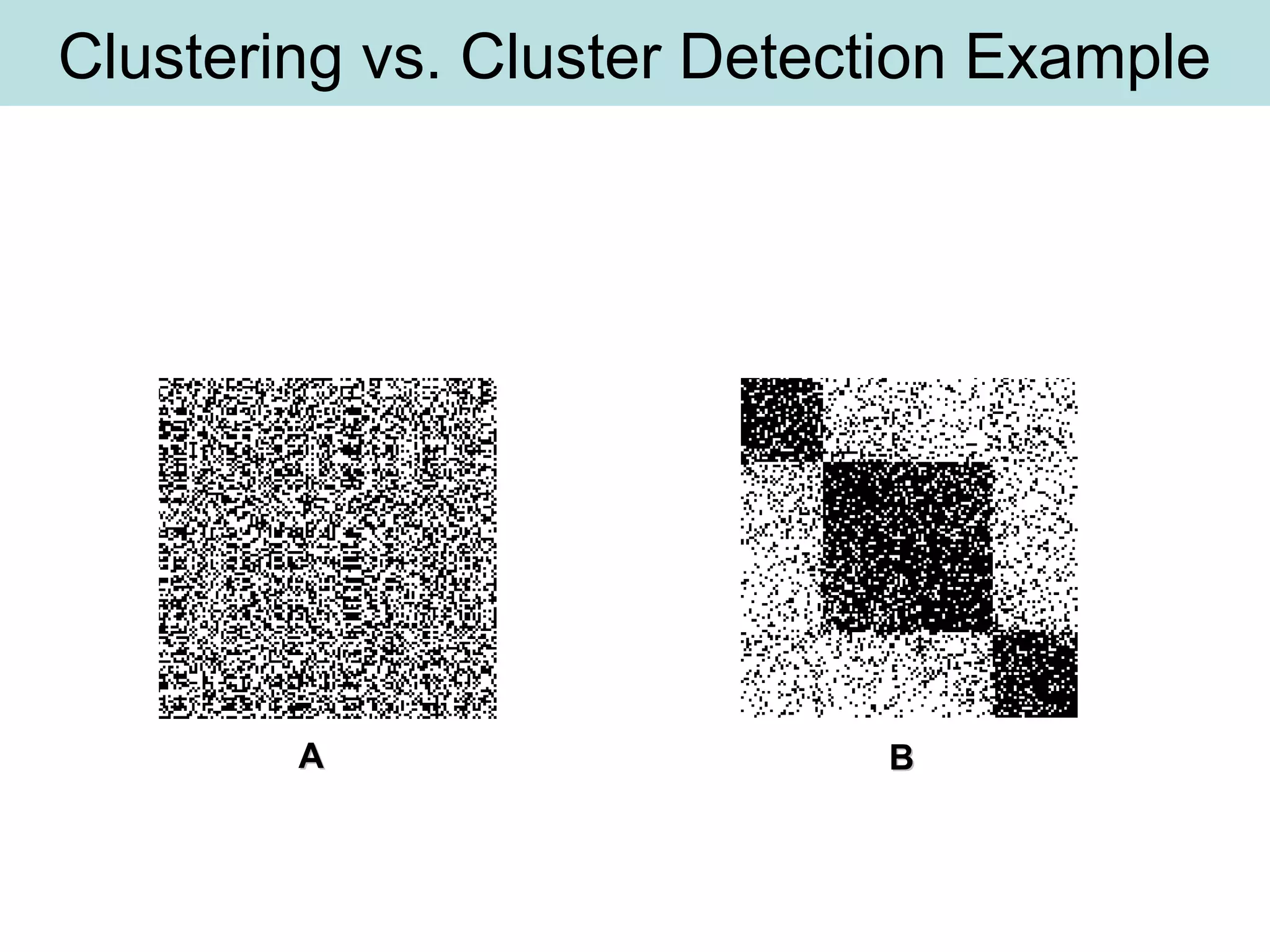
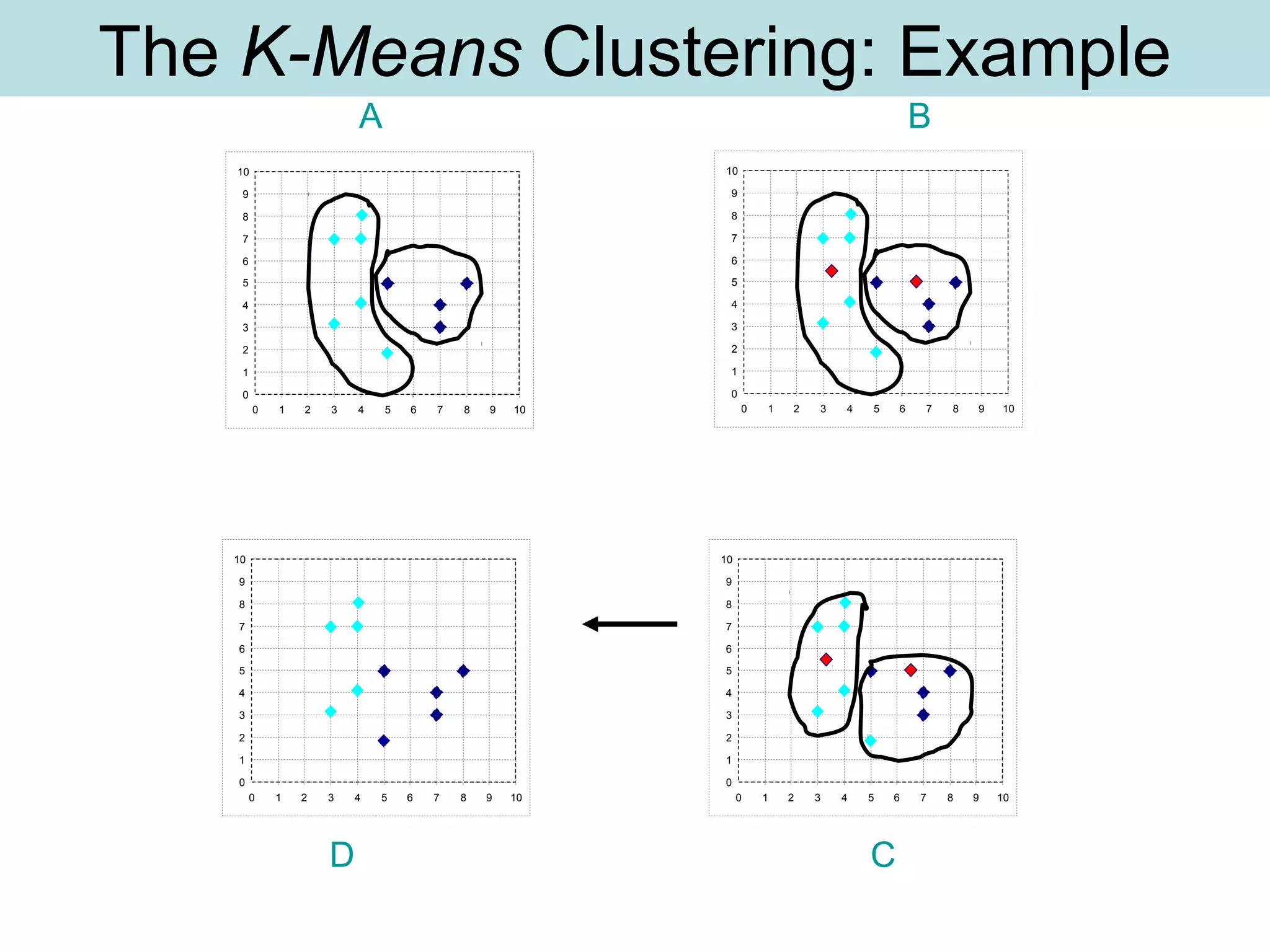
The document discusses supervised and unsupervised learning in data mining. It describes the main types of data mining as supervised, which includes techniques like Bayesian modeling and decision trees when the type and number of classes are known in advance, and unsupervised, which includes clustering techniques like one-way and two-way clustering when the types and number of classes are not known in advance. It provides examples of clustering, including min-max distance clustering to maximize inter-cluster distances and minimize intra-cluster distances, and k-means clustering to group similar data points into k number of clusters.