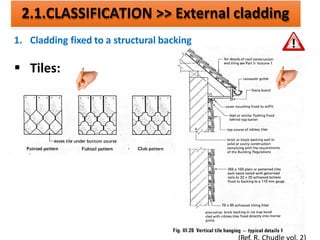
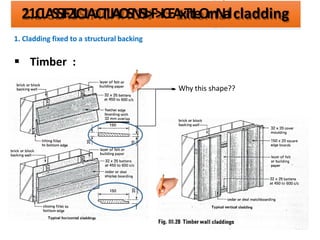
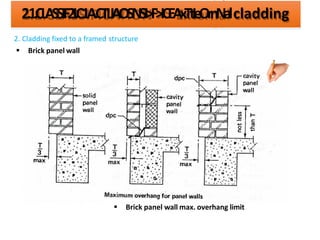
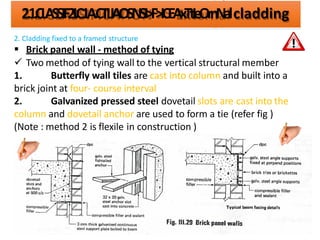
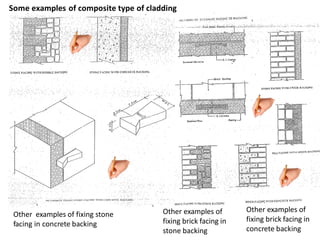
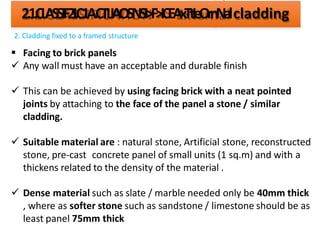
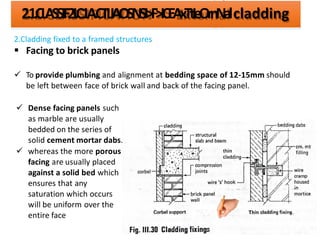
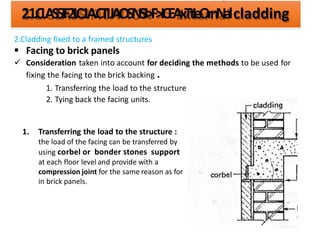
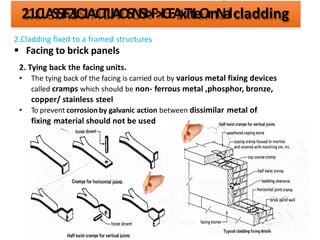
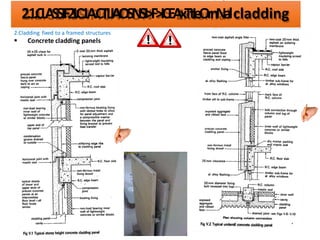
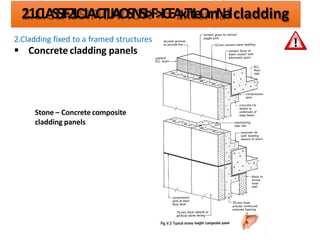
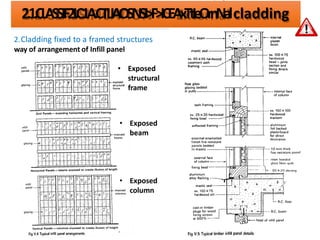
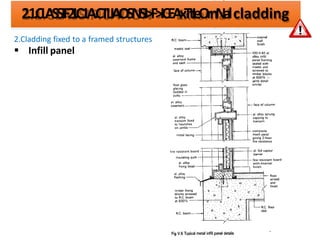
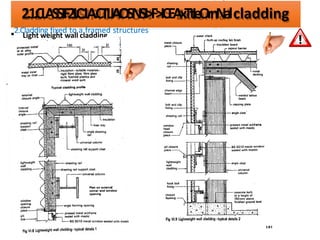
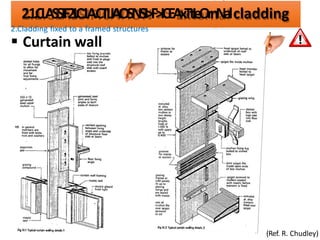
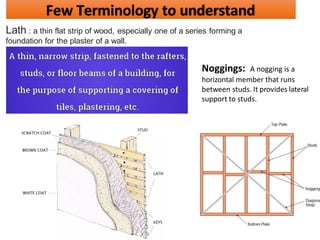
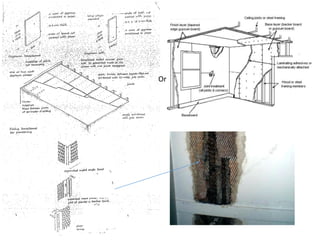
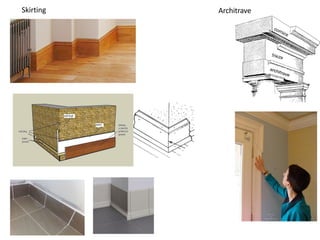
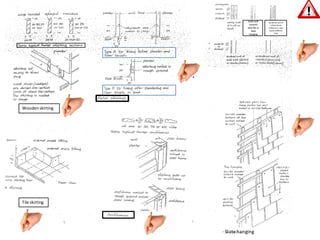
The document discusses different types of cladding used for internal and external finishes in building construction. It defines cladding and its objectives such as resistance to weather elements. For interior cladding, it classifies and describes different materials like plastering with various finishes, paints by explaining their constituents, and tiles. It also covers dry lining materials like plaster boards, hardboards and their fixing details. For external cladding, it discusses materials fixed to structural backing or framed structures. The document provides detailed information about classification and technical specifications of various cladding materials.










![2.1.CLASSIFICATION >>Interior cladding
Smooth Cast Plaster Finish
• mortar used should be in the
ratio 1: 3 [cement: sand]
• Fine Sand should be taken
• For spreading the mortar,
skimming float or wood float is
best suitable tool
https://theconstructor.org/building/types-plaster-finishes-external-
rendering-buildings/14532/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2claddingforexternalinternalde032d2ac2d537a21824b10c3719a2101dc6cb07fae0d8981e03f591185f96ef-230312092759-b1b815fe/85/lecture-2-Cladding-for-external-internal-pdf-11-320.jpg)