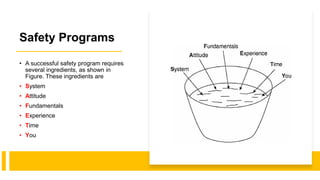
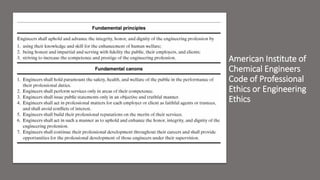
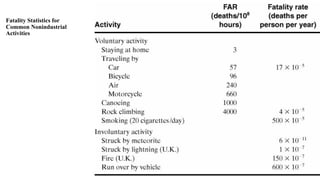
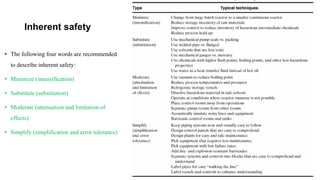
This document provides an introduction to process safety management. It discusses chemical engineering and safety, defining key terms like safety, hazard, and risk. It outlines the key ingredients to a successful safety program and distinguishes between a good and outstanding safety program. Metrics for measuring safety performance like OSHA incidence rate, fatal accident rate, and fatality rate are also introduced. The document provides examples and glossaries to define common safety terms.