Embed presentation
Downloaded 165 times

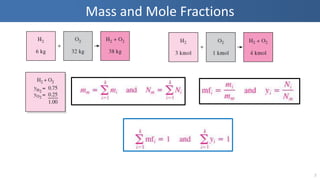

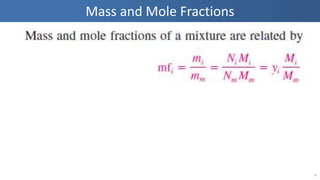
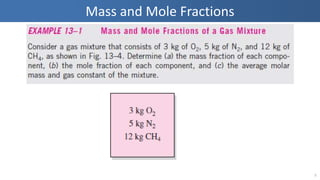

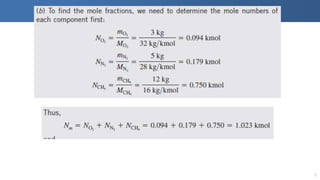


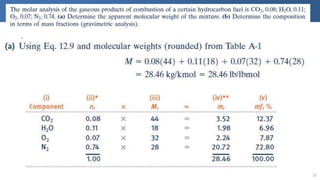

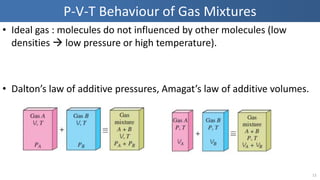


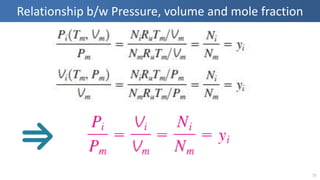
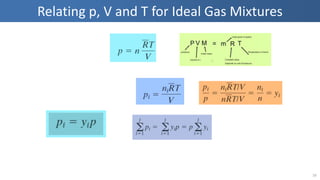

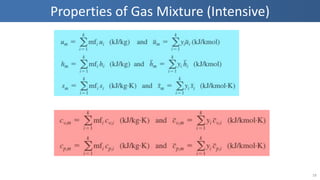


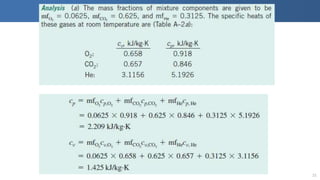



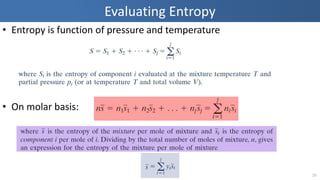
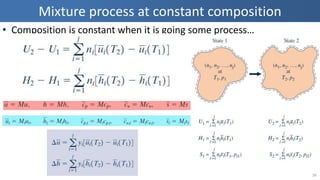

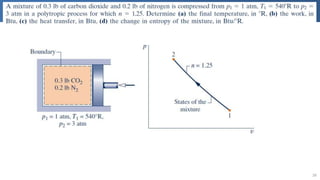






The document covers thermodynamics concepts related to gas mixtures, including mass and mole fractions, and key laws such as Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures and Amagat's Law of Additive Volumes. It discusses the behavior of ideal gas mixtures and the relationships between pressure, volume, and mole fraction, as well as properties of gas mixtures. Additionally, the document explains the evaluation of entropy in relation to gas mixtures at constant composition.
































