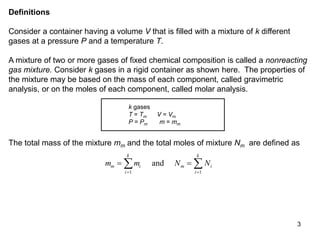
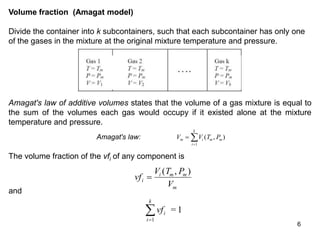
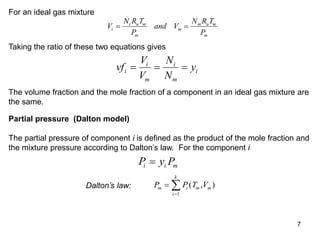
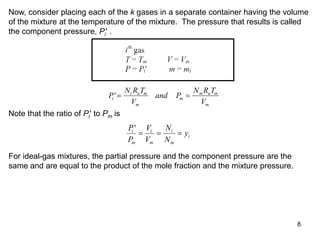
1) The document discusses ideal gas mixtures, including definitions of mole fraction, mass fraction, partial pressure, and volume fraction. It also covers calculating properties of mixtures such as specific heat and entropy.
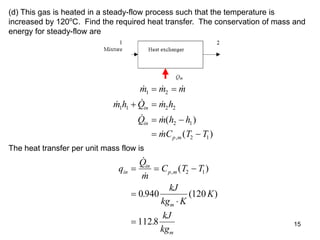
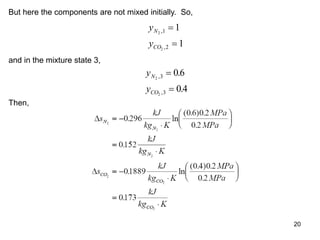
2) An example problem is presented that involves calculating properties of a nitrogen-carbon dioxide gas mixture such as composition by mass, specific heat, required heat transfer, and entropy changes during compression and mixing.
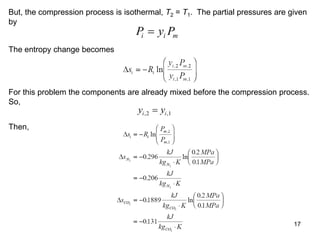
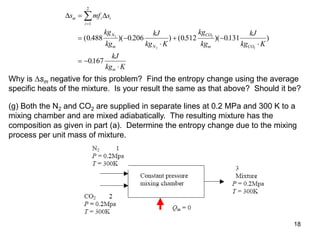
3) Key results shown include that for ideal gases, mole fraction equals volume fraction, and partial pressure equals mole fraction times total pressure. Entropy changes are calculated using mole fractions and specific properties of the individual components.