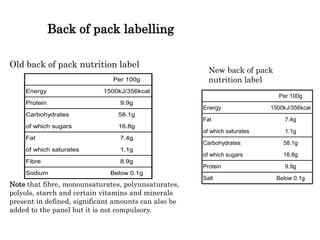
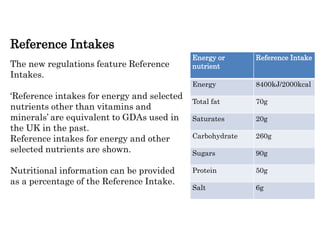
This document provides information on food labelling requirements in the European Union. It discusses what information must be included on food labels by law, such as the name of the food, ingredients, weight/volume, date marks, storage instructions, manufacturer details, and country of origin. It also describes regulations for listing allergens and providing nutrition information on the back of packaging. Front-of-pack labelling remains optional but commonly uses color-coding to indicate levels of nutrients.