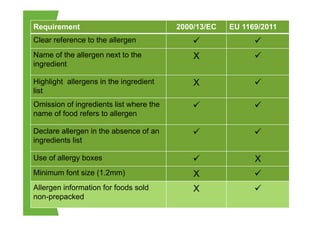
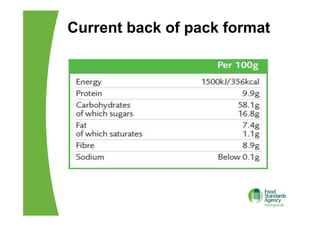
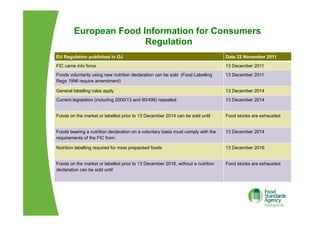
The EU Regulation on food information to consumers consolidates and updates existing legislation on food labelling and nutrition labelling. Key provisions include mandatory nutrition declarations and clearer allergen labelling. It aims to harmonize rules and ensure consumers receive essential information to make informed choices while facilitating the EU internal market. National measures allow member states to require non-prepacked food businesses to provide allergen information.