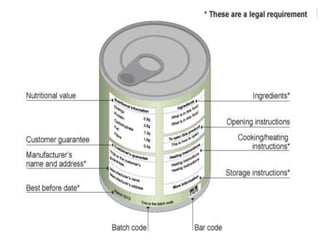
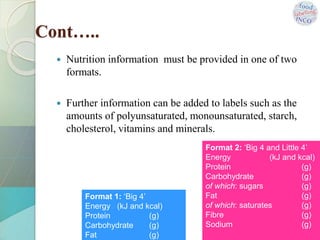
The document outlines the essential elements and regulations of food labeling, emphasizing its importance as a communication tool between producers and consumers. Key components of a label include the name of food, ingredients, nutritional information, and allergen information, while also addressing legal requirements to prevent misbranding. It concludes that effective labeling aids in informed consumer choices and promotes public health by providing vital nutritional insights.