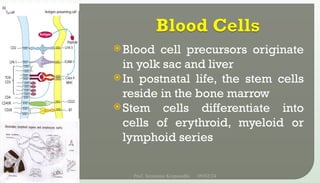
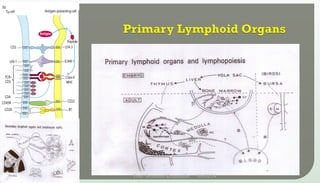
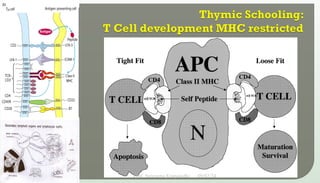
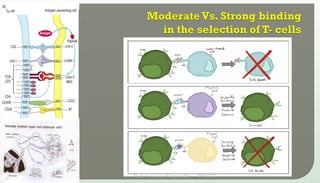
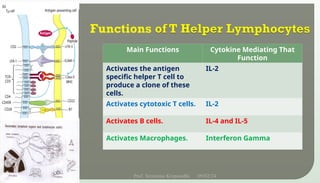
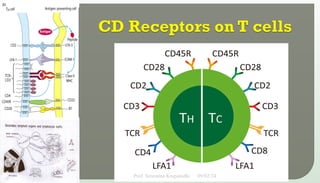
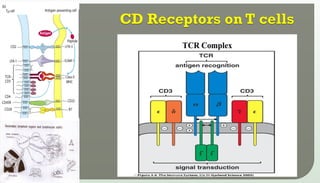
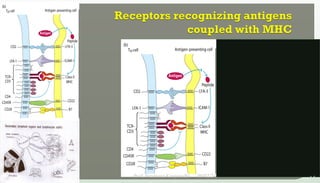
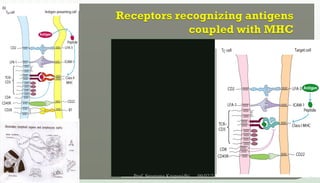
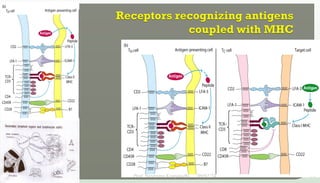
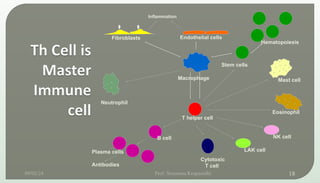
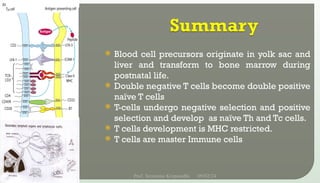
The document discusses T cell development, including their origin, maturation processes, and the distinctions between CD4 and CD8 T cells. It highlights the importance of positive and negative selection in the thymus and the role of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. Additionally, it outlines the functions of various cytokines in activating T cells and acknowledges the use of online resources for developing teaching materials.