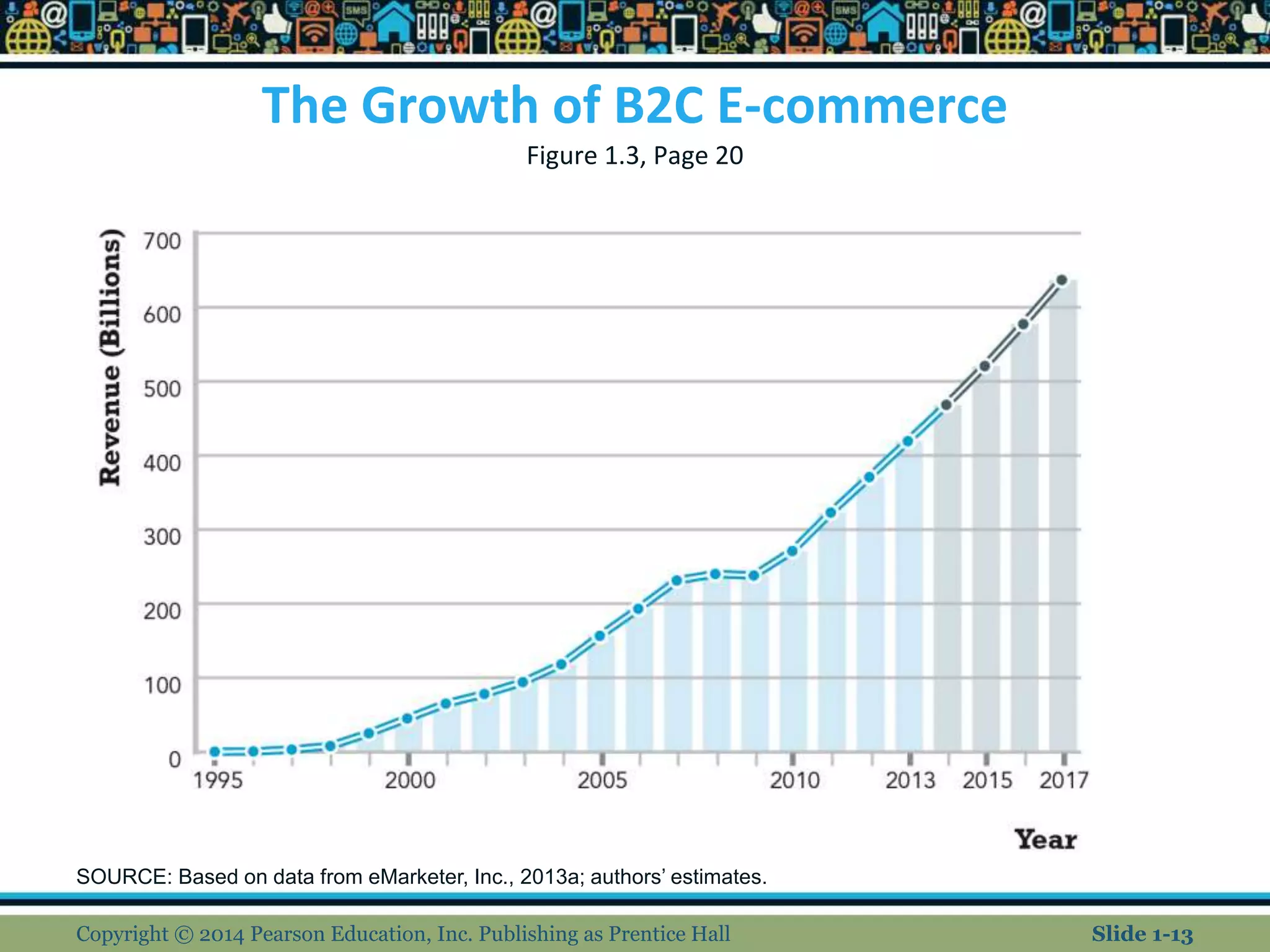
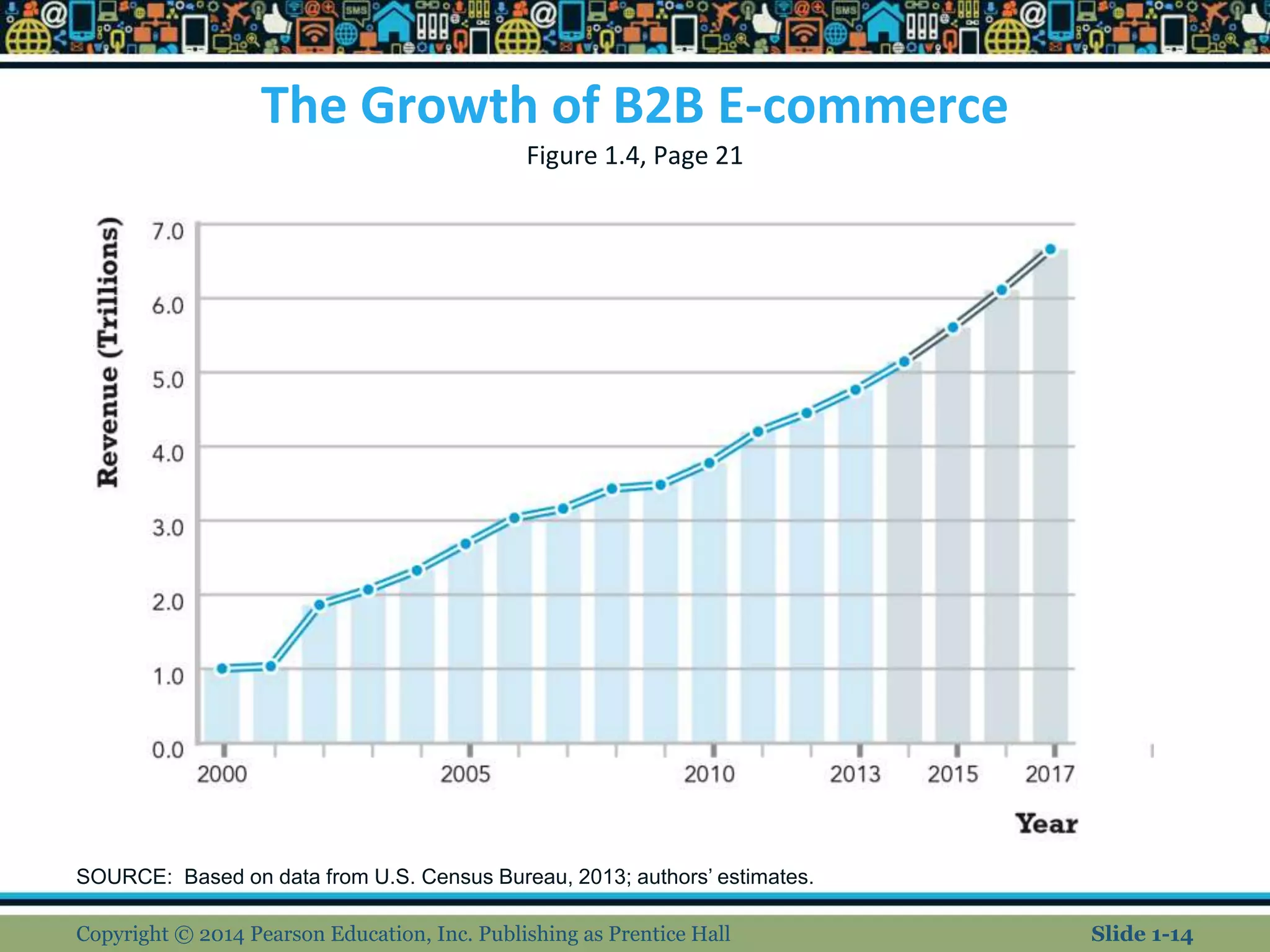
The document is a chapter from an e-commerce textbook. It discusses the evolution of e-commerce from its early beginnings in the 1990s to the present day. It covers topics such as the growth of B2C and B2B e-commerce, the development of technologies like the internet, web and mobile platforms, and different types of e-commerce models. The chapter also examines some of the unique features of e-commerce technology and how it has impacted business and society. It concludes by noting how e-commerce will continue to propagate through commercial activities and be shaped by emerging technologies.