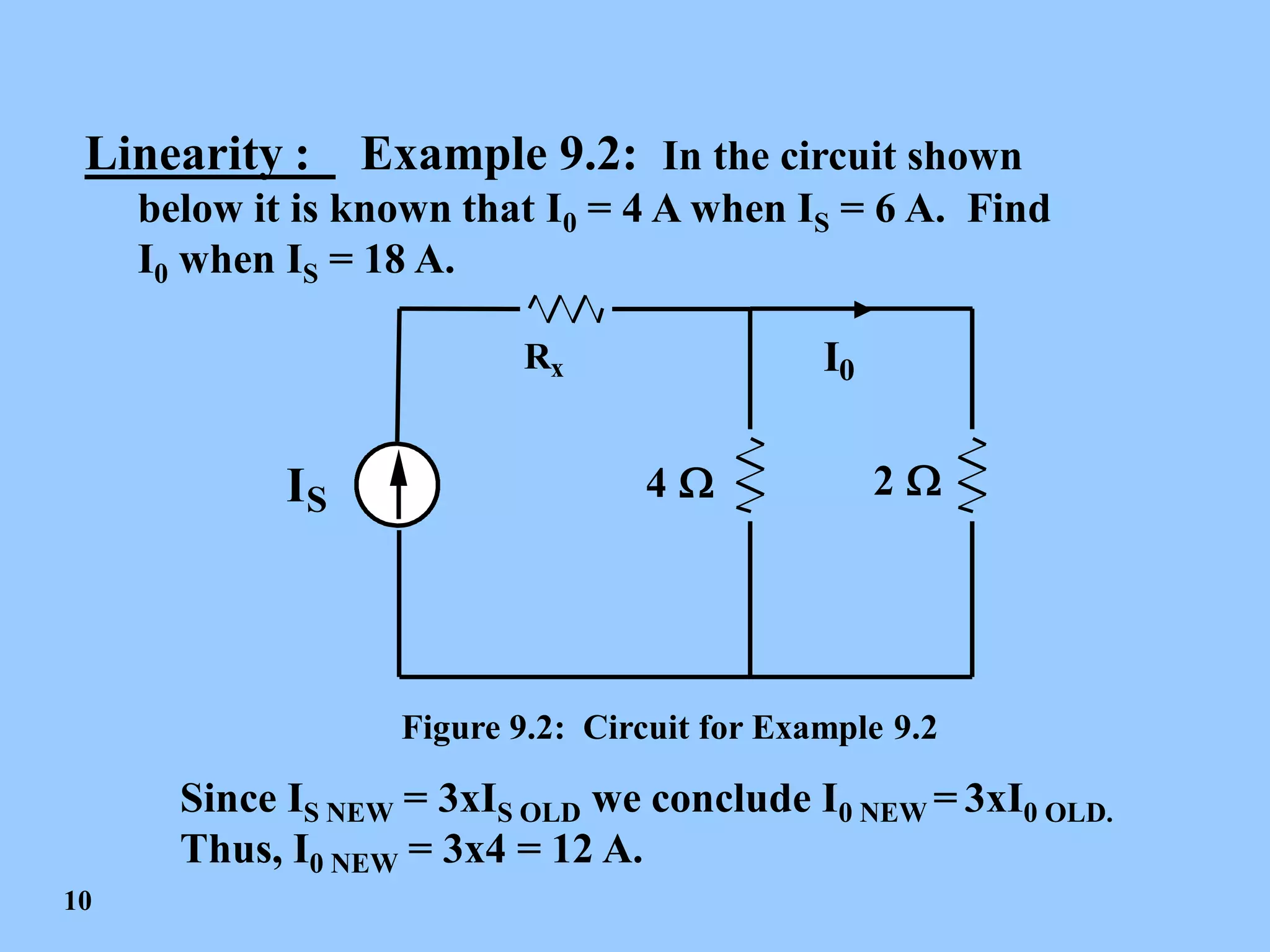
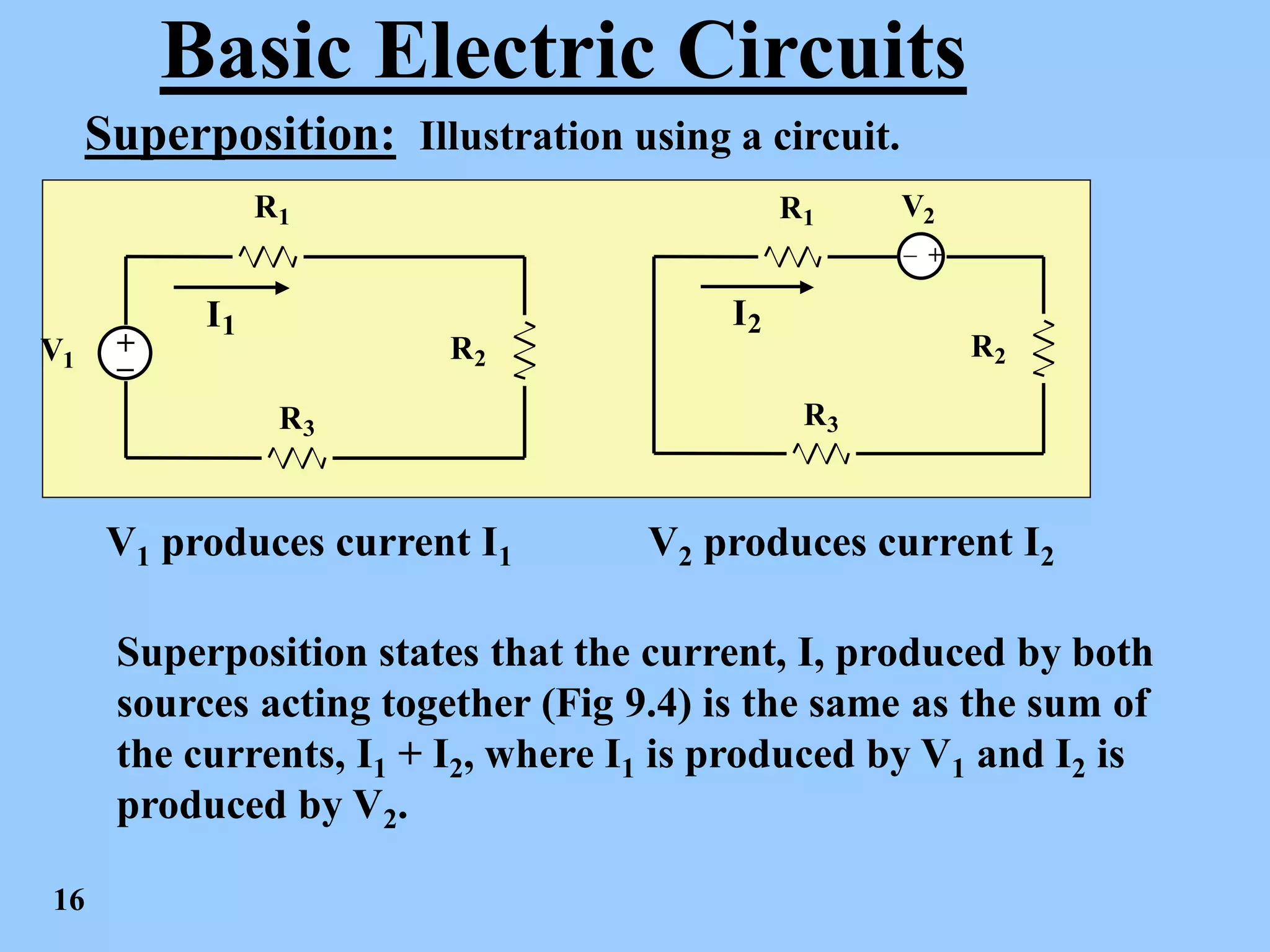
This document discusses linear circuits and Thevenin's theorem. It begins by defining linearity and explaining that linear circuits obey homogeneity (scaling) and additivity. It then discusses these properties in more detail using equations and circuit examples. Next, it introduces the superposition principle, which states that the response of a linear circuit to combined inputs is the sum of its responses to individual inputs. The document provides examples of applying superposition to find currents in circuits. Finally, it explains Thevenin's theorem, which allows a linear circuit to be reduced to a voltage source in series with a resistor for analysis of an external load. An example demonstrates calculating the Thevenin voltage and resistance of a given circuit.