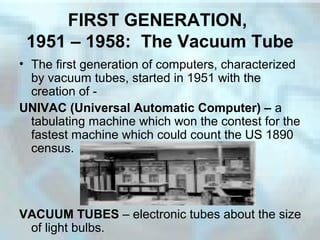
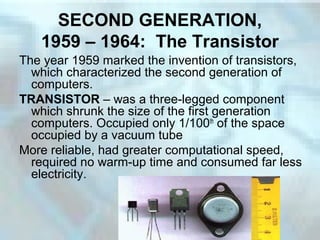
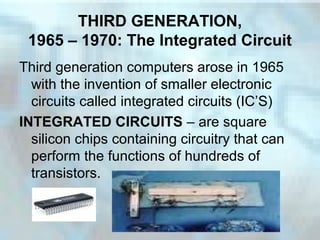
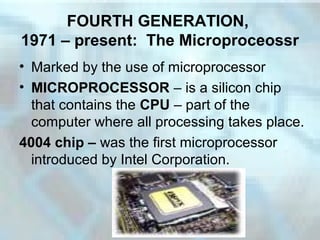
The document summarizes the five generations of computers from the earliest use of counting tools to today's microprocessor-powered computers. The first generation used vacuum tubes, which generated heat and were prone to burning out. The second generation introduced transistors, which were more reliable and efficient. Integrated circuits, containing hundreds of transistors on a silicon chip, marked the third generation. The fourth generation began in 1971 with the invention of the microprocessor, which incorporated a CPU onto a single silicon chip. Today's computers are classified as fourth generation and are faster, more powerful, and ubiquitous in homes, schools and offices compared to earlier models.